- Professional Development
- Medicine & Nursing
- Arts & Crafts
- Health & Wellbeing
- Personal Development
448 Running courses in Manchester delivered Live Online
AZ-040T00 Automating Administration with Powershell
By Nexus Human
Duration 5 Days 30 CPD hours This course is intended for This course is intended for IT Professionals who are already experienced in general Windows Server, Windows client, Azure, and Microsoft 365 administration, and who want to learn more about using Windows PowerShell for administration. No prior experience with any version of PowerShell or any scripting language is assumed. This course is also suitable for IT Professionals already experienced in server administration, including Microsoft Exchange Server, Microsoft SharePoint Server, and Microsoft SQL Server. This course provides students with the fundamental knowledge and skills to use PowerShell for administering and automating administration of Windows servers. This course provides students the skills to identify and build the command they require to perform a specific task. In addition, students learn how to build scripts to accomplish advanced tasks such as automating repetitive tasks and generating reports. This course provides prerequisite skills supporting a broad range of Microsoft products, including Windows Server, Windows Client, Microsoft Azure, and Microsoft 365. In keeping with that goal, this course will not focus on any one of those products, although Windows Server, which is the common platform for all of those products, will serve as the example for the techniques this course teaches. Prerequisites Before attending this course, students must have: -Experience with Windows networking technologies and implementation. - Experience with Windows Server administration, maintenance, and troubleshooting. 1 - Review Windows PowerShell Learn about Windows PowerShell Get familiar with Windows PowerShell applications Identify factors to install and use Windows PowerShell Configure the Windows PowerShell console Configure the Windows PowerShell Integrated Scripting Environment (ISE) Use Visual Studio Code with PowerShell 2 - Understand the command syntax in Windows PowerShell Discover the structure of PowerShell cmdlets Discover the parameters for using PowerShell cmdlets Review the tab completion feature in PowerShell Display the About files content in PowerShell 3 - Find commands and Get-Help in Windows PowerShell Define modules in PowerShell Find cmdlets in PowerShell Use command aliases in PowerShell Use Show-Command and Get-Help in PowerShell Interpret the help file contents and update the local help content in PowerShell 4 - Manage Active Directory Domain Services using PowerShell cmdlets Manage user accounts in PowerShell Manage groups and group memberships in PowerShell Manage computer accounts in PowerShell Manage organizational units and Active Directory objects in PowerShell 5 - Manage network service settings for Windows devices using PowerShell cmdlets Manage IP addresses in PowerShell Manage IP routing in PowerShell Manage DNS clients in PowerShell Manage Windows Firewall settings in PowerShell 6 - Manage Windows Server settings using PowerShell cmdlets Automate management tasks using the Group Policy management cmdlets Manage server roles and services using PowerShell cmdlets Manage Hyper-V Virtual Machines using PowerShell cmdlets Manage Internet Information Services using PowerShell cmdlets 7 - Manage settings for a local Windows machine using PowerShell cmdlets Manage Windows 10 using PowerShell Manage permissions with PowerShell 8 - Understand the Windows PowerShell pipeline Review Windows PowerShell pipeline and its output Discover object members in PowerShell Control the formatting of pipeline output 9 - Select, sort, and measure objects using the pipeline Sort and group objects by property in the pipeline Measure objects in the pipeline Select a set of objects in the pipeline Select object