- Professional Development
- Medicine & Nursing
- Arts & Crafts
- Health & Wellbeing
- Personal Development
684 Practitioner courses in Leeds delivered Live Online
Certified Professional for Usability and User Experience – Usability Testing and Evaluation (CPUX-UT)
By Bunnyfoot
This one-day course introduces the field of user experience and provides an excellent entry point to our other specialised training courses. UX processes and practices have become a central component of product design, service design and web design.

Awareness of Safeguarding
By Madeleys First Aid Plus
RQF level 1 Awareness of Safeguarding The RQF Level 1 Awareness of Safeguarding course is designed to provide individuals with a basic understanding of safeguarding principles and practices. It aims to raise awareness about the importance of safeguarding and promote the well-being and protection of vulnerable individuals, such as children, young people, and adults at risk. The course covers the following topics: Introduction to Safeguarding: Definition and importance of safeguarding. Key legislation, policies, and guidance related to safeguarding. Roles and responsibilities of individuals and organizations in safeguarding. Types of Abuse and Neglect: Overview of different types of abuse, including physical, emotional, sexual, and financial abuse. Recognizing signs and indicators of abuse and neglect. Understanding the impact of abuse on individuals' well-being. Vulnerable Groups: Identifying vulnerable groups, such as children, young people, older adults, and individuals with disabilities or mental health issues. Understanding the specific safeguarding concerns and considerations for each group. Reporting and Responding to Safeguarding Concerns: Procedures for reporting safeguarding concerns or disclosures. Understanding the importance of maintaining confidentiality and handling sensitive information appropriately. Responding to safeguarding concerns in a timely and appropriate manner. Promoting Safeguarding and Preventing Abuse: Strategies for promoting a safe and inclusive environment. Recognizing potential risk factors and implementing preventative measures. Understanding the importance of creating a culture of safeguarding within organizations. Multi-Agency Collaboration: Collaboration between different agencies and organizations involved in safeguarding, such as social services, law enforcement, and healthcare. Sharing information and working together to ensure effective safeguarding practices. Case Studies and Scenarios: Reviewing case studies and scenarios to apply safeguarding principles and practices. Analysing potential safeguarding dilemmas and decision-making processes. Personal Responsibilities: Recognizing personal boundaries and limitations when working with vulnerable individuals. Understanding the importance of self-care and managing emotional well-being when dealing with safeguarding issues. It is important to ensure that the course meets local safeguarding guidelines and requirements. Suitability - Who should attend? The RQF Level 1 Awareness of Safeguarding course is suitable for a wide range of individuals who may come into contact with vulnerable individuals or have a general interest in understanding safeguarding principles. Here are some key groups of people who should attend the course: Employees and Staff: The course is relevant for employees and staff members across various sectors and industries, including but not limited to education, healthcare, social services, hospitality, sports and recreation, and community organizations. It helps them develop a basic understanding of safeguarding principles and their responsibilities in ensuring the well-being and protection of vulnerable individuals they may encounter in their work. Volunteers: Individuals who volunteer their time and services in organizations that work with vulnerable individuals should attend the course. It equips them with essential knowledge and awareness of safeguarding issues, helping them provide appropriate support and maintain the safety and dignity of those they interact with. Parents and Caregivers: The course can benefit parents, guardians, and caregivers by providing them with a foundation in safeguarding principles. It helps them recognize potential risks and signs of abuse or neglect, enabling them to create safer environments for the children or vulnerable individuals under their care. Community and Youth Workers: Individuals involved in community work, youth organizations, or youth clubs should attend the course to enhance their understanding of safeguarding. It enables them to promote the well-being and safety of young people and recognize signs of potential abuse or exploitation. Volunteers or Trustees of Charitable Organizations: Individuals serving as volunteers or trustees in charitable organizations that work with vulnerable populations can benefit from the course. It helps them fulfill their responsibilities in safeguarding the individuals the organization serves and ensures they are aware of their legal and ethical obligations. General Public: The course is open to the general public as it provides valuable knowledge and awareness of safeguarding principles. It can benefit individuals who have an interest in understanding the rights and protection of vulnerable individuals in society. It's important to note that the RQF Level 1 Awareness of Safeguarding course provides foundational knowledge and awareness. For individuals who require more in-depth training or who have specific safeguarding roles or responsibilities, higher-level courses may be more suitable. Outcome / Qualification etc. Certification The qualification does not have an expiry date but refresher training and keeping up to date with changes to policies, procedures and new legislation through ongoing CPD is vital. Training Course Content Module 1 Introductions Module 2 Safeguarding legislation and guidance Module 3 Roles and responsibilities Module 4 Abuse and neglect Module 5 Identifying concerns and disclosure Module 6 Making judgements Module 7 Reporting concerns Module 8 Course closure and assessment MODULE 1 INTRODUCTIONS Session content Trainer/Assessor introduction Learner introductions Course syllabus Learning outcomes and assessment criteria Session duration 20 minutes MODULE 2 SAFEGUARDING LEGISLATION AND GUIDANCE Session content Introduction to safeguarding Definitions Assessment framework Safeguarding statistics Safeguarding legislation and guidance Rights of a child/adult at risk Session duration 40 minutes MODULE 3 ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES Session content Safeguarding partnerships Local authority safeguarding officer Social care services Multi-agency safeguarding hubs Organisational safeguarding policies Safeguarding lead Session duration 30 minutes MODULE 4 ABUSE AND NEGLECT Session content Definitions Types of abuse and neglect Physical abuse Emotional abuse