- Professional Development
- Medicine & Nursing
- Arts & Crafts
- Health & Wellbeing
- Personal Development
130 Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) courses
CT11: How to Gain Authorisation for Clinical Research Under the EU Clinical Trials Regulation
By Zenosis
This course sets out the procedures that sponsors need to follow to gain authorisation to conduct clinical trials under the Regulation, and it summarises and links to the extensive guidance available from the European Commission and the European Medicines Agency. Its companion course CT12 sets out the procedures that sponsors need to follow to conduct authorised clinical trials in compliance with the Regulation. The two courses therefore provide an ideal foundation for understanding and complying with the new law.
GLP01 - Good Laboratory Practice
By Zenosis
The purpose of GLP is to provide assurance of the quality and reliability of nonclinical study data. GLP covers the planning, performance, monitoring, recording and reporting of studies. Regulatory authorities typically require GLP rules to be followed for nonclinical studies intended to support an application for approval of clinical research or marketing of a product containing the test item. This course outlines the history of GLP and explains why it is important, identifies the penalties that may be incurred for noncompliance, and sets out requirements that need to be met. Learners are also referred to the two main sources of GLP rules: The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development’s Principles on Good Laboratory Practice and US Regulation 21 CFR 58: Good Laboratory Practice for Nonclinical Laboratory Studies.

ICT01: Compliance with Regulation 21 CFR Part 11 on Electronic Records and Electronic Signatures
By Zenosis
21CFR11 applies to records that are required to be submitted to the FDA, or that are subject to FDA inspection, and that are in electronic form – that is, as computer files. It applies to all computer systems used to create, modify, maintain, archive, retrieve, or transmit such records – from a humble spreadsheet program to a complex information management system.

SUB04: Preparing Submissions in the Common Technical Document (CTD) Format
By Zenosis
The CTD is the internationally recognised standard format for submissions to medicines regulatory authorities. In the European Economic Area, the USA and Canada, the CTD, in its electronic format (eCTD), is mandatory for all applications for marketing approval and all subsequent related submissions. The CTD is accepted in many other countries, being mandatory for new prescription medicines in some. This module explains the rationale for the CTD and provides guidance on its structure and format and the ways in which it is used.

PV04: Signal Detection and Management in Pharmacovigilance
By Zenosis
This module provides a guide to signal detection and management for approved products. The subject is presented as a process comprising four stages: signal detection, signal validation, signal analysis and prioritisation, and risk assessment and minimisation.

