- Professional Development
- Medicine & Nursing
- Arts & Crafts
- Health & Wellbeing
- Personal Development
286 Pharmacology courses delivered Online
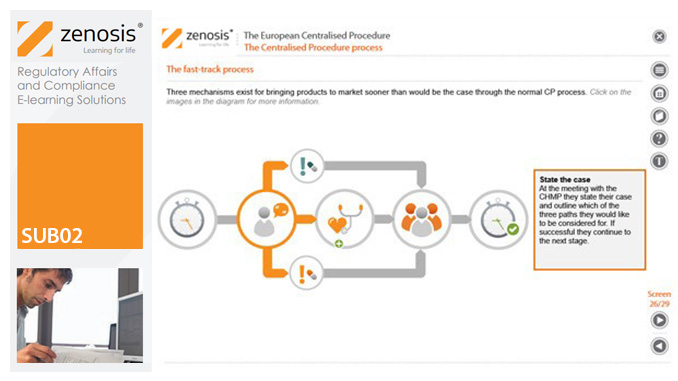
SUB02: The European Centralised Procedure (CP)
By Zenosis
The Centralised Procedure (CP) is one of three routes available to applicants to gain multinational marketing authorisation within the European Economic Area (EEA) on the basis of a single application. In the CP, one successful application leads to a marketing authorisation being issued by the European Commission that applies throughout the EEA. The CP is mandatory for certain types of products.
PKPD01: An Introduction to Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics in Drug Development and Registration
By Zenosis
Pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) studies provide a bridge between science and medicine in the development of a drug. In this module we describe the role of in-vivo PK and PD studies in a drug development programme, set out the uses to which the findings can be put, and discuss their implications for clinical development and application for marketing approval.

SUB04: Preparing Submissions in the Common Technical Document (CTD) Format
By Zenosis
The CTD is the internationally recognised standard format for submissions to medicines regulatory authorities. In the European Economic Area, the USA and Canada, the CTD, in its electronic format (eCTD), is mandatory for all applications for marketing approval and all subsequent related submissions. The CTD is accepted in many other countries, being mandatory for new prescription medicines in some. This module explains the rationale for the CTD and provides guidance on its structure and format and the ways in which it is used.

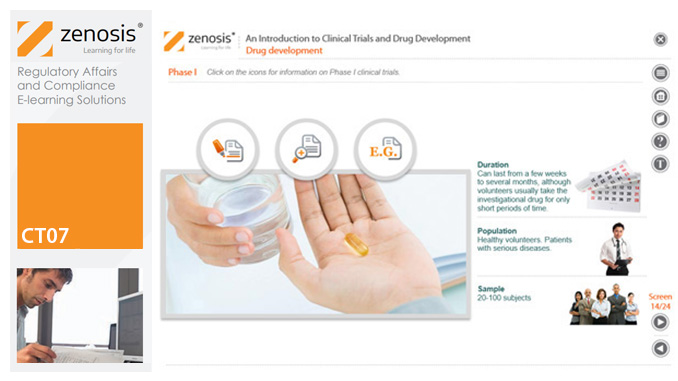
CT07: An Introduction to Clinical Trials and Drug Development
By Zenosis
This module provides an understanding of how clinical trials fit into the drug development process. It outlines the key historical events leading to the development of controlled clinical trials. It specifies the purpose of trials, outlines their features, and identifies codes and regulations that apply to them. Finally, it describes the environment of cost control in which the modern pharmaceutical industry operates.
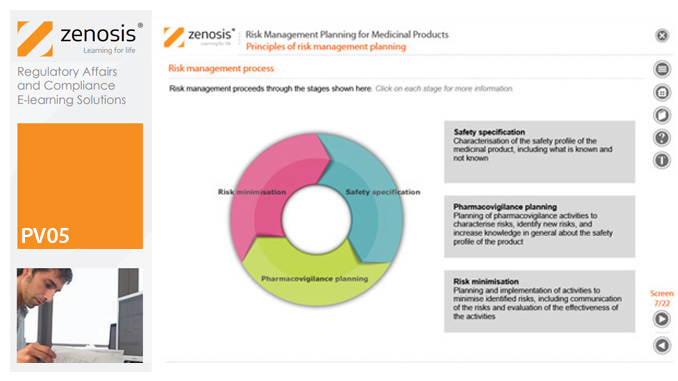
PV05: Risk Management Planning for Medicinal Products
By Zenosis
Proactive risk management is a major component of good pharmacovigilance practice. This module sets out the principles of risk management planning and outlines regulatory requirements for risk management plans in regions that are major markets for medicinal products.
SUB16: The 505(b)(2) Application for Marketing Approval in the USA
By Zenosis
A 505(b)(2) New Drug Application (NDA) is a submission to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for approval to market a drug in the USA. It differs from a ‘stand-alone’ NDA in that some of the data on which the applicant relies to demonstrate safety and efficacy have been obtained from publicly available sources rather than from the applicant’s own studies. The applicant typically proposes to market a drug that is based on an approved reference product but modified in its formulation or uses. A 505(b)(2) NDA also differs from an Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA) for approval of a generic drug in that the applicant’s product need not be a duplicate of the reference listed drug. The 505(b)(2) pathway may be said to lie part-way between the ‘stand-alone’ NDA and generics pathways, offering a unique combination of advantages to developers. It facilitates the modification of drugs to address unmet medical needs. The 505(b)(2) application pathway accounts for about half of all new drug approvals in the USA.

ICT03: Assuring Data Integrity in Clinical Research
By Zenosis
Pharmaceutical, biotechnology and medical device companies and clinical researchers need to assure regulatory authorities of the reliability of the data that they generate during product development and testing – that is, to demonstrate data integrity. Practices that provide assurance of data integrity in clinical research are required by law and/or established as expectations in regulatory guidance. The data are reviewed in regulatory applications or during regulatory inspections of clinical trial sponsor and investigational sites. Inadequacies of data integrity are frequently reported by inspectors and result in regulatory actions against the organizations or individuals concerned. This course explains the requirements and describes principles and practices that should be followed by trial sponsors, investigators and other clinical research personnel to assure regulators of data integrity.

CT12: How to Conduct Clinical Research Under the EU Clinical Trials Regulation
By Zenosis
This course describes the requirements that must be met by, and options available to, the sponsor during the conduct of an authorised clinical trial. It identifies the various interactions with MSCs that occur via the Clinical Trials Information System (CTIS), and it summarises and links to the extensive guidance available from the European Commission and the European Medicines Agency. Its companion course CT11 sets out the European legal and regulatory context for clinical trials and describes how to apply via the CTIS for authorisation to conduct trials. The two courses therefore provide an ideal foundation for understanding and complying with the new law.

MD01: An Introduction to the Regulation of Medical Devices
By Zenosis
This module provides an introduction to the basics of medical device regulation, especially the requirements that manufacturers must meet in order to market devices in Europe and the USA.

ICT02: Assuring Data Integrity in the Manufacture of Medicinal Products
By Zenosis
Pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies and researchers need to assure regulatory authorities of the reliability of the data that they generate or acquire during product development and manufacturing – that is, to demonstrate data integrity. Data integrity is assessed during regulatory inspections of manufacturing and research sites. Inadequacies of data integrity are frequently reported by inspectors and result in regulatory actions against the companies or individuals concerned. Practices that assure data integrity are required by law and/or expected by regulators in the fields of nonclinical and clinical research, manufacturing and distribution, and pharmacovigilance of medicinal products. This course explains the requirements and describes principles and practices that should be followed to assure regulators and contractual partners of data integrity in the manufacture of medicinal products.