Sexual abuse Neglect Signs and indicators Parent/carer abuse Radicalisation FGM Forced marriage Modern slavery County line gangs Electronic media abuse - Internet and social networking dangers Session duration 50 minutes MODULE 5 IDENTIFYING CONCERNS AND DISCLOSURE Session content Identifying concerns Being a point of disclosure Recording disclosure information Session duration 20 minutes MODULE 6 MAKING JUDGEMENTS Session content Child development needs Identifying a safeguarding concern Group activity making judgements Session duration 30 minutes MODULE 7 REPORTING CONCERNS Session content Silencing factors Barriers to raising concerns Reporting concerns Importance of sharing concerns Session duration 20 minutes MODULE 8 COURSE CLOSURE AND ASSESSMENT Session content Course summary Assessment paper Course evaluation Course closure Session duration 30 minutes Course delivery details Qualification delivery The qualification has 4 assigned guided learning hours (GLH) and 5 hours total qualification time (TQT). GLH indicates the number of classroom contact hours that the learner will undertake. TQT includes GLH but also takes into account any unsupervised learning and is an estimate of how long the average learner will take to complete the qualification. The minimum classroom contact time of 4 hours should be delivered over a minimum of half a day. The course can be spread over a maximum of 2 weeks, ensuring that each session is a minimum of two hours. The class ratio for this qualification is a maximum of 16 learners to 1 Trainer/Assessor Why choose Madeleys First Aid Plus Founded in 2021 after Louise left 30 years in the NHS as an Advanced practitioner in A&E/ITU, had spent 1.5 years in Covid ITU Won FSB Best start-up business in the West Midlands in May 2023 Now trained 100's of delegates in Physical and Mental Health First Aid Expenses Travel costs and lunch required, there are many cafes and sandwich bars here in Much Wenlock to buy your lunch, you may eat it in the training room. All training material, books, qualification certificates are included in the price Continuing Studies The RQF Level 1 Awareness of Safeguarding course serves as an introductory course that provides individuals with a basic understanding of safeguarding principles. While it is a standalone qualification, individuals who complete the course may choose to progress further in their safeguarding training and education. Here are some potential progression options: RQF Level 2 Award in Safeguarding: This qualification builds upon the knowledge gained in the Level 1 course and provides a more comprehensive understanding of safeguarding principles, policies, and procedures. It covers topics such as risk assessment, responding to safeguarding concerns, and effective communication in safeguarding contexts. Specialized Safeguarding Courses: Individuals who wish to focus on specific areas of safeguarding can pursue specialized courses related to their field of interest. These courses may include Child Protection, Adult Safeguarding, Domestic Abuse Awareness, Online Safety, or Safeguarding in Healthcare. Specialized courses delve deeper into the specific risks, regulations, and best practices associated with safeguarding vulnerable individuals in those particular contexts. Safeguarding Training for Specific Professions: Many professions have specific safeguarding training requirements tailored to their sector. For example, teachers may need to complete safeguarding training specific to the education setting, healthcare professionals may have training focused on safeguarding vulnerable patients, and social workers may have specialized safeguarding training in line with their role. Progression may involve undertaking profession-specific safeguarding courses or qualifications. Safeguarding Leadership and Management Training: Individuals in supervisory or managerial positions may consider pursuing training that focuses on the leadership and management aspects of safeguarding. This can include courses on developing and implementing safeguarding policies and procedures, managing safeguarding incidents, conducting internal investigations, and providing guidance and support to staff. Continued Professional Development (CPD): Engaging in ongoing CPD activities is essential for staying updated with the latest developments in safeguarding practices and policies. Individuals can attend conferences, workshops, or seminars related to safeguarding, child protection, or specific areas of interest within the field. This allows for continued learning and networking with other professionals. Higher Education: Individuals who wish to pursue a more in-depth study of safeguarding can consider higher education programs in social work, psychology, criminology, or related fields. These programs provide comprehensive knowledge and training in safeguarding practices, policies, and research. They may lead to professional certifications or degrees that enhance career opportunities in safeguarding roles. It's important for individuals to research and explore progression options that align with their specific career goals, interests, and local requirements. Different countries or regions may have varying certification or training requirements for safeguarding roles, so it's advisable to check with relevant regulatory bodies or professional associations for specific guidance.

Nutritional Consultancy Diploma
By Plaskett International
BECOME A NUTRITIONAL CONSULTANT AND LEARN HOW TO STEER YOUR CLIENTS TOWARDS BETTER HEALTH A MESSAGE FROM THE AUTHOR This course is a must for anyone who is passionate about health & well-being and would like to fast-track to a practitioner role whereby you can confidently advise your clients on the best route to achieving good health in a world where ill-health is prevalent. The hope is expressed that this course will lead you feeling well informed, on a deeper naturopathic level, and provide you with a range of measures that you can apply to practice as you steer your clients towards better health. DR. LAWRENCE PLASKETT Course Duration 12 months Study Hours 300 hours Course Content 27 sections Course Fee £595 Course Overview The Plaskett Diploma in Nutritional Consultancy is especially useful for those whereby holistic health is a feature of your line of work and you would like to enhance the service that you provide, or for those that wish to set up an independent practice as a Nutritional Consultant. In Part One you will: Be introduced to the concept of naturopathy Gain a general understanding of the subject of health and nutrition Grasp the fundamentals of the cell's need for nutrients Appreciate the role of carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins and minerals and understand the basics of how these nutrients work in the body Be aware of the enormous health benefits that can come from favourable dietary change Appreciate the merits of particular foods and