- Professional Development
- Medicine & Nursing
- Arts & Crafts
- Health & Wellbeing
- Personal Development
253 Biotechnology courses delivered Online
GMP03: Good Manufacturing Practice in Cleaning and Sanitation
By Zenosis
Cleaning and sanitation of premises and equipment are essential to efforts to prevent contamination of product, and they need to be done in compliance with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) regulatory requirements. This module shows why it is so important to do a good job, what to consider before and during each job, and how best to go about the work.
GMP02: Good Documentation Practice
By Zenosis
Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) for medicinal products relies on documentation. Good Documentation Practice (GDocP) is that part of GMP that applies to the creation, maintenance, use, and retention of documents to provide assurance of the quality of products.
PV07: Good Pharmacoepidemiology Practice
By Zenosis
Pharmacoepidemiology is the study of the use and effects of drugs in large numbers of people. It provides a bridge between clinical pharmacology and epidemiology. The increasing demand for real-world evidence of the safety, efficacy and utility of medicinal products has focused greater attention on pharmacoepidemiological research. This module will help those who plan and conduct such research, and analyse and report the findings, to follow good practice.

PV06: Urgent Safety Restrictions
By Zenosis
An Urgent Safety Restriction (USR) is a regulatory action taken, in response to a safety signal, to make an interim change to the terms of the marketing authorisation for a medicinal product in Europe. This module describes the principles and procedures for USRs.
GXP01- Good Practices (GxP) in Drug Development and Manufacturing
By Zenosis
This short entry-level module introduces the learner to good practices (GxP) in drug development and manufacturing. It outlines how the industry operates and how it is regulated. It identifies regulatory authorities and other important sources of guidance on Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP), Good Clinical Practice (GCP), and Good Laboratory Practice (GLP).

GXP01: Good Practices (GxP) in Drug Development and Manufacturing
By Zenosis
This short entry-level module introduces the learner to good practices (GxP) in drug development and manufacturing. It outlines how the industry operates and how it is regulated. It identifies regulatory authorities and other important sources of guidance on Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP), Good Clinical Practice (GCP), and Good Laboratory Practice (GLP).

GMP01c - Hygiene, cleaning, and sanitation
By Zenosis
Prevention of contamination is one of the most important goals of GMP. Contamination of product is often difficult to detect, so GMP rules emphasise preventive measures, including: attention to personal health and hygiene, and the wearing of special clothing, by staff; and cleaning and sanitation of premises and equipment. In this short course we set out the basics of GMP requirements in these vital areas.
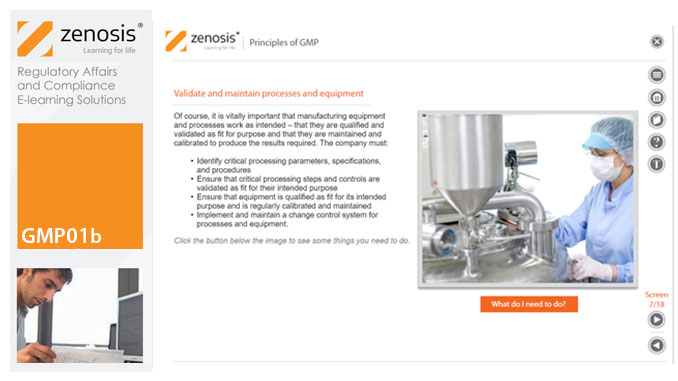
GMP01b - Principles of GMP
By Zenosis
In this short course we present an overview of the main principles of GMP, and we outline some things that manufacturing personnel need to do to comply with requirements. We identify the principal goals of GMP as: prevention of contamination; prevention of mix-ups; scrupulous documentation; validation and maintenance of processes and equipment; quality assurance by an independent unit; and training. We place GMP in the context of a company’s quality management system.
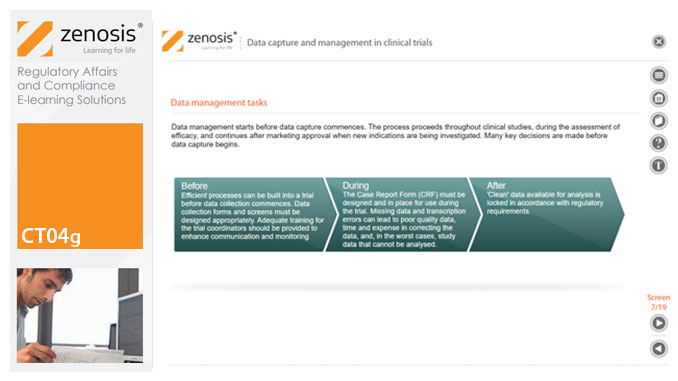
CT04g - Data capture and management in clinical trials
By Zenosis
Capture and management of clinical trial data is a challenge. The industry is under pressure to obtain and analyse such data more quickly, while maintaining data integrity, so that products can be brought to market sooner. Effective planning and adequate resources can ensure clinical trials yield high quality data within strict timelines and budget requirements, at the same time satisfying regulatory standards. This short course describes the purpose of data capture and explores efficiencies in data management as part of the evolving regulatory landscape.
CT04f - Clinical study design
By Zenosis
Clinical trial design establishes the framework upon which the clinical trial process will be conducted, and sets the objectives of the trial. The application for marketing approval, submitted to the regulatory authorities, will provide clinical data reflecting the trial design. Since trial design impacts the whole drug development process and lifecycle, particular care and due diligence is essential. This short course provides an overview of the main types of study design.
