- Professional Development
- Medicine & Nursing
- Arts & Crafts
- Health & Wellbeing
- Personal Development
4496 Courses
Writing Analytical Queries for Business Intelligence
By Nexus Human
Duration 3 Days 18 CPD hours This course is intended for This course is intended for information workers and data science professionals who seek to use database reporting and analysis tools such as Microsoft SQL Server Reporting Services, Excel, Power BI, R, SAS and other business intelligence tools, and wish to use TSQL queries to efficiently retrieve data sets from Microsoft SQL Server relational databases for use with these tools. Overview Identify independent and dependent variables and measurement levels in their own analytical work scenarios. Identify variables of interest in relational database tables. Choose a data aggregation level and data set design appropriate for the intended analysis and tool. Use TSQL SELECT queries to produce ready-to-use data sets for analysis in tools such as PowerBI, SQL Server Reporting Services, Excel, R, SAS, SPSS, and others. Create stored procedures, views, and functions to modularize data retrieval code. This three-day instructor-led course is about writing TSQL queries for the purpose of database reporting, analysis, and business intelligence. Specifically, this course presents TSQL within the context of data analysis in other words, making meaning from the data rather than transaction-oriented data-tier application development. The course starts with a brief discussion of levels of measurement and quantitative research methodogy, and integrates these concepts into each TSQL topic presented. The goal is to provide a consistent, direct, and purposeful learning path from RDBMS data retrieval through analytical tools such as SQL Server Reporting Services, PowerBI, Excel, R, SAS, and SPSS. Module 1: Introduction to TSQL for Business Intelligence Two Approaches to SQL Programming TSQL Data Retrieval in an Analytics / Business Intelligence Environment The Database Engine SQL Server Management Studio and the CarDeal Sample Database Identifying Variables in Tables SQL is a Declarative Language Introduction to the SELECT Query Module 2: Turning Table Columns into Variables for Analysis: SELECT List Expressions, WHERE, and ORDER BY Turning Columns into Variables for Analysis Column Expressions, Data Types, and Built-in Functions Column aliases Data type conversions Built-in Scalar Functions Table Aliases The WHERE clause ORDER BY Module 3: Combining Columns from Multiple Tables into a Single Dataset: The JOIN Operators Primary Keys, Foreign Keys, and Joins Understanding Joins, Part 1: CROSSJOIN and the Full Cartesian Product Understanding Joins, Part 2: The INNERJOIN Understanding Joins, Part 3: The OUTERJOINS Understanding Joins, Part 4: Joining more than two tables Understanding Joins, Part 5: Combining INNER and OUTERJOINs Combining JOIN Operations with WHERE and ORDER BY Module 4: Creating an Appropriate Aggregation Level Using GROUP BY Identifying required aggregation level and granularity Aggregate Functions GROUP BY HAVING Order of operations in SELECT queries Module 5: Subqueries, Derived Tables and Common Table Expressions Non-correlated and correlated subqueries Derived tables Common table expressions Module 6: Encapsulating Data Retrieval Logic Views Table-valued functions Stored procedures Creating objects for read-access users Creating database accounts for analytical client tools Module 7: Getting Your Dataset to the Client Connecting to SQL Server and Submitting Queries from Client Tools Connecting and running SELECT queries from: Excel PowerBI RStudio Exporting datasets to files using Results pane from SSMS The bcp utility The Import/Export Wizard Additional course details: Nexus Humans Writing Analytical Queries for Business Intelligence training program is a workshop that presents an invigorating mix of sessions, lessons, and masterclasses meticulously crafted to propel your learning expedition forward. This immersive bootcamp-style experience boasts interactive lectures, hands-on labs, and collaborative hackathons, all strategically designed to fortify fundamental concepts. Guided by seasoned coaches, each session offers priceless insights and practical skills crucial for honing your expertise. Whether you're stepping into the realm of professional skills or a seasoned professional, this comprehensive course ensures you're equipped with the knowledge and prowess necessary for success. While we feel this is the best course for the Writing Analytical Queries for Business Intelligence course and one of our Top 10 we encourage you to read the course outline to make sure it is the right content for you. Additionally, private sessions, closed classes or dedicated events are available both live online and at our training centres in Dublin and London, as well as at your offices anywhere in the UK, Ireland or across EMEA.