nutrients Ultimately gain the knowledge that will lead towards a better standard of well-being now, and a prolonging of good health in the future In Part Two you will:Gain a deeper understanding of naturopathy and its principles which you can then apply to practise in nutritional therapies.Obtain the skills to understand the depth of disease in your patients to then find a route back from chronic disease and enable you to advise the best treatment plan.Develop an understanding of the role of the practitioner from the initial consultation, the taking of a case history, the interpretation and the subsequent advising of a treatment plan.Learn the ‘tools of the trade’ in using diets, supplements, herbs, phytonutrients in treatment, with flexibility and insight. BREAKDOWN OF THE COURSE SECTIONS PART ONE includes the following 12 sections: SECTION 1 THE PRINCIPLE BULK NUTRIENTS & ASSOCIATED FOODS In Section 1, we begin the study of nutrients and foods by looking at the main bulk nutrients that our diets contain: protein, carbohydrate and fat. Before one can consider individual vitamins and minerals, one has to know about the nutrients that make up most of our diets, namely the bulk nutrients. These are the suppliers of food energy, essential amino acids and fatty acids. You will need to understand these so as to manipulate them with skill. Areas Covered Proteins The carbohydrates Fibre Fats Classes of foods based upon composition SECTION 2 THE CELL & CELL ENERGY This section will illuminate the nature of the cell and explain how the energy of the cell is generated and what functions the cell must perform using that energy. It explains calories as units of energy measurement and the dynamic role of the enzymes in the cells. Areas Covered The cell Cell energy The energy content of food What else does the body have to do with its energy? How does the body release energy from food? Enzymes The overwhelming importance of cell energy The vitality of cells and tissues The key role of blood glucose What key factors are most likely to erode good vitality? Go-factors for enzymes Internal cell environment Enzyme poisons SECTION 3 THE ENVIRONMENT INSIDE THE CELL This section explains the importance of the controlled environment inside the cell. It particularly stresses how important it is to maintain the balance between sodium and potassium and between calcium and magnesium. Areas covered Out of balance intakes of sodium and potassium Calcium and magnesium balance Calcium mishandling SECTION 4 THE NEED FOR THE CELL TO SELF CLEANSE This section shows you how the cell needs to remain vital and active and to maintain the integrity of its energy systems and enzymes. It stresses the cell's need to excrete waste and toxic materials and to actively cleanse. This approach is both naturopathic and science-based. Areas covered Naturopathic elimination The concept of self-cleansing Naturopathy Vitality Chronic and acute Suppression SECTION 5 THE MICRO-MINERALS & THEIR CONTRIBUTION TO THE CELL This section emphasises and explains the importance of micro-minerals. It shows them in their role as enzyme activators and how they contribute in this way to cell energy and to maintaining the cell's integrity and function. It explains the key roles and characteristics of individual micro-minerals. Areas covered How metals act as enzyme activators Iron Zinc Manganese Copper Chromium Selenium Molybdenum General supplementation policy on trace metals Non-metallic micro-minerals Toxic metals Notes on metallic macro-minerals SECTION 6 THE VITAMINS This section covers the entire group of vitamins. It shows how they activate enzymes, contribute to cell energy and increase vitality. It explains their differing functions and characteristics. Areas covered Vitamins defined Intakes and rnis for vitamins How vitamins work The vitamins Non-vitamin nutrients How vitamins contribute to cell energy and increase the life force Food sources of the vitamins SECTION 7 BOWEL FLORA – HOW IT AIDS CLEANSING & MAINTENANCE OF A GOOD BODY ENVIRONMENT This section explains how the complex population of bacteria in the intestines contribute to maintaining vitality and health. In particular, it will become clear how these bacteria aid cleansing and the maintenance of a good environment within the body, which is so essential to good health. It includes how to nurture your own bowel flora organisms. Areas covered The bacteria of the large intestine (the bowel) The alternative view of desirable and undesirable bowel flora The benefits from an acidic lower bowel The effect of bowel flora upon cleansing Association of lactobacillus with milk Synthesis and absorption of b vitamins The reciprocal effects of bowel flora The bowel flora from infancy to adulthood Candida albicans How to maintain the bowel flora The use of bowel flora products SECTION 8 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE MAIN FOODS. SUPPRESSIVE VERSUS ELIMINATIVE FOODS This section identifies the 'suppressive' foods - those which block the body's elimination of toxins. It separates them from the 'eliminative' foods - those which enable or enhance the voiding of toxins. It gives the characteristics (in this respect) of the main food groups. It will tell you what problem foods to avoid and identify the acid-producing foods. Areas Covered Milk as a problem food Wheat and rye as problem foods Vegetables Relation of elimination to acidity The two-step process of elimination The neutral grains Salt Sugar SECTION 9 THE COMPOSITION OF FOODS This section provides a great deal of data on the composition of foods, their content and the main differences between them. This is a working mass of data to enable your own design of health-giving diets. Areas Covered Commentary on food tables The spread of bulk nutrients The spread of mineral nutrients SECTION 10 ALLERGIES, INTOLERANCE & SENSITIVITY. MICRO-MINERALS & THEIR CONTRIBUTION TO THE CELL This section is an introduction to allergies or intolerances - what they are; physical signs and symptoms, the most frequent; masked/hidden and/or addictive allergies; causes of allergy - food, chemical, emotional and mental; stages of allergy; different types of allergy - fixed, variable, cyclic; managing allergies and sensitivities - how to handle them; rotation diets (including the rotation chart); allergy testing and its limitations; food additives and chemicals; the role of nutrition in all this. Areas Covered Allergic reactions defined The nature of allergies and the effect they have Obvious reactions The four main classes of allergy The possible underlying causes of allergy Viewing allergy tests and their limitations What help is available to deal with allergies The key role of nutrition in the underlying case and treatment of allergy How allergies interfere with treatment The concept of neutralisation The allopathic or orthodox drug approach SECTION 11 DESIGNING DIETS This section provides clear guidance on