- Professional Development
- Medicine & Nursing
- Arts & Crafts
- Health & Wellbeing
- Personal Development
NPORS Suction Excavator (N021)
By Dynamic Training and Assessments Ltd
NPORS Suction Excavator (N021)

Public Speaking 1 Day training in Bristol
By Mangates
Public speaking Training

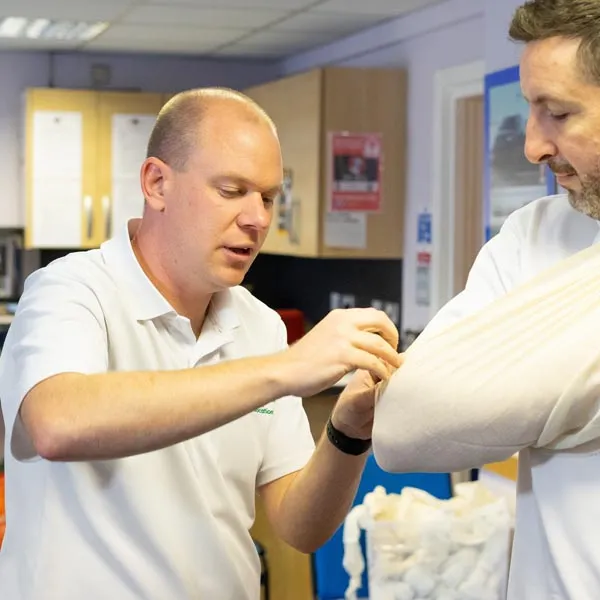
First Aid at Work (Initial) - Level 3 Award
By Immerse Medical
This first aid at work course is ideal for organisations whose needs assessment has identified a requirement for additional first aid training, such as having employees with a disability or a medical condition. In addition to the topics covered on an emergency first aid at work course, this course covers treatment for a variety of injuries and medical conditions. For more information click on the tabs below, or get in touch, we’d be more than happy to answer any queries. At Immerse Training we pride ourselves on offering First Aid and Pre-Hospital Care Training that meets your specific needs. All our courses meet the requirements of the relevant awarding body. On top of that, we are more than happy to create bespoke elements that tailor each programme to suit your first aid or care responsibilities. Qualification Information This qualification and learning outcomes are based on the recommendations of: The Resuscitation Council (UK) Skills for Health Assessment Principles for First Aid Qualifications Course Content Following this course students will be able to Understand the role and responsibilities of a first aider. Be able to administer first aid to a casualty with injuries to bones, muscles and joints. Assess an incident. Be able to administer first aid to a casualty with suspected head and spinal injuries. Manage an unresponsive casualty who is breathing normally. Be able to administer first aid to a casualty with suspected chest injuries. Manage an unresponsive casualty who is not breathing normally. Be able to administer first aid to a casualty with burns and scalds. Be able to recognise and assist a casualty who is choking. Be able to administer first aid to a casualty with an eye injury. Be able to manage a casualty with external bleeding. Be able to administer first aid to a casualty with sudden poisoning. Be able to manage a casualty who is in shock. Be able to administer first aid to a casualty with anaphylaxis. Be able to manage a casualty with a minor injury. Be able to provide first aid to a casualty with suspected major illness. Be able to conduct a secondary survey. Who should attend? This qualification is for people who deal with first aid at work. Enabling them to be workplace first aiders under the Health and Safety (First Aid) Regulations 1981. This qualification is also for people who have a specific responsibility at work, or in voluntary and community activities. This will allow them to provide basic first aid to people in a range of situations. Pre-requisites Students must be at least 14 years old on the first day of training. Assessment and Certifications Assessment of this course is continuous and includes two theory/multiple choice question papers. Successful students will receive an Immerse Training Certificate, which is valid for three years. This certificate will be issued by Qualsafe, the awarding body for Immerse Training. Additional Information Completion of the Level 3 Award in First Aid at Work includes 3 credits at Level 3 of the Regulated Qualifications Framework (RQF). Workplace First Aid Courses First Aid courses for employers and employees. Our workplace courses are fully accredited, registered and meet Health and Safety Executive (HSE) guidelines. From 1 day Emergency First Aid at Work (previously appointed person) to 3 day First Aid at Work courses. We specialise in on-site courses at your workplace, tailored to the specific risks associated with your business. All courses can be delivered at our training centre in Poole, Dorset or we can deliver on-site across Bournemouth, Poole, Dorset, Hampshire and the South of England.

NPORS Marine Knuckle Boom Crane (N014)
By Dynamic Training and Assessments Ltd
NPORS Marine Knuckle Boom Crane (N014)

NPORS Reach Lift Truck (N003)
By Dynamic Training and Assessments Ltd
NPORS Reach Lift Truck (N003)

The Portable Appliance Testing course or PAT testing course as it is more commonly known is one of our most popular courses as it does not require you to have any formal previous qualifications and once completed, will enable you to offer your services. In the commercial setting, the law places a responsibility on all employers to ensure that the electrical equipment to be used by their staff and the public, should be fit for purpose and safe for use. Hence, all portable appliances have to be regularly checked and maintained by a competent person.

If you want to start installing independently or with an electrical contractor look no further as this course will give you the skills and knowledge required. This package which will allow you to become a fully qualified domestic installer and enable you to join a Competent Person Self-Certification Scheme and certify your own domestic work.