Dare to Lead
By Nexus Human
Duration 3 Days 18 CPD hours This course is intended for Team leaders, managers, executives, and other business and IT professionals who lead others as well as Individual contributors ready for transformational self-development as a leader. Overview Recognize vulnerability as the emotion we feel during times of uncertainty, risk, and emotional exposure. Explain why courage requires vulnerability. Establish a link between what I learned and behaviors I want to change. Recognize the critical role that self-awareness plays in daring leadership. Give examples to support how armor - not fear -is the greatest obstacle to daring leadership. Identify the four skill sets that make up courage: rumbling with vulnerability, living into our values, BRAVING trust, and learning to rise. Recognize that courage is a collection of four skill sets that are measurable, observable, and teachable. Recognize that vulnerability is the birthplace of many of the behaviors that define daring leadership, including creativity, accountability, and difficult conversations. Give examples of why daring leadership requires showing up for hard conversations and rumbles, including giving and receiving feedback. This workshop is all about your own leadership self-awareness, identifying your call to courage as a leader and the learning, practice and integration of the four courage skills sets so you can show up authentically in life and leadership. Dare to Lead? is the ultimate playbook for developing brave leaders and courageous cultures. The greatest barrier to daring leadership is not fear; the greatest obstacle is armor ? how we self-protect when we feel uncertainty, risk and emotional exposure. Learn the skills to move from armored leadership to daring leadership. Daring leaders are self-aware, know how to have hard conversations, hold themselves and others accountable, build trust, lead with empathy and connection, take smart risks that lead to innovation, reset quickly after disappointments and setbacks, and give and receive feedback. This interactive curriculum is delivered in five, half-day sessions and is based on the research by Brenâ Brown. This course comes with a PDF workbook and an Amazon gift card to purchase the Dare to Lead? book in the version of your choice. You also have access to a series of leadership and personal development assessments and exclusive training videos led by Dr. Brenâ Brown. At the end of the event, a digital badge is awarded to those who complete 24 hours of course content. The Heart of Daring Leadership Permission Slips Container Building Armored Leadership versus Daring Leadership Call to Courage Assembling Our Armor Building Grounded Confidence to Replace our Armor Aplying the 5Cs Self-Awareness & Emotional Literacy Developing Emotional Literacy Getting Curious About Emotions Exploring the Iceberg The Myths of Vulnerability Rumbling with Vulnerability The Six Myths of Vulnerability Exploring Your Arena Shame Resilience Shame 101 Defining Shame The Physiology of Shame Shame Shields How Shame Shows Up in Organizations How Shame Shows up at Work Empathy and Self-Compassion Attributes of Empathy What Does Empathy Look Like? Empathy Misses Comparative Suffering Self-Compassion Talk to Yourself the Way You Talk to Someone You Love Empathy & Self-Compassion Commitment Supplemental Exercise: Kristin Neff?s Self-Compassion Scale Supplemental Exercise: Putting Empathy, Curiosity, and Rumble Tools in Action Living Into Our Values Living Into Our Values Values Clarification Taking Values from Professing Words to Practicing Behaviors Grounded Confidence and Rumbling Skills Grounded Confidence and Rumbling Skills Rumble Starters The 5Cs of Strategic Thinking, Decision Making, and Delegation Using the 5Cs Supplemental Exercise ? Gritty Faith & Gritty Facts Supplemental Exercise ? Horizon Conflict Engaged Feedback Giving Engaged Feedback Recognizing Defensiveness in Feedback Conversations BRAVING Trust BRAVING Trust Square Squad Rumbling with Self-Trust Trust with Others Trust on Teams Rumbling with Living BIG Learning to Rise: The Reckoning Learning to Rise: The Rising Strong Process The Rising Strong Process Getting Emotionally Hooked Offloading Hurt: Barriers to Reckoning with Emotion Strategies for Reckoning with Emotion The Rumble and The Revolution Writing My SFD The Delta The Revolution: When the Process Becomes a Daily Practice Supplemental Exercise ? Reset and Resilience Practices Integration Dare to Lead Integration Plan

Google Cloud Engineer Associate Certification Bootcamp
By Nexus Human