designing maintenance nutritional diets that, compared to most ordinary diets, should improve health. Areas Covered Dietary paragraphs Using the dietary paragraphs to make up diets SECTION 12 THE USE OF SUPPLEMENTS This section explains and demystifies the subject of vitamin and mineral supplements and their use. It enables you to design simple maintenance and health-giving programmes of supplementation. Areas Covered General guidelines in the use of supplements Always attend to the diet first Preparing for mineral and vitamin supplementation Steps in supplement intake Simple and effective combinations The eliminative qualities of magnesium and calcium Less frequently used combinations Use of multiple formulations Adding in the trace elements as a further stimulant of toxin elimination & for correction of deficiencies On to the next stage – zinc and manganese Conditions where practitioners of nutritional medicine might use such formulae Vitamins a & d Vitamins c & e Choline & inositol Calcium pantothenate The role of the practitioner of nutritional medicine PART TWO includes the following 15 sections: SECTION 1 NATUROPATHY, ITS NATURE AND ITS HISTORY In this section we introduce the medical system known as “naturopathy”. We do so because this system provides the basis for understanding and using naturopathic nutritional therapies. Throughout this Course we shall refer to naturopathy and naturopathic principles and in learning and using these principles, you will hopefully discover a dynamic view of health and illness that will excite you and will inform and motivate your future practice. Areas Covered The Basic Principles of Naturopathy The Early Days: Hydrotherapy as the Core Therapy Progress of Naturopathy in the United States The Halycon Years of Naturopathy in Britain The Suppression of Naturopathy and its Rebirth The Details of Hydrotherapy Techniques The Range of Today’s Naturopathic Techniques Published Research into Naturopathy and General Acceptance Today’s Activities at Health Spas Naturopathy in Relation to Scientific Medicine Naturopathy in Relation to Biochemistry: the Principles of “General Chronicity” Naturopathy as the Philosophical Base for other Therapies SECTION 2 PHILOSOPHY OF NATUROPATHIC NUTRITIONAL THERAPEUTICS In order to begin to understand Nutritional Therapeutics, we have to understand the philosophy that is at its very basis. One will be departing quite fundamentally from conventionality and as the truth about natural medicine and natural nutrition unfolds in this Course, the student will, in all probability, come to realise that holism is a higher form of knowledge; one that transcends the materialistic and the mechanistic and will lead you on the first steps of this most exciting of all journeys. Areas Covered The status of knowledge about diet in relation to health The pressure of conventional opinion The limitations of the conventional approach What goes in must affect health in the long run The body's resistance to deterioration Profound effects from treatment The life force in relation to scientific concepts The nature of toxins Starting to look at the route for recovery Acute conditions, inflammation and hyperactivity Routes by which toxins enter the body Routes of exit of toxins Movement of toxins within the body: toxic locations Iridology Knife edge between healing and non-healing The effects to be expected from toxins residing in tissues SECTION 3 SYNTHESIS OF NATUROPATHY & SCIENCE What is to be presented in this Section is pertinent to the whole question of the initiation of chronic diseases. If we look in the pathology texts and consult the sections on individual types of chronic disease, we usually find an explanation of the cause (aetiology) on a superficial level. However, when we begin to probe into the cause of the causes, we soon hit an impenetrable wall of “not knowing”. It is in this Section that we aim to open the door to this question and therefore give a route back from chronic disease. Areas covered Introduction: a specialized meaning of “Chronicity” The Nature of Toxic Damage – Non-Specific Cell Toxicity The Nature of Membranes Mechanisms of Protein Synthesis and their Vulnerability to Toxins Damage to Mitochondria and the Endoplasmic Reticulum Relationship of General Cellular Damage to Cancer The Nucleus, DNA and their Vulnerability to Toxins DNA Repair Mechanisms The Nature of Toxic Damage – Specific Cell Toxicity Cell Damage and the “General Chronicity” Theory SECTION 4 THE PRACTITIONER’S ROLE In this Section we wish to paint a picture that fairly fully describes this role. It is important to build a set of views about your future role that is fully compatible and interwoven with the naturopathic philosophy and data given in the previous Sections of the Course. Areas covered Introduction to the Role of the practitioner The Wider Environment The Microcosm of the Consulting Room patient & treatment pimary components of the Practitioner’s role a working relationship & commitment to each patient physical examination communicating & recording the prescription providing nutritional products required for therapy communication with doctors spreading the word SECTION 5 UNDERSTANDING THE DEPTH OF DISEASE Here is where the clinical work begins. We begin by thinking about this one aspect – how sick is your patient? You need some idea as to how big the problem is that lies before you. Areas covered The Nature of Health and Disease and the Approach to Treatment Some of the Misconceptions Flexibility of Disease Definitions Arthritis as an Example Do You Need a Hospital Diagnosis When You Are Not Unwell? Homotoxicology and the Teachings of Reckeweg Reckeweg’s Six Levels of Deterioration Examples of Progressive Sequences of Medical Conditions The Miasmic Background: Important but Disputed territory The Three Basic Homeopathic Miasms The Tubercular Miasm The Carcinocin Miasm The Sub-divisions of the Tubercular Miasm Note on Iridology SECTION 6 THE CONCEPT OF ELIMINATORY PRESSURE & ITS MANAGEMENT Eliminatory pressure is the term we use to denote the combined effect of all the various naturopathic-type measures we apply to help the body biochemistry of a sick person to return to normal. According to the “Theory of General Chronicity”, the normality of the biochemistry of the body cells, and hence their degree of freedom from toxicity and damage, is our yardstick of general health and vitality. Areas covered The Nature of Eliminatory Pressure Differences of Response to Naturopathic Pressure The Interactions between Toxins and Toxic Damage Regulating Eliminative Pressure at Manageable Levels The Basics of Generating Eliminatory Pressure Fasting: Free Radicals and Antioxidants “Firing up” Eliminatory Pressure with Fruit The Stage I and Stage 2 Elimination Using Foods to Generate Controlled Levels of Eliminatory Pressure Using Supplements to Generate Controlled Levels of Eliminatory Pressure Contributions to Eliminatory