properties in the pipeline Create and format calculated properties in the pipeline 10 - Filter objects out of the pipeline Learn about the comparison operators in PowerShell Review basic filter syntax in the pipeline Review advanced filter syntax in the pipeline Optimize the filter performance in the pipeline 11 - Enumerate objects in the pipeline Learn about enumerations in the pipeline Review basic syntax to enumerate objects in the pipeline Review advanced syntax to enumerate objects in the pipeline 12 - Send and pass data as output from the pipeline Write pipeline data to a file Convert pipeline objects to other forms of data representation in PowerShell Control additional output options in PowerShell 13 - Pass pipeline objects Pipeline parameter binding Identify ByValue parameters Pass data by using ByValue Pass data by using ByPropertyName Identify ByPropertyName parameters Use manual parameters to override the pipeline Use parenthetical commands Expand property values 14 - Connect with data stores using PowerShell providers Define Windows PowerShell providers Review the built-in providers in PowerShell Access provider help in PowerShell 15 - Use PowerShell drives in PowerShell Explain PowerShell drives in PowerShell Use PowerShell drive cmdlets in PowerShell Manage the file system in PowerShell Manage the registry in PowerShell Work with certificates in PowerShell Work with other PowerShell drives in PowerShell 16 - Review CIM and WMI Review architecture of CIM and WMI Review repositories in CIM and WMI Locate online class documentation by using CIM and WMI cmdlets 17 - Query configuration information by using CIM and WMI List local repository namespaces and classes by using CIM and WMI Query instances by using commands and WMI Query Language Connect to remote computers by using CIM and WMI cmdlets Query repository classes from remote computers by using CIMSession objects 18 - Query and manipulate repository objects by using CIM and WMI methods Discover methods of repository objects by using CIM and WMI Locate class methods and documentation by using CIM and WMI Invoke methods of repository objects by using CIM and WMI 19 - Manage variables in Windows PowerShell scripts Define variables in Windows PowerShell scripts Create variable names in Windows PowerShell scripts Assign values and types to variables in Windows PowerShell scripts Identify the methods and properties of variables in Windows PowerShell scripts Use string variables and methods in Windows PowerShell scripts Use date variables and methods in Windows PowerShell scripts 20 - Work with arrays and hash tables in Windows PowerShell scripts Define an array in Windows PowerShell scripts Work with array lists in Windows PowerShell scripts Define hash tables in Windows PowerShell Scripts Work with hash tables in Windows PowerShell scripts 21 - Create and run scripts by using Windows PowerShell Review Windows PowerShell scripts Modify scripts in the PowerShell Gallery Create scripts using Windows PowerShell Review the PowerShellGet module in Windows PowerShell Run scripts and set the execution policy in Windows PowerShell Review Windows PowerShell and AppLocker Sign the scripts digitally in Windows PowerShell 22 - Work with scripting constructs in Windows PowerShell Review and use the ForEach loop in Windows PowerShell scripts Review and use the If construct in Windows PowerShell scripts Review and use the Switch construct in Windows PowerShell scripts Review the For construct in Windows PowerShell scripts Review other loop constructs in Windows PowerShell scripts Review Break and Continue in Windows PowerShell scripts 23 - Import data in different formats for use in scripts by using Windows PowerShell cmdlets Use the Get-Content command in Windows PowerShell scripts Use the Import-Csv cmdlet in Windows PowerShell scripts Use the Import-Clixml cmdlet in Windows PowerShell scripts Use the ConvertFrom-Json cmdlet in Windows PowerShell scripts 24 - Use methods to accept user inputs in Windows PowerShell scripts Identify values that might change in Windows PowerShell scripts Use the Read-Host cmdlet in Windows PowerShell scripts Use the Get-Credential cmdlet in Windows PowerShell scripts Use the Out-GridView cmdlet in Windows PowerShell scripts Pass parameters to a Windows PowerShell script 25 - Troubleshoot scripts and handle errors in Windows PowerShell Interpret error messages generated for Windows PowerShell commands Add output to Windows PowerShell scripts Use breakpoints in Windows PowerShell scripts Interpret error actions for Windows PowerShell commands 26 - Use functions and modules in Windows PowerShell scripts Review functions in Windows PowerShell scripts Use variable scope in Windows PowerShell scripts Create modules in Windows PowerShell scripts Use the dot sourcing feature in Windows PowerShell 27 - Manage single and multiple computers by using Windows PowerShell remoting Review the remoting feature of Windows PowerShell Compare remoting with remote connectivity Review the remoting security feature of Windows PowerShell Enable remoting by using Windows PowerShell Use one-to-one remoting by using Windows PowerShell Use one-to-many remoting by using Windows PowerShell Compare remoting output with local output 28 - Use advanced Windows PowerShell remoting techniques Review common remoting techniques of Windows PowerShell Send parameters to remote computers in Windows PowerShell Set access protection to variables, aliases, and functions by using the scope modifier Enable multi-hop remoting in Windows PowerShell 29 - Manage persistent connections to remote computers by using Windows PowerShell sessions Review persistent connections in Windows PowerShell Create and manage persistent PSSessions by using Windows PowerShell Disconnect PSSessions by using Windows PowerShell Review the feature of implicit remoting in Windows PowerShell 30 - Review Azure PowerShell module Review Azure PowerShell Review the benefits of the Azure PowerShell module Install the Azure PowerShell module Migrate Azure PowerShell from AzureRM to Azure Review Microsoft Azure Active Directory module for Windows PowerShell and Azure Active Directory PowerShell for Graph modules 31 - Review the features and tools for Azure Cloud Shell Review the characteristics of Azure Cloud Shell Review the features and tools of Azure Cloud Shell Configure and experiment with Azure Cloud Shell 32 - Manage Azure resources with Windows PowerShell Create a new Azure virtual machine by using Windows PowerShell commands Manage Azure virtual machines by using Windows PowerShell commands Manage Azure related storage by using Azure PowerShell Manage Azure subscriptions by using Azure PowerShell 33 - Manage users, groups, and licenses in Microsoft Entra ID by using Windows PowerShell Review benefits to manage Microsoft 365 services by using Windows PowerShell Connect to the Microsoft 365 tenant by using Windows PowerShell Manage users in Microsoft 365 by using Windows PowerShell Manage groups in Microsoft 365 by using Windows PowerShell Manage roles in Microsoft 365 by using Windows PowerShell Manage licenses in Microsoft 365 by using Windows PowerShell 34 - Manage Exchange Online by using Windows PowerShell Connect to Exchange Online by using Windows PowerShell Manage mailboxes in Exchange Online by using Windows PowerShell Manage resources in Exchange Online by using Windows PowerShell Manage admin roles in Exchange Online by using Windows PowerShell 35 - Manage SharePoint Online by using Windows PowerShell Install and connect to SharePoint Online Management Shell by using Windows PowerShell Manage SharePoint Online users and groups by using Windows PowerShell Manage SharePoint sites by using Windows PowerShell Manage SharePoint Online external user sharing by using Windows PowerShell 36 - Manage Microsoft Teams by using Windows PowerShell Review Microsoft Teams PowerShell module Install the