Emergency First Aid at Work - Level 3 Award
By Immerse Medical
Our 8 hour course will enable students to attain the knowledge and practical competencies needed to deal with a range of emergency first aid situations and/or take on the role of emergency first aider in the workplace. At Immerse Training we specialise in bespoke on-site courses, delivered at your premises, based on your industry. Qualification Information This qualification and learning outcomes are based on the recommendations of: The Resuscitation Council (UK) Skills for Health Assessment Principles for First Aid Qualifications Course Content Following this course students will: Understand the role and responsibilities of a first aider. Be able to assess an incident. Be able to manage an unresponsive casualty who is breathing normally. Be able to manage an unresponsive casualty who is not breathing normally. Be able to recognise and assist a casualty who is choking. Be able to manage a casualty with external bleeding. Be able to manage a casualty who is in shock. Be able to manage a casualty with a minor injury. Who should attend? This qualification is for people who deal with first aid at work enabling them to be workplace emergency first aiders under the Health and Safety (First Aid) Regulations 1981. This qualification is also for people who have a specific responsibility at work, or in voluntary and community activities, to provide basic first aid to people in a range of emergency first aid situations. Pre-requisites Students must be at least 14 years old on the first day of training. Assessment and Certifications Assessment of this course is continuous and also includes 1 theory/multiple choice question paper. Successful students will receive an Immerse Training Certificate, which is valid for three years. This certificate will be issued by Qualsafe, the awarding body for Immerse Training. Additional Information Completion of the Level 3 Award in Emergency First Aid at Work includes 1 credit at Level 3 of the Regulated Qualifications Framework (RQF). Workplace First Aid Courses First Aid courses for employers and employees. Our workplace courses are fully accredited, registered and meet Health and Safety Executive (HSE) guidelines. From 1 day Emergency First Aid at Work (previously appointed person) to 3 day First Aid at Work courses. We specialise in on-site courses at your workplace, tailored to the specific risks associated with your business. All courses can be delivered at our training centre in Poole, Dorset or we can deliver on-site across Bournemouth, Poole, Dorset, Hampshire and the South of England.
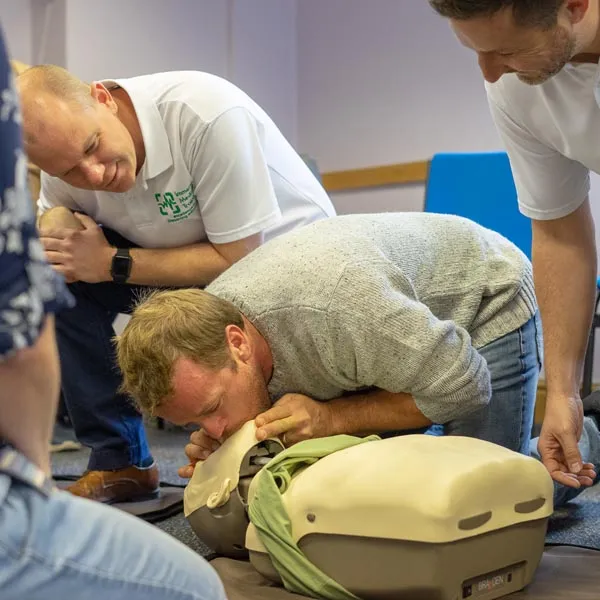

An emergency can happen anywhere, so it's better to be prepared at all instances, specially at the workplace. Come to Knight Training and ensure your employees are safe with our Emergency First Aid At Work Course now!

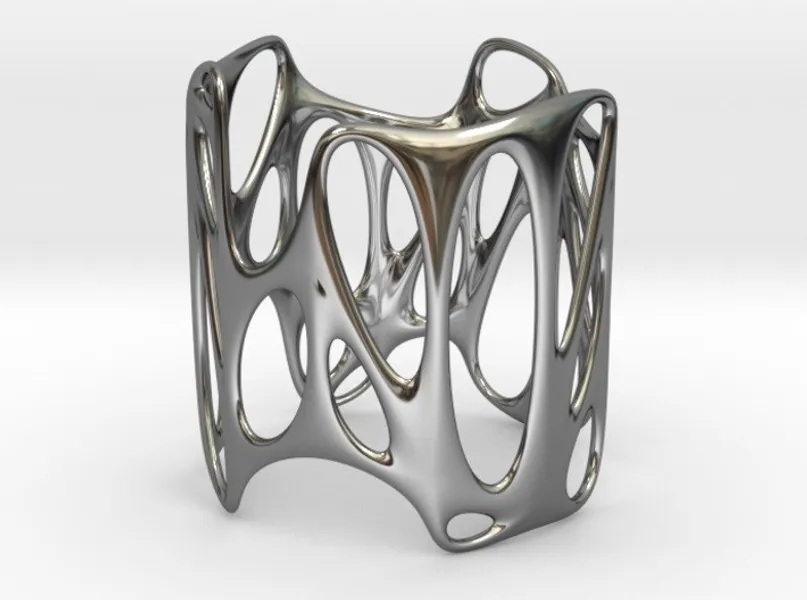
Jewellery Design Course - Create Personalised Jewellery (Blender)
By FluidDesigner
Learn to use 3D printing software to design and create your own pendants, earrings, rings and bracelets. The course is on a one-to-one basis. If you want to be in the jewellery trade as a designer and seller of modern jewellery or you simply want to create designs for yourself and your family then you should be learning how to create your own designs using apps such as Fluid Designer for 3D Printing.
Search By Location
- Basic Courses in London
- Basic Courses in Birmingham
- Basic Courses in Glasgow
- Basic Courses in Liverpool
- Basic Courses in Bristol
- Basic Courses in Manchester
- Basic Courses in Sheffield
- Basic Courses in Leeds
- Basic Courses in Edinburgh
- Basic Courses in Leicester
- Basic Courses in Coventry
- Basic Courses in Bradford
- Basic Courses in Cardiff
- Basic Courses in Belfast
- Basic Courses in Nottingham