Pressure from Herbs and Special Nutrients Levels of Eliminatory Pressure, Understanding and Managing Them The Effectiveness’, or Otherwise, of Eliminatory Reactions The Concept of the “Chronically Acute” The Approach to Overall Management of the Case SECTION 7 TAKING THE CASE HISTORY & UNDERSTANDING ORGANS AND ORGAN FUNCTIONS In this Section we concern ourselves with the actual technique for taking down the particulars of the case. Before we can carry out a full naturopathic diagnosis, we shall need to understand the principles of ‘Plotting the Course of Disease’. It is from this that we will gain a full appreciation of how the sick person came to be in their present condition and this will then lead us on to the question of what to do about it. Areas covered The More Basic Facts The Aims and Objectives in Taking the Case The Organ States Assessing the Naturopathic State of Organs Hierarchy of Organs Organ-Specific Diagnosis Individually Important Organs and Systems Blood Sugar in Relation to Vitality: Hypoglycaemia The Adrenal Glands how should we recognise adrenal exhaustion clinically? The Liver The Kidneys The Immune System Location of Immune System Components. Functions of Immune System Components. Nutritional Therapy Interpretation of Immune System Signs The Skin SECTION 8 INTERPRETATION OF CASE HISTORY AND UNDERSTANDING INDIVIDUAL REACTIVITY In this Section, we would like you to consider the inevitability of the rules that apply to progression along the pathway to chronic disease, and to the possibility of return from any position that is well down that path. From understanding the case, you will be able to determine what the treatment should be. Areas Covered The Naturopathic Laws and Observational Skills The Progression of Disease More about the Acute and the Chronic The Nutritional Therapist’s View of Disease The Allopathic View of Disease More about “Charting the Naturopathic Ebb and Flow” The Multifactorial Diagnosis See What’s Moving, What’s Changing Assessing Individual Reactivity Let the Case Taking Stage Foreshadow the Interpretation just a Little Note on The Chinese Medicine Connections SECTION 9 THE TOOLS OF THE TRADE & USING DIETS AS TREATMENT Using the information presented to you in Part One of the course, you will be able to use those same dietary paragraphs and move towards a very flexible prescribing of individually designed diets. You will make up a diet for each patient that will embody a carefully thought out modulation of the elimination/suppression aspect of our approach to health. Areas Covered What we have covered already Many people may seem not to need special diets Avoid becoming paranoid Choices in dietary design More about the food classes Facing realism in your range of non-therapeutic prescriptions Adaptation for vegetarians Elements of directional dietary prescribing The approach to actual therapeutic prescription SECTION 10 THE TOOLS OF THE TRADE & USING SUPPLEMENTS AS TREATMENT We provided advice in Part One of the Course on the use of supplements. We introduced the ratio between magnesium and calcium, the use of micro-minerals and the use of zinc and manganese to name but a few. Here we explain further the steps needed to apply these essential tools to ensure that your treatment advice is successful. Areas Covered The latest advice provided by the Introductory Nutritional Course supplementation Legal Restraint upon use of Supplements SECTION 11 THE TOOLS OF THE TRADE & USING HERBS AS TREATMENT In the course of our treatment we often need to deal with common herbs. This is to produce certain organ-specific or system-specific effects, not obtainable with other nutrients. The effect of this is not to make Herbalists of us, but to ensure that these remedies are very carefully selected for their compatibility with other nutrients. Areas Covered Aloe vera Bromelain St john’s wort Gingko biloba Silymarin SECTION 12 ACTIONS OF GROUPS OF PHYTONUTRIENTS This Section begins to delve into what lies behind the known fact that fruit and vegetable consumption inhibits many diseases. What are the substances within them that are responsible for such an important protection of the human body? Each of the main groups is examined with the main purpose being to familiarize the Student with these substances and to offer scientific evidence that some of these really do protect against disease. Areas Covered The Position of Phytonutrients Among Other Factors What are Phytonutrients? The Place of Phytonutrients among Secondary Plant Metabolites The Different Groups of Beneficial Phytonutrients Evidence for anti-disease activity SECTION 13 SPECIAL SUPPLEMENTS & THE COMBINED PRESCRIPTION When we write about “special supplements”, we mean to refer to those substances that are used as nutritional supplements and which do not fit into any of the previous categories mentioned. Here we teach the Student that they may in fact include many substances from many groups, leading to a diversified classification that each has their own special effects, conferring unique advantages upon the taker of them. Areas Covered Special Supplements & combined prescription Conducting the Consultation SECTION 14 STEERING A COURSE THROUGH TREATMENT – FLEXIBILITY AND INSIGHT Having not specifically addressed the question of what happens after the initial consultation, it is here that we bring together all the information that has been presented to you in the pages of this Nutritional Therapeutics Course, therefore, making this Section a recapitulation of things we have covered already, but brought together in a cohesive treatment of the subject. Areas Covered Progressing the Case Things to do at the First Consultation to help towards the Second The Second Consultation the meaning of different outcomes Constipation and Diarrhoea as incidents in Treatment. Titration of Bowel Flora The Nutritional Therapy Intensive Cleanse Diet Enemas Supplements Juices Duration Supplement Sequences in Treatment From Calcium Formulations to Calcium-Free Formulations Other Progressions Allergies, Intolerances and Hypersensitivities SECTION 15 SNAGS, CLEANSES AND CASE HISTORIES TESTIMONIALS Here's what students have to say about the course Kate Woolger, pilates instructor UK I chose the Plaskett College as I wanted something which was flexible and could be done in my own time. The content of the course really appealed. The study experience has been enjoyable - sometimes hard if a subject wasn’t so interesting. In regards to changes I have already implemented, I’m more thoughtful of thinking things through from the inception rather than just looking at the problem"

Immerse.
By The Harmony Principle
Immerse will enrich your understanding of the interplay of yin & yang, the elements that make up everything in the universe - water, wood, fire, earth, metal - and what it means to be a fully expressed human being. You are invited to look deep within and engage consciously without.