Microsoft Teams PowerShell module Manage teams with Microsoft Teams PowerShell module 37 - Create and manage background jobs using Windows PowerShell Define the types of background jobs in Windows PowerShell Start remote jobs and CIM/WMI jobs in Windows PowerShell Monitor jobs in Windows PowerShell Retrieve results for running jobs in Windows PowerShell 38 - Create and manage scheduled jobs using Windows PowerShell Create and run Windows PowerShell scripts as scheduled tasks Define scheduled jobs in Windows PowerShell Create job option and job trigger objects in Windows PowerShell Create and register a scheduled job in Windows PowerShell Retrieve the results from a scheduled job in Windows PowerShell

Architecting with Google Kubernetes Engine
By Nexus Human
Duration 3 Days 18 CPD hours This course is intended for This class is intended for the following participants: Cloud architects, administrators, and SysOps/DevOps personnel Individuals using Google Cloud Platform to create new solutions or to integrate existing systems, application environments, and infrastructure with the Google Cloud Platform. Overview This course teaches participants the following skills: Understand how software containers work Understand the architecture of Kubernetes Understand the architecture of Google Cloud Platform Understand how pod networking works in Kubernetes Engine Create and manage Kubernetes Engine clusters using the GCP Console and gcloud/ kubectl commands Launch, roll back and expose jobs in Kubernetes Manage access control using Kubernetes RBAC and Google Cloud IAM Managing pod security policies and network policies Using Secrets and ConfigMaps to isolate security credentials and configuration artifacts Understand GCP choices for managed storage services Monitor applications running in Kubernetes Engine This class introduces participants to deploying and managing containerized applications on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) and the other services provided by Google Cloud Platform. Through a combination of presentations, demos, and hands-on labs, participants explore and deploy solution elements, including infrastructure components such as pods, containers, deployments, and services; as well as networks and application services. This course also covers deploying practical solutions including security and access management, resource management, and resource monitoring. Introduction to Google Cloud Platform Use the Google Cloud Platform Console Use Cloud Shell Define cloud computing Identify GCPs compute services Understand regions and zones Understand the cloud resource hierarchy Administer your GCP resources Containers and Kubernetes in GCP Create a container using Cloud Build Store a container in Container Registry Understand the relationship between Kubernetes and Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) Understand how to choose among GCP compute platforms Kubernetes Architecture Understand the architecture of Kubernetes: pods, namespaces Understand the control-plane components of Kubernetes Create container images using Google Cloud Build Store container images in Google Container Registry Create a Kubernetes Engine cluster Kubernetes Operations Work with the kubectl command Inspect the cluster and Pods View a Pods console output Sign in to a Pod interactively Deployments, Jobs, and Scaling Create and use Deployments Create and run Jobs and CronJobs Scale clusters manually and automatically Configure Node and Pod affinity Get software into your cluster with Helm charts and Kubernetes Marketplace GKE Networking Create Services to expose applications that are running within Pods Use load balancers to expose Services to external clients Create Ingress resources for HTTP(S) load balancing Leverage container-native load balancing to improve Pod load balancing Define Kubernetes network policies to allow and block traffic to pods Persistent Data and Storage Use Secrets to isolate