- Professional Development
- Medicine & Nursing
- Arts & Crafts
- Health & Wellbeing
- Personal Development
713 Other courses in Cumbernauld
Network management technologies course description A comprehensive tour of the available network management technologies available for todays networks. The course starts with basic tools such as syslog along with Python network automation. SNMP is then covered with the *flow technologies and streaming telemetry. Configuration management with ansible, Python, NETCONF and RESTCONF is then studied. The final part of the course looks at SDN. Hands on sessions are used throughout to reinforce the theory rather than teach specific manufacturer equipment. Note that sections are available as individual courses. What will you learn Evaluate network management technologies. Evaluate network management technologies. Recognise the weaknesses of SNMP versus NETCONF and streaming telemetry. Explain the role of NETCONF and RESTCONF. Compare & contrast *flow and streaming telemetry. Explain the role of SDN in network management. Automate network configuration with ansible and Python. Network management technologies course details Who will benefit: Those wishing to manage networks. (Previous Python experience is NOT needed) Prerequisites: Intro to data comms Duration 5 days Network management technologies course content Basic network management Network management What is network management? Benefits, issues. FCAPS model. Fault management, Configuration management, accounting, performance, security. What to manage, what not to manage. Managing network devices, managing servers. Monitoring networks Traditional network tools Ping..., SSH, syslog, TFTP for configurations. nmap. Wireshark. CLI. Web based management. Splunk. Nessus, snort, Kali. Hands on syslog, network inventories. Network automation using the CLI Programming and automating networks, netOps. Python, Git. Python network modules, SSH, paramiko, netmiko. EVE-NG. Hands onPython network modules. Structured versus unstructured data Problems with automation and unstructured data. XML, JSON, YAML. The role of YANG. Hands on Parsing data. SNMP SNMP architecture, SNMP MIBs, SMI, the SNMP protocol, polling security. Configuring SNMP. SNMPv1, v2, v3, SNMP security. Which version should you use? MIBs and MIB structure. mib-2, extra parts of mib-2, Private enterprise MIBs. Summary: What SNMP is good/bad at. Hands on Configuring agents and a NMS. MIB browsing. Server management Microsoft, Linux, application polling. WMI vs SNMP. Hands on: Application polling. Performance management *flow Polling, push vs pull, netflow, sflow, IPFIX, *flow. Flows. Where to monitor traffic. Comparing *flow with SNMP. Architecture: Generators and collectors. When flows are exported. NetFlow reporting products. SolarWinds. Hands on Netflow configuration. Collectors. Streaming telemetry Model driven telemetry, periodic/on change. Structured data. Telemetry protocol stack. gRPC and gNMI. Protobuf. gNMI operations. Telemetry architecture. Telegraf, databases, Grafana. Hands on Telemetry example. Configuration management Configuration management tools Chef, puppet, ansible, saltstack. Ansible architecture, controlling machines, nodes, agentless, SSH, modules. Inventories, playbooks, modules, network modules, jinja2 templates. Hands on Network configuration with ansible. NETCONF What is NETCONF? Protocol stack, Data stores, traffic flows, validating configurations, rollback. YANG data models and how YANG is used by NETCONF. XML. Explorers and other tools. Hands on anx, Python and NETCONF. RESTCONF The REST API, HTTP, What is RESTCONF? Tools including Postman. Comparison with NETCONF. Hands on Configuration with RESTCONF. Python network automation: configuration SSH issues. Using structured data. Jinja2. ncclient, requests, NAPALM, Nornir. Automated testing. Hands on Python network device configuration with nornir. Software Defined Networks and orchestration Classic SDN What is SDN? benefits. SDN architecture. SDN applications, SDN switches, SDN controllers, Network Operating Systems. Control plane, data plane. Northbound interfaces. SDN components. Southbound interfaces. OpenFlow. ONF, OpenFlow ports, Flow tables. Network virtualization Virtual networks, virtual switches, NfV. Service chaining. NfV and SDN. SDN implementations Classic SDN, Hybrid SDN, SDN via APIs, SDN via overlays. Data centre SDN, VXLAN, Service Provider SDN, SD WAN, Enterprise SDN, WiFi. SDN and open source OpenDaylight, OpenVSwitch, Open Networking Forum, Open Network Operating System. Hands onOpenStack. SD-WAN What is SD-WAN? Architecture: Edge, gateway, orchestrator, controller. Overlay and underlay. Use of MPLS, 4G/5G. Benefits and features. Secure Access Service Edge (SASE).

Time Management for Healthcare Professionals
By M&K Update Ltd
This workshop is designed to help you manage your time more effectively. It will explore issues with time management, prioritisation and delegation, managing meetings and emails, Managing other peoples priorities and action planning.