ITIL 4 Specialist: High Velocity IT: In-House Training
By IIL Europe Ltd
ITIL® 4 Specialist: High Velocity IT: In-House Training The ITIL® 4 Specialist: High-Velocity IT module is part of the Managing Professional stream for ITIL® 4. Candidates need to pass the related certification exam for working towards the Managing Professional (MP) designation. This course is based on the ITIL® 4 Specialist: High-Velocity IT exam specifications from AXELOS. With the help of ITIL® 4 concepts and terminology, exercises, and examples included in the course, candidates acquire the relevant knowledge required to pass the certification exam. This module addresses the specifics of digital transformation and helps organizations to evolve towards a convergence of business and technology, or to establish a new digital organization. It was designed to enable practitioners to explore the ways in which digital organizations and digital operating models function in high-velocity environments. Working practices such as Agile and Lean, and technical practices and technologies such as Cloud, Automation, and Automatic Testing are included. What You Will Learn At the end of this course, participants will be able to: Understand concepts regarding the high-velocity nature of the digital enterprise, including the demand it places on IT. Understand the digital product lifecycle in terms of the ITIL operating model. Understand the importance of the ITIL guiding principles and other fundamental concepts for delivering high-velocity IT. Know how to contribute to achieving value with digital products. Course Introduction Let's Get to Know Each Other Course Learning Objectives Target Audience Characteristics ITIL® 4 Certification Scheme Course Components Course Agenda Module-End Exercises Exam Details Introduction to High-Velocity IT High-Velocity IT Digital Technology Digital Organizations Digital Transformation High-Velocity IT Approaches Relevance of High-Velocity IT Approaches High-Velocity IT Approaches in Detail High-Velocity IT Operating Models Introduction ITIL® Perspective High-Velocity IT Aspects High-Velocity IT Applications ITIL® Building Blocks for High-Velocity IT Digital Product Lifecycle Service Value Streams Four Dimensions of Service Management ITIL® Management Practices High-Velocity IT Culture Key Behavior Patterns ITIL® Guiding Principles Supporting Models and Concepts for Purpose Ethics Design Thinking Supporting Models and Concepts for People Reconstructing for Service Agility Safety Culture Stress Prevention Supporting Models and Concepts for Progress Working in Complex Environments Lean Culture ITIL® Continual Improvement Model High-Velocity IT Objectives and Techniques High-Velocity IT Objectives High-Velocity IT Techniques Techniques for Valuable Investments Prioritization Techniques Minimum Viable Products and Services Product / Service Ownership A/B Testing Techniques for Fast Developments Basic Concepts Related to Fast Development Infrastructure as Code Reviews Continual Business Analysis Continuous Integration / Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) Continuous Testing Kanban Techniques for Resilient Operations Introduction to Resilient Operations Technical Debt Chaos Engineering Definition of Done Version Control Algorithmic IT Operations ChatOps Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) Techniques for Co-created Value Basic Concepts of Co-created Value Service Experience Techniques for Assured Conformance DevOps Audit Defense Toolkit DevSecOpsPeer Review

ITIL 4 Specialist: High Velocity IT: Virtual In-House Training
By IIL Europe Ltd
ITIL® 4 Specialist: High Velocity IT: Virtual In-House Training The ITIL® 4 Specialist: High-Velocity IT module is part of the Managing Professional stream for ITIL® 4. Candidates need to pass the related certification exam for working towards the Managing Professional (MP) designation. This course is based on the ITIL® 4 Specialist: High-Velocity IT exam specifications from AXELOS. With the help of ITIL® 4 concepts and terminology, exercises, and examples included in the course, candidates acquire the relevant knowledge required to pass the certification exam. This module addresses the specifics of digital transformation and helps organizations to evolve towards a convergence of business and technology, or to establish a new digital organization. It was designed to enable practitioners to explore the ways in which digital organizations and digital operating models function in high-velocity environments. Working practices such as Agile and Lean, and technical practices and technologies such as Cloud, Automation, and Automatic Testing are included. What You Will Learn At the end of this course, participants will be able to: Understand concepts regarding the high-velocity nature of the digital enterprise, including the demand it places on IT. Understand the digital product lifecycle in terms of the ITIL operating model. Understand the importance of the ITIL guiding principles and other fundamental concepts for delivering high-velocity IT. Know how to contribute to achieving value with digital products. Course Introduction Let's Get to Know Each Other Course Learning Objectives Target Audience Characteristics ITIL® 4 Certification Scheme Course Components Course Agenda Module-End Exercises Exam Details Introduction to High-Velocity IT High-Velocity IT Digital Technology Digital Organizations Digital Transformation High-Velocity IT Approaches Relevance of High-Velocity IT Approaches High-Velocity IT Approaches in Detail High-Velocity IT Operating Models Introduction ITIL® Perspective High-Velocity IT Aspects High-Velocity IT Applications ITIL® Building Blocks for High-Velocity IT Digital Product Lifecycle Service Value Streams Four Dimensions of Service Management ITIL® Management Practices High-Velocity IT Culture Key Behavior Patterns ITIL® Guiding Principles Supporting Models and Concepts for Purpose Ethics Design Thinking Supporting Models and Concepts for People Reconstructing for Service Agility Safety Culture Stress Prevention Supporting Models and Concepts for Progress Working in Complex Environments Lean Culture ITIL® Continual Improvement Model High-Velocity IT Objectives and Techniques High-Velocity IT Objectives High-Velocity IT Techniques Techniques for Valuable Investments Prioritization Techniques Minimum Viable Products and Services Product / Service Ownership A/B Testing Techniques for Fast Developments Basic Concepts Related to Fast Development Infrastructure as Code Reviews Continual Business Analysis Continuous Integration / Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) Continuous Testing Kanban Techniques for Resilient Operations Introduction to Resilient Operations Technical Debt Chaos Engineering Definition of Done Version Control Algorithmic IT Operations ChatOps Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) Techniques for Co-created Value Basic Concepts of Co-created Value Service Experience Techniques for Assured Conformance DevOps Audit Defense Toolkit DevSecOpsPeer Review

Learning & Development Level 3
By Rachel Hood
Identifying learning and training needs, designing and sourcing training and learning solutions, delivering and evaluating training.