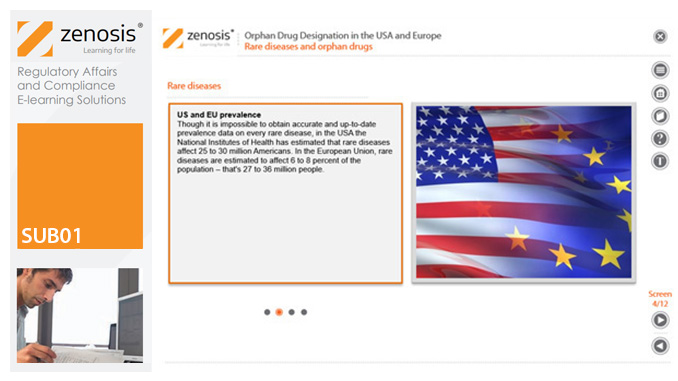
SUB01: Orphan Drug Designation in the USA and Europe
By Zenosis
Medicines for the prevention, diagnosis, or treatment of rare diseases have become known as ‘orphan drugs’ because of their commercial unattractiveness. Development of such products is successfully encouraged through incentives offered by regulatory authorities. To qualify for important incentives, the sponsor of a drug must gain ‘orphan designation’ for its use in an indication. This module describes the requirements for orphan designation and how to apply for it in the USA and the European Economic Area.
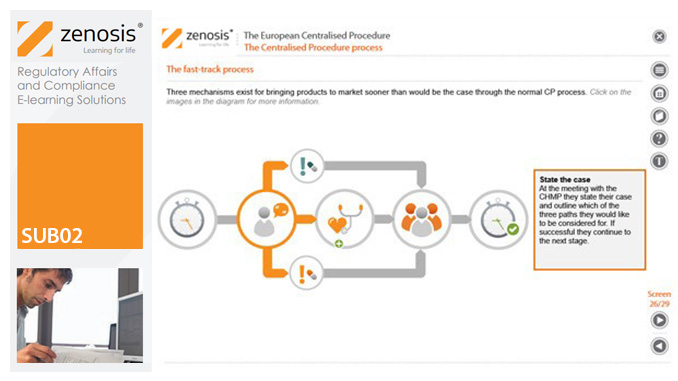
SUB02: The European Centralised Procedure (CP)
By Zenosis
The Centralised Procedure (CP) is one of three routes available to applicants to gain multinational marketing authorisation within the European Economic Area (EEA) on the basis of a single application. In the CP, one successful application leads to a marketing authorisation being issued by the European Commission that applies throughout the EEA. The CP is mandatory for certain types of products.
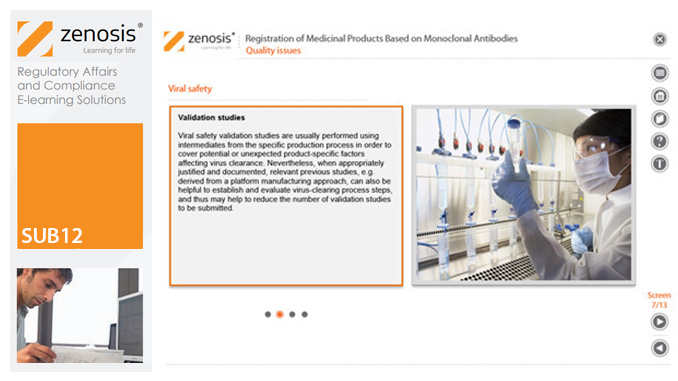
SUB12: Registration of Medicinal Products Based on Monoclonal Antibodies
By Zenosis
This module addresses characteristic issues influencing the registration of medicinal products based on monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), for use in humans. Regulatory requirements for the registration of biological medicinal products such as those based on mAbs differ in certain respects from those for small-molecule products. This is because of the distinct characteristics of biologics, such as complex structure and susceptibility to variation during manufacture.
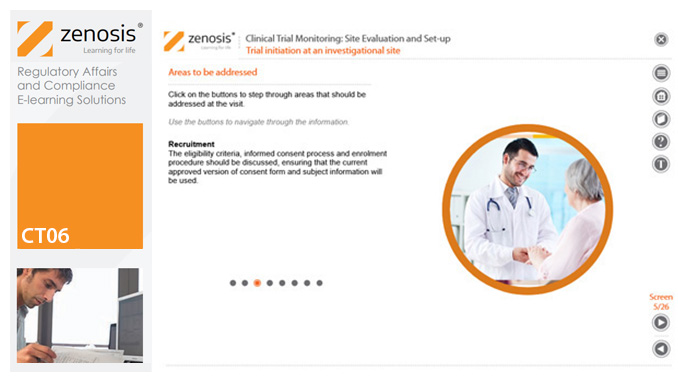
CT06: Clinical Trial Monitoring: Site Evaluation and Setup
By Zenosis
The sponsor of a clinical trial needs to reach agreement with clinical investigators to conduct the trial. The suitability of investigators and their institutional sites, typically hospitals, has to be evaluated, and the trial has to be set up at each site. This module describes the processes involved, focusing particularly on the role of a Clinical Research Associate (CRA) employed or contracted by the sponsor to monitor the trial.
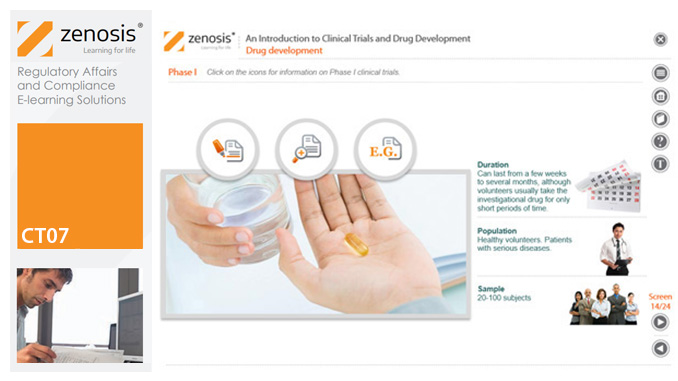
CT07: An Introduction to Clinical Trials and Drug Development
By Zenosis
This module provides an understanding of how clinical trials fit into the drug development process. It outlines the key historical events leading to the development of controlled clinical trials. It specifies the purpose of trials, outlines their features, and identifies codes and regulations that apply to them. Finally, it describes the environment of cost control in which the modern pharmaceutical industry operates.
Search By Location
- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) Courses in London
- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) Courses in Birmingham
- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) Courses in Glasgow
- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) Courses in Liverpool
- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) Courses in Bristol
- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) Courses in Manchester
- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) Courses in Sheffield
- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) Courses in Leeds
- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) Courses in Edinburgh
- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) Courses in Leicester
- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) Courses in Coventry
- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) Courses in Bradford
- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) Courses in Cardiff
- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) Courses in Belfast
- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) Courses in Nottingham