Essential SD-WAN training course description SD-WAN is rapidly growing in use. This vendor neutral course starts with an introduction to what SD-WAN is and when it is useful. Each main area of SD-WAN is then studied in more detail to enable delegates to recognise the technologies used in SD-WAN and then use this information to evaluate SD-WAN products. What will you learn Describe what SD-WAN is (and isn't). Explain how SD-WAN works. Evaluate SD-WAN products. Compare and contrast SD-WAN with other technologies such as MPLS, Ethernet, SDN, NFV and WAN optimisation. Essential SD-WAN training course details Who will benefit: Anyone wishing to learn about SD-WAN. Prerequisites: Network fundamentals. Duration 1 day Essential SD-WAN training course contents What is SD-WAN? What is SD and SDN? What is WAN? Branch/ Office. MPLS, MPLS vs Internet, Ethernet, Broadband, LTE/4G, Cable, Satellite. The impact of the cloud. Single console, Dynamic path selection, automation. Why SD-WAN? Single console Network management, orchestration, administration. Example GUI interfaces. Northbound and southbound APIs. Dynamic path selection SD-WAN transports, Overlay networks, security. VPNs, IPsec. QoS and prioritization. Policies, traffic path rules. Application specific routing, bonding, optimisation. Automation Time saving, removing errors. Zero touch, ZOOM, ZTP. The role of the orchestrator. Real time monitoring of the network. APIs. Architecture and products Hardware solutions, software solutions, virtual appliances. Clouds. SD-WAN edge devices, SDWAN controllers, Orchestrators. HA and SD-WAN. Riverbed, Cisco, Juniper, others. Summary SD-WAN doesn't replace MPLS, virtualisation and SD-WAN. Relationship with SDN and NFV. SDWAN versus WAN optimisation.

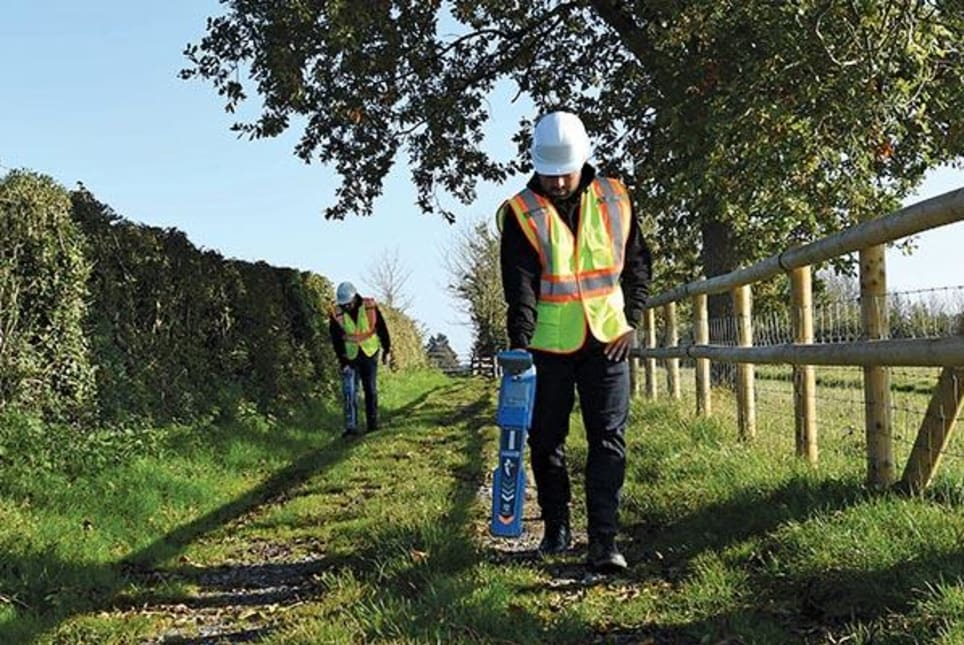
EUSR Category 1 Locate Utility Services (HSG47)
By Vp ESS Training
EUSR Category 1 Locate Utility Services (HSG47) - This course is designed for personnel who are involved in excavating and/or other activities involving breaking ground. This course is often referred to Cat and Genny Training, Cable Avoidance Training or HSG47. Book via our website @ https://www.vp-ess.com/training/utility-detection/eusr-category-1-locate-utility-services-(hsg47)/ or via email at: esstrainingsales@vpplc.com or phone on: 0800 000 346

Search By Location
- Other Courses in London
- Other Courses in Birmingham
- Other Courses in Glasgow
- Other Courses in Liverpool
- Other Courses in Bristol
- Other Courses in Manchester
- Other Courses in Sheffield
- Other Courses in Leeds
- Other Courses in Edinburgh
- Other Courses in Leicester
- Other Courses in Coventry
- Other Courses in Bradford
- Other Courses in Cardiff
- Other Courses in Belfast
- Other Courses in Nottingham