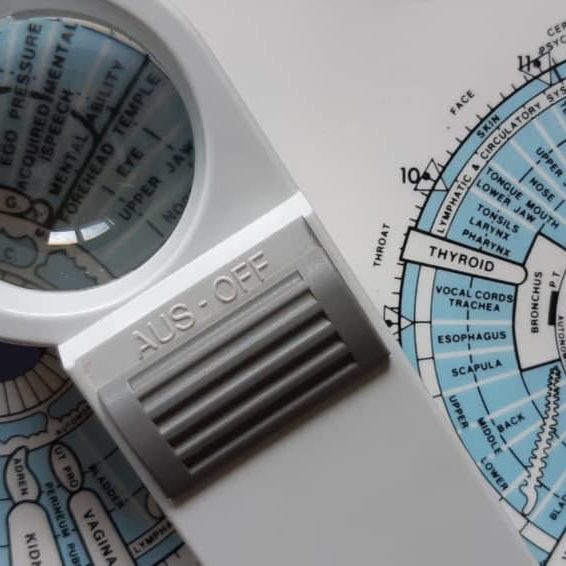
Iridology Diploma
By Plaskett International
LEARN HOW IRIDOLOGY CAN MAKE A HUGE CONTRIBUTION TO ANY COMPLEMENTARY PRACTICE A MESSAGE FROM THE AUTHOR I want to welcome you most warmly to the study of Iridology. Students of our course have taken their knowledge out into the world of practice and they have been able to see more penetratingly into the health of their patients. They have seen many truths about causes and effects in health and disease - that is what allows you to understand those extra things that make you into an even better healer. I think you are going to find this the most intriguing and absorbing study and, certainly, that is my sincere hope. As you precede, much of what you learn will amaze you and inspire wonder at the ways of the human body and mind. As you tread this very special road, I pass on to you the words that Bernard Jensen gave me years ago when I was his student, inscribed upon the inside cover of his book: “Seek the Higher Values in Life”. DR. LAWRENCE PLASKETT WHAT IS IRIDOLOGY? Iridology is the art of iris analysis. The iris is connected to the brain via the hypothalamus and can give naturopathic read outs on tissue conditions in various parts of the body. With training and practice it is possible to read signs indicative of biochemical, emotional and environmental influences that are hard to determine by other means. We can thus interpret health (and even aspects of personality) by close examination of the eyes, using suitable illumination and a magnifying glass. The close relationship between naturopathic iridology as an assessment tool and nutritional therapy and other naturopathic disciplines continues and grows closer. Now Iridology can make a huge contribution to complementary therapeutic practice and enhanced by our wonderful digital collection of eye photographs, the learning process with the Plaskett International College is a profound and exciting one. We teach Iridology quite separately from other topics and anyone who possesses, or expects to possess, a practitioner's qualification in any therapeutic discipline, may join the course. Course Duration 12 months Study Hours 200 hours Course Content 9 sections Course Fee £495 How Can Iridology Help Practitioners? Examples of how iridology can help practitioners Did you know that some iris features are so very plain that you can see them with the naked eye in ordinary social contact? You can see from two or three feet away in many cases that the person has a toxic digestive system (a strong wide dark ring around the pupil margin). You can often tell that the person has an overactive stomach (a narrow bright white ring very close to the pupil). You can tell when the skin is overlaid with toxins so that the skin's function in excreting toxins from the body is jeopardised (very narrow dark ring around the iris margin). You can tell in some people (rather advanced cases) that they suffer badly from sodium and potassium imbalance and have placed themselves at potential risk from cholesterol accumulation (the so-called corneal arcus, a white or off-white cloudy deposit, usually fairly thick, around the iris margin). Another example is the ring of spots or 'tophi' represented by the lymphatic rosary. Its mere presence tells one that there is sluggishness in the lymphatic system. When these tophi are darkly pigmented, the situation gives rise to concern for the possible generation of lymphatic illness. Using the precise positioning of iris reflex areas contained on the iris chart, one may distinguish many key points of analysis. Areas of stress and tension can be pinpointed by identifying 'contraction furrows’. Past injuries and adhesions show themselves as contortions of the normally regular and even iris fibres. You can answer questions like:- Is it the pancreas or the liver that is responsible for the trouble? Is the patient's hypertension caused by a defect of or toxic deposits in the particular brain area that is geared to control blood pressure? One of Jensen's rather dramatic illustrations is of the iris of a man who has just been shot. It shows the precise areas of tissue damage within the body and the response is very fast. The number of potential examples is almost without limit. The above may suffice to show the types of things that iridology can do for practitioners. We hope it will help you decide to study Iridology with the Plaskett International College. Course Overview The course covers the nature of iris observation, the nutritive zone, the iris chart, the chronic and acute, the intestinal and stomach zones and nerve collarette, the constitution type, respiratory system, lacunae, open lacuna, inherent weaknesses, the organs of elimination, other organs, special signs, complete diagnosis of a subject. The treatment of the topic follows the principles of Bernard Jensen in the USA. Once the basics have been learnt, the course teachings then extend considerably by bringing in the work of Dorothy Hall and of Dr Josef Deck, both of which are the subject of a special presentation during the course. The published insights of Farida Sharan and Harri Wolf, while not separately presented, also influence the presentation of the course material. Both the Australian School, (Dorothy Hall) and the German School, (Dr Deck/Harri Wolf), offer an added dimension to the study and interpretation of the constitution. PERSONALITY ASPECTS & CONSTITUTIONAL TYPES The study focuses upon the different personality aspects, which show up in different constitutional types. Dorothy Hall gives insights into what contributes to various different types of personality and their emotional and mental responses and their pre-dispositions to health or disease. Different sorts of people can have different priorities, preferences and imperatives built into their very nature from or before birth, sometimes determining the course of their entire lives and their attitudes to the world and to other people. AN EMPATHY BETWEEN PATIENT & PRACTITIONER The course teaches an understanding of these types and facilitates an