security credentials Use ConfigMaps to isolate configuration artifacts Push out and roll back updates to Secrets and ConfigMaps Configure Persistent Storage Volumes for Kubernetes Pods Use StatefulSets to ensure that claims on persistent storage volumes persist across restarts Access Control and Security in Kubernetes and Kubernetes Engine Understand Kubernetes authentication and authorization Define Kubernetes RBAC roles and role bindings for accessing resources in namespaces Define Kubernetes RBAC cluster roles and cluster role bindings for accessing cluster-scoped resources Define Kubernetes pod security policies Understand the structure of GCP IAM Define IAM roles and policies for Kubernetes Engine cluster administration Logging and Monitoring Use Stackdriver to monitor and manage availability and performance Locate and inspect Kubernetes logs Create probes for wellness checks on live applications Using GCP Managed Storage Services from Kubernetes Applications Understand pros and cons for using a managed storage service versus self-managed containerized storage Enable applications running in GKE to access GCP storage services Understand use cases for Cloud Storage, Cloud SQL, Cloud Spanner, Cloud Bigtable, Cloud Firestore, and Bigquery from within a Kubernetes application

F5 Networks Configuring BIG-IQ
By Nexus Human
Duration 2 Days 12 CPD hours This course is intended for This course is intended for system and network administrators or operators responsible for the installation, setup, configuration, and administration of the BIG-IQ system or management of BIG-IP devices and F5 products running on those devices. This course uses lectures and hands-on exercises to give participants real-time experience in configuring and using the BIG-IQ© product. Students are introduced to BIG-IQ, its interface, and its various functionality. We first look at administering and operating the BIG-IQ system itself, then detail how it is used to remotely manage BIG-IP devices running BIG-IP Local Traffic Manager (LTM). We then look configuring a BIG-IQ Data Collection Device (DCD) system and see how it is used for the remote storage and examination of BIG-IP log events and statistics. Module 1: BIG-IQ Overview BIG-IQ Centralized Management BIG-IQ Components BIG-IQ Core Functionality REST API BIG-IQ Data Collection Device (DCD) BIG-IP Cloud Edition (CE) Setting up the BIG-IQ System Module 2: Administering the BIG-IQ System Controlling Access to the BIG-IQ Creating, Authenticating, Configuring Users Backups Local Host Settings Configuring DNS, NTP, and SMTP Monitoring BIG-IQ, DCD, and BIG-IP Events with Alerts Monitoring BIG-IQ with iHealth Post Installation Issues; Licensing, Changing Management IP, Master Key, Restoring Backups Module 3: Managing BIG-IP LTM Devices BIG-IP LTM Device Discovery BIG-IP Device Backup Deploying to BIG-IP Devices Deployment and Deployment Logs Configuration Snapshots Managing BIG-IP Certificates Managing BIG-IP Licenses Monitoring BIG-IP Devices with iHealth Management of QKView Reports from Managed BIG-IP Devices Module 4: Setting Up the BIG-IQ Data Collection Device Custom Roles Types and Groups Setting up User Accounts with custom roles and privileges Managing BIG-IP DSC Discovery and management of BIG-IP Device Clusters (DSC) with BIG-IQ Administering BIG-IQ High Availability Configuration and management of BIG-IQ systems in a High Availability pair

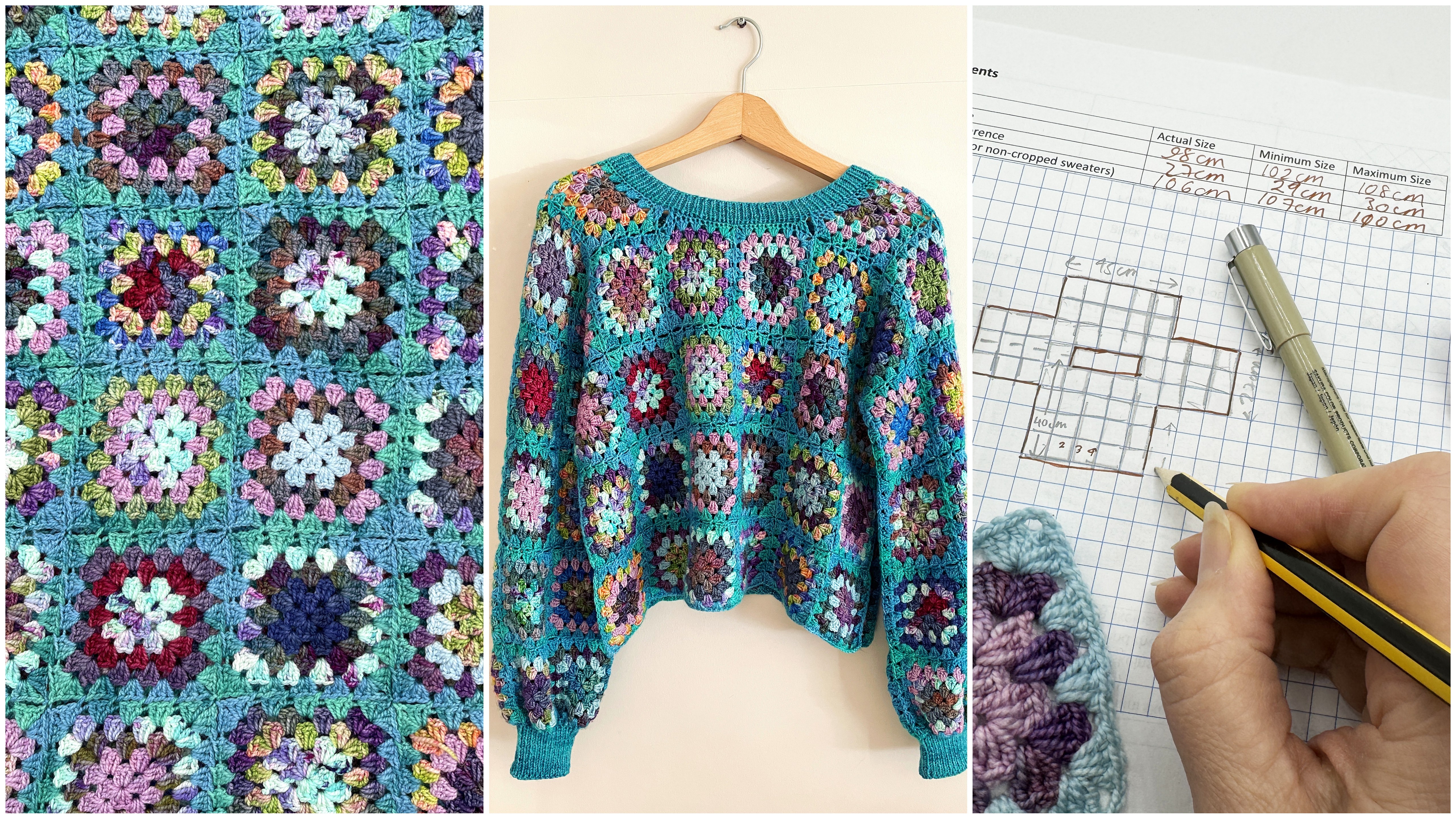
Design & Make Your Own Granny Square Sweater - Online Course Starting 22nd April 2024
By Merrian Holland
Learn how to design and customize a perfect fitting sweater using DK or 4ply/fingering weight yarn. From layout and shape to color placement and professional finishing, this 12-week course will guide you through every step with personalized assistance from expert crochet tutor, Merrian. You'll also be part of a small community of crochet students, all making the sweater together over the 12 weeks.