empathy between patient and practitioner. It shows how people of the differing constitutional types are likely to go out of balance either mentally or emotionally and how their vulnerability to various physical ailments varies. The German School offers a very exciting and precise approach to the constitutional types, which is really quite different, but no less helpful. It highlights variations in the susceptibility to diseases of different organs and systems. THE 3 SCHOOLS OF THOUGHT It is a prime purpose of this course, not only to teach these differing positions, but also to demonstrate how it is that all three of these major schools of Iridology embody different aspects of the truth, how each is individually valuable and how a full and deep understanding of the meaning of 'constitution' can be gained through a sympathetic synthesis of the contributions from all three of these schools. BREAKDOWN OF THE COURSE SECTIONS In total there are 9 sections comprising of text, videos and iris images to study: SECTION 1 GENERAL PRACTICE AND AN ACCOUNT OF THE NUTRITIVE ZONE Areas Covered Iris colour Information that iridology can give us The structure of the eye and the iris Using the iris as an assessment tool The principle of reflex areas The Nutritive Zone Abnormality in the colon The Collarette (autonomic nerve wreath or anw) Diagnosis of the constitution based upon fibre structure Studies on images of real eyes SECTION 2 FEATURES OF THE FIBRES OUTSIDE THE COLLARETTE Areas Covered The general layout of fibres outside the collarette Inherent weaknesses First stage in further deterioration of an inherent weakness The meaning of darkness in the iris The development of discrete – open lacunae Lacunae Further notes about lightness and darkness amongst the fibres Healing lines Crypts Round the iris chart – the left iris Round the iris chart – the right iris Checking which structures and inside and which outside the collarette The organ systems The neural arc reflex SECTION 3 SPECIAL SIGNS Areas covered The corneal arcus (sodium ring, cholesterol ring, lipemic ring) The tophi (also lymphatic tophi or lymphatic rosary) Corneal Arcus The anaemia sign The catarrhal sign Acidity Grey background Scurf rim Circulatory ring Sphincter muscle (also called pupillary sphincter) Pigments (topastible or topolabile) Psoric spots Contrcation furrows Radial furrows SECTION 4 THE CONSTITUTIONS IN RELATION TO PERSONALITY TYPE AND DISEASE DISPOSITION Areas covered Very resilient Resilient average Moderately resilient Mildly resilient SECTION 5 MORE ABOUT WHITE SIGNS Areas covered Revision of distinctions between the different white signs Pictures of irises with white signs, with commentaries Further interpretation of the corneal arcus Further interpretation of the lytophi More general interpretation of the colour white SECTION 6 COLOURS IN THE IRIS AND OTHER SPECIAL SIGNS Areas Covered Yellow pigment in the iris Orange pigment Brown pigment Contraction furrows Radial furrows Psoric spots Pupillary border The “friendly fibrils” sign Summary of remedies SECTION 7 THE CONSTITUTION AND SIGNS ACCORDING TO THE GERMAN SCHOOL Areas Covered The German school of iridology Our approach to teaching the German school Introduction to the German constitutional types The lymphatic constitutions Mixed biliary constitution or biliary constitution Haematogenic (or haematogenous) constitution The way to use information on the German constitutions New signs that are specific to the German school Treatment recommendations for constitutional types SECTION 8 ADVANCED STUDIES OF THE IRIS Areas Covered Further details of the iris chart – its layout and its implications Neural arc reflex Deformation of pupil shape and position Advanced study of fibre separations, sinuosity, injuries & adhesions Lacunae of different shape and appearance The b3 bulge and the pterygium Working with genetically brown eyes SECTION 9 THE CONSULTATION & THE PRACTICALITIES Areas Covered Diagnosing pathology of individual critical organs Personality interpretations based upon the German school Conducting an iridology consultation Practical aspects of iris examination Making drawings of the iris and recording the data The uses, advantages and limitations of iris photography and its place in iridology practice Equipments and techniques of iris photography Using the computer to store and process digital images The interaction of signs Interpreting the whole iris in conjunction with the case study Pointers to treatment Carrying out case histories TESTIMONIALS Here's what students have to say about the course Emma Rubio, Health Coach Spain "As a Health Coach I decided to pursue my studies with the Plaskett College to become a Nutritional Therapist. For that, I am also studying Iridology. I am happy to have a tutor to answer my doubts and I like the flexibility that the College offers me. I love the subject of Iridology and the way it is explained, I also like having some videos of Dr Plaskett teaching Iridology as I admire him." Dr Ezequiel Lafontaine, Iridologist Puerto Rico "I LOVE IRIDOLOGY. I have over 30 iridology books, Italian, French, German, Spanish and English, plus over 4,000 photos from my own practice. I took this course for a refresher course and found the material was second to none." Mrs D. Moothy, Nutritional Therapist Mauritius “The distance learning courses have given me the opportunity to pursue my dreams through a program that was not only flexible and convenient for my schedule, but was also challenging and rewarding. I thoroughly enjoyed the readings and the assignments but most importantly, I enjoyed being able to do things at my pace. I must say that the most exciting and challenging course was the Iridology Diploma, and I am happy that I was able to do well in all the courses."
EXPORT PROCEDURES
By Export Unlocked Limited
This module aims to develop knowledge and understanding of the exporting process used in international trade from novice to practitioner. It includes documentation, incoterms, responsibilities of an exporter, commodity codes, origin and duties and taxes.