AEROLATINO CERTIFICATION
By Aerolatino
JOIN THE LATEST LATIN AMERICA DANCE WORKOUT!

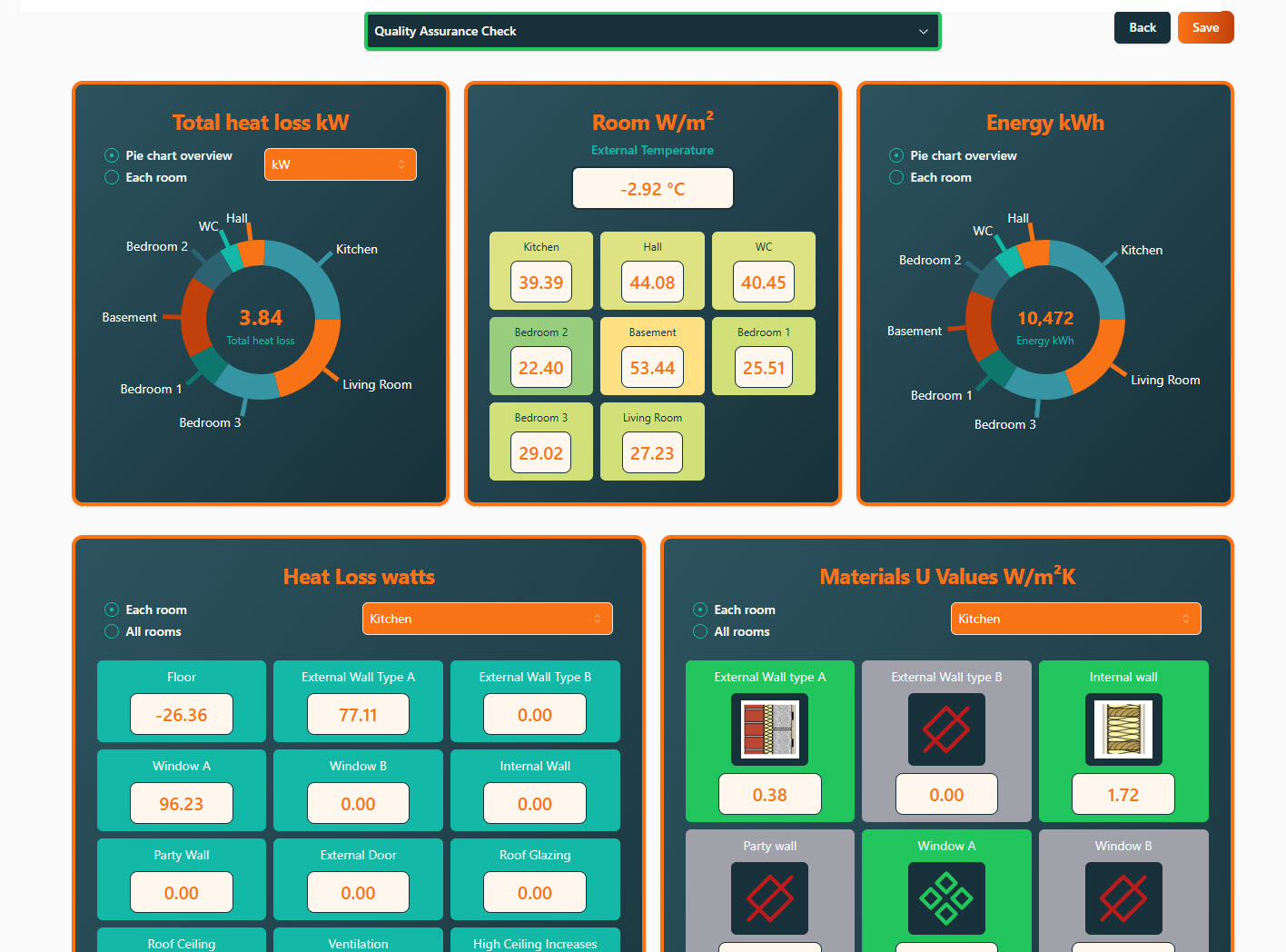
For new users and the curious. Hello, For new users and the curious. IMPORTANT: Firstly, once you are signed up, send us your requests on what you would like to see within the demonstration and learn on the course. We will then cater for your needs and answer them during the session. This is designed to be an introduction into how to start a room by room survey using the Heat Engineer app, then sending this survey to the online dashboard. We will then go through the different steps to complete this heat loss report. Optional pages will also be worked through and shown. Examples of how to select the flow temperature and the heat source (heat pumps and boilers) will be presented once the heat loss result is completed.
Reiki Power Hour Coaching Session
By Margaret Cook - Learn More About Reiki
A 60 minute power hour coaching session online to help answer any questions that you may have about Reiki. Whether you are new to Reiki or have been practising it for many years, there will always be questions that we would like answering. Or sometimes just having the opportunity to talk things through with another experienced Reiki teacher, healer or reiki practitioner.

WB396 IBM Managing Decisions in IBM Operational Decision Manager V8.7.1
By Nexus Human
Duration 5 Days 30 CPD hours This course is intended for This course is designed for business analysts. Overview After completing this course, you should be able to:Describe the benefits of implementing an Operational Decision Manager solution, and the collaboration that is required between the business and development teamsIdentify the main user roles that are involved in designing and developing an Operational Decision Manager solution, and the tasks that are associated with each roleExplain modeling concepts and the UML notation that is relevant to modeling for business rules and eventsDefine and implement object models for business rulesSet up the rule authoring environment in Designer by working with decision services and synchronizing across development and business environmentsCustomize the vocabulary that is used in rulesDiscover and analyze business rules for implementationUse the Operational Decision Manager rule editors to author business rules and decision tablesRun tests and simulations in the Decision Center Enterprise console to validate decision logic and rule changesExplain governance issues and work with Operational Decision Manager features that support decision governance This course introduces business analysts to IBM Operational Decision Manager V8.7.1. You learn the concepts and skills that are necessary to capture, author, validate, and manage business rules with Operational Decision Manager. Course Outline Course introduction Introducing IBM Operational Decision Manager V8.7.1 Exercise: Operational Decision Manager in action Modeling for business rules Exercise: Building the model on paper Exercise: Implementing the model Understanding decision services Exercise: Setting up a decision service Working with the BOM Exercise: Working with the BOM Introducing Decision Center Exercise: Exploring the Decision Center Business console Exercise: Exploring the Decision Center Enterprise console Introducing rule authoring Exercise: Understanding the case study Discovering and analyzing rules Exercise: Discovering rules Exercise: Analyzing rules Working with conditions in rules Exercise: Working with conditions in rules Working with definitions in rules Exercise: Working with definitions in rules Writing complete rules Exercise: Writing complete rules Authoring decision tables and trees Exercise: Authoring decision tables and trees Exercise: Authoring rules: Putting it all together Running tests and simulations in the Enterprise console Exercise: Running tests and simulations in the Enterprise console Introducing decision governance Exercise: Working with the decision governance framework Course summary

Python Introduction
By Nexus Human
Duration 3.5 Days 21 CPD hours This course is intended for This course is aimed at students new to the language who may or may not have experience with other programming languages. Overview Learn how Python works and what it's good for. Understand Python's place in the world of programming languages Learn to work with and manipulate strings in Python. Learn to perform math operations with Python. Learn to work with Python sequences: lists, arrays, dictionaries, and sets. Learn to collect user input and output results. Learn flow control processing in Python. Learn to write to and read from files using Python. Learn to write functions in Python. Learn to handle exceptions in Python. Learn to work with dates and times in Python. In this Python training course by Webucator, Inc, students learn to program in Python. Python Basics Running Python Hello, World! Literals Python Comments Data Types Variables Writing a Python Module print() Function Named Arguments Collecting User Input Getting Help Functions and Modules Defining Functions Variable Scope Global Variables Function Parameters Returning Values Importing Modules Math Arithmetic Operators Modulus and Floor Division Assignment Operators Built-in Math Functions The math Module The random Module Seeding Python Strings Quotation Marks and Special Characters String Indexing Slicing Strings Concatenation and Repetition Common String Methods String Formatting Built-in String Functions Iterables: Sequences, Dictionaries, and Sets Definitions Sequences Unpacking Sequences Dictionaries The len() Function Sets *args and **kwargs Flow Control Conditional Statements The is and is not Operators Python's Ternary Operator Loops in Python The enumerate() Function Generators List Comprehensions File Processing Opening Files The os and os.path Modules Exception Handling Wildcard except Clauses Getting Information on Exceptions The else Clause The finally Clause Using Exceptions for Flow Control Exception Hierarchy Dates and Times Understanding Time The time Module The datetime Module Running Python Scripts from the Command Line The sys Module sys.argv

VMware Kubernetes Fundamentals and Cluster Operations
By Nexus Human
Duration 4 Days 24 CPD hours This course is intended for Anyone who is preparing to build and run Kubernetes clusters Overview By the end of the course, you should be able to meet the following objectives: Build, test, and publish Docker container images Become familiar with YAML files that define Kubernetes objects Understand Kubernetes core user-facing concepts, including pods, services, and deployments Use kubectl, the Kubernetes CLI, and become familiar with its commands and options Understand the architecture of Kubernetes (Control plane and its components, worker nodes, and kubelet) Learn how to troubleshoot issues with deployments on Kubernetes Apply resource requests, limits, and probes to deployments Manage dynamic application configuration using ConfigMaps and Secrets Deploy other workloads, including DaemonSets, Jobs, and CronJobs Learn about user-facing security using SecurityContext, RBAC, and NetworkPolicies This four-day course is the first step in learning about Containers and Kubernetes Fundamentals and Cluster Operations. Through a series of lectures and lab exercises, the fundamental concepts of containers and Kubernetes are presented and put to practice by containerizing and deploying a two-tier application into Kubernetes. Course Introduction Introductions and objectives Containers What and Why containers Building images Running containers Registry and image management Kubernetes Overview Kubernetes project Plugin interfaces Building Kubernetes Kubectl CLI Beyond Kubernetes Basics Kubernetes objects YAML Pods, replicas, and deployments Services Deployment management Rolling updates Controlling deployments Pod and container configurations Kubernetes Networking Networking within a pod Pod-to-Pod Networking Services to Pods ClusterIP, NodePort, and LoadBalancer Ingress controllers Service Discovery via DNS Stateful Applications in Kubernetes Stateless versus Stateful Volumes Persistent volumes claims StorageClasses StatefulSets Additional Kubernetes Considerations Dynamic configuration ConfigMaps Secrets Jobs, CronJobs Security Network policy Applying a NetworkPolicy SecurityContext runAsUser/Group Service accounts Role-based access control Logging and Monitoring Logging for various objects Sidecar logging Node logging Audit logging Monitoring architecture Monitoring solutions Octant VMware vRealize Operations Manager Cluster Operations Onboarding new applications Backups Upgrading Drain and cordon commands Impact of an upgrade to running applications Troubleshooting commands VMware Tanzu portfolio overview