Duration 5 Days 30 CPD hours This course is intended for Cloud Solutions Architects DevOps Engineers Individuals using Google Cloud Platform who deploy applications, monitor operations, and manage enterprise solutions Overview At course completion, you will have attained knowledge of: Fundamentals of Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Google Cloud Storage Google Compute Engine Google Cloud SQL Load Balancing (LB) Google Cloud Monitoring Auto-Scaling Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) Network Cloud Identity and Access Management (IAM) Cloud CDN and DNS Cloud VPN Google Cloud Deployment Manager Google Container Engine Cloud Run Cloud Bigtable Cloud Datastore Cloud BigQuery Cloud DataFlow Cloud DataProc Cloud Pub/Sub In this course you will attain a deep knowledge of Google Cloud Platform infrastructure and design patterns on developing applications on GCP. This course will prepare you for the Google Cloud Architect Associate Certification Exam. Fundamentals of Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Overview Regions and Zones Review of major GCP services Google Cloud Storage Fundamental APIs Consistency Cloud Storage Namespace Buckets and Objects Bucket and Object Naming Guidelines Encryption Object Versioning Object Lifecycle Management Access Control Access Control Lists Signed URL Multipart upload Resumable upload Understanding Pricing for Cloud Storage Offline Media Import/Export Architecture case study of common Use Cases of Google Cloud Storage Hands-on: Cloud Storage Lab; Creating Buckets, objects, and managing access control Google Compute Engine Compute Engine Architecture VM Instances types Persistence Disks Images Generating Custom Images IP Addresses Static IPs Ephemeral Access Control Options IAM Service Account Monitoring Instances with Google Cloud Monitoring Compute Engine Networks and Firewalls Hands-on: Hosting an Application on Compute Engine Google Cloud SQL Core advantages of Cloud SQL Cloud SQL database instance types Access Control High availability options Failover Read replica Backup options On Demand Automated Understanding Pricing of Cloud SQL Load Balancing (LB) Fundamentals of a Load Balancer Network Load balancing HTTPS Load balancing Cross region Load balancing Content Load balancing Target proxies SSL Load Balancing Internal Load Balancing Network Load Balancing Understanding Pricing for Load Balancer Google Cloud Monitoring Architecture of Cloud Monitoring Supported metrics Stackdriver Monitoring APIs Auto-Scaling Overview of Autoscaling Auto-scaling Fundamentals Instance groups Templates Policies Decisions Hands-on: Deploying a scale application on GCP using Autoscaling, Compute Engine, Cloud SQL, Load Balancers. Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) Network Salient features of Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) Network Infrastructure Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) Networking Fundamentals Subnetworks Firewall Internal DNS Network Routes Hands-on: Hosting Secure Applications in Google Cloud VPC Networks Cloud Identity and Access Management (IAM) Introduction User and Service Accounts IAM Roles Policy Hands-on: Managing Users, Policies and Granting Roles using Service Accounts Cloud CDN and DNS What is CDN Google Cloud CDN Cloud CDN Concepts Some of the Cloud CDN Edge locations Cloud DNS Cloud DNS Terminologies Supported Record Types Hands-on: Moving an Existing Domain Name to Cloud DNS Cloud VPN Cloud VPN overview Types of Cloud VPN Specifications Maintenance and Availability Google Cloud Deployment Manager Deployment Manager Deployment Manager Fundamentals Runtime Configurator Quotas Hands-on: Generating and Creating Cloud Deployment Manager Template Google Container Engine Google Container Engine Overview Docker Overview Kubernetes Terminologies Replication Controller Deployment Price and Quotas Hands-on: Deploying WordPress Cluster using Container Engine Cloud Run Overview of Cloud Run Deploy a Prebuilt Sample container Cloud Bigtable Overview of Cloud Bigtable Access Control Performance Locations Cloud Datastore Overview of Cloud Datastore Limits Storage Size Multitenancy Benefits of Multitenancy Encryption Locations Cloud BigQuery BigQuery Overview Interacting with BigQuery Datasets, Tables, and Views Partitioned Tables Query Plan Explanation Hands-on: Getting Started with BigQuery Cloud DataFlow Overview Programming Model DataFlow SDK 1.x for java Cloud Dataflow SDK 2.x Security and Permissions Advanced Access Control Cloud DataProc Overview Clusters Versioning Cloud Pub/Sub Overview of Cloud Pub/Sub Pub/Sub Concepts and Message Flow Data Model Cleanup of All Services Hands-on: Cloud Pub/Sub Lab with Background Cloud Function Additional course details: Nexus Humans Google Cloud Engineer Associate Certification Bootcamp training program is a workshop that presents an invigorating mix of sessions, lessons, and masterclasses meticulously crafted to propel your learning expedition forward. This immersive bootcamp-style experience boasts interactive lectures, hands-on labs, and collaborative hackathons, all strategically designed to fortify fundamental concepts. Guided by seasoned coaches, each session offers priceless insights and practical skills crucial for honing your expertise. Whether you're stepping into the realm of professional skills or a seasoned professional, this comprehensive course ensures you're equipped with the knowledge and prowess necessary for success. While we feel this is the best course for the Google Cloud Engineer Associate Certification Bootcamp course and one of our Top 10 we encourage you to read the course outline to make sure it is the right content for you. Additionally, private sessions, closed classes or dedicated events are available both live online and at our training centres in Dublin and London, as well as at your offices anywhere in the UK, Ireland or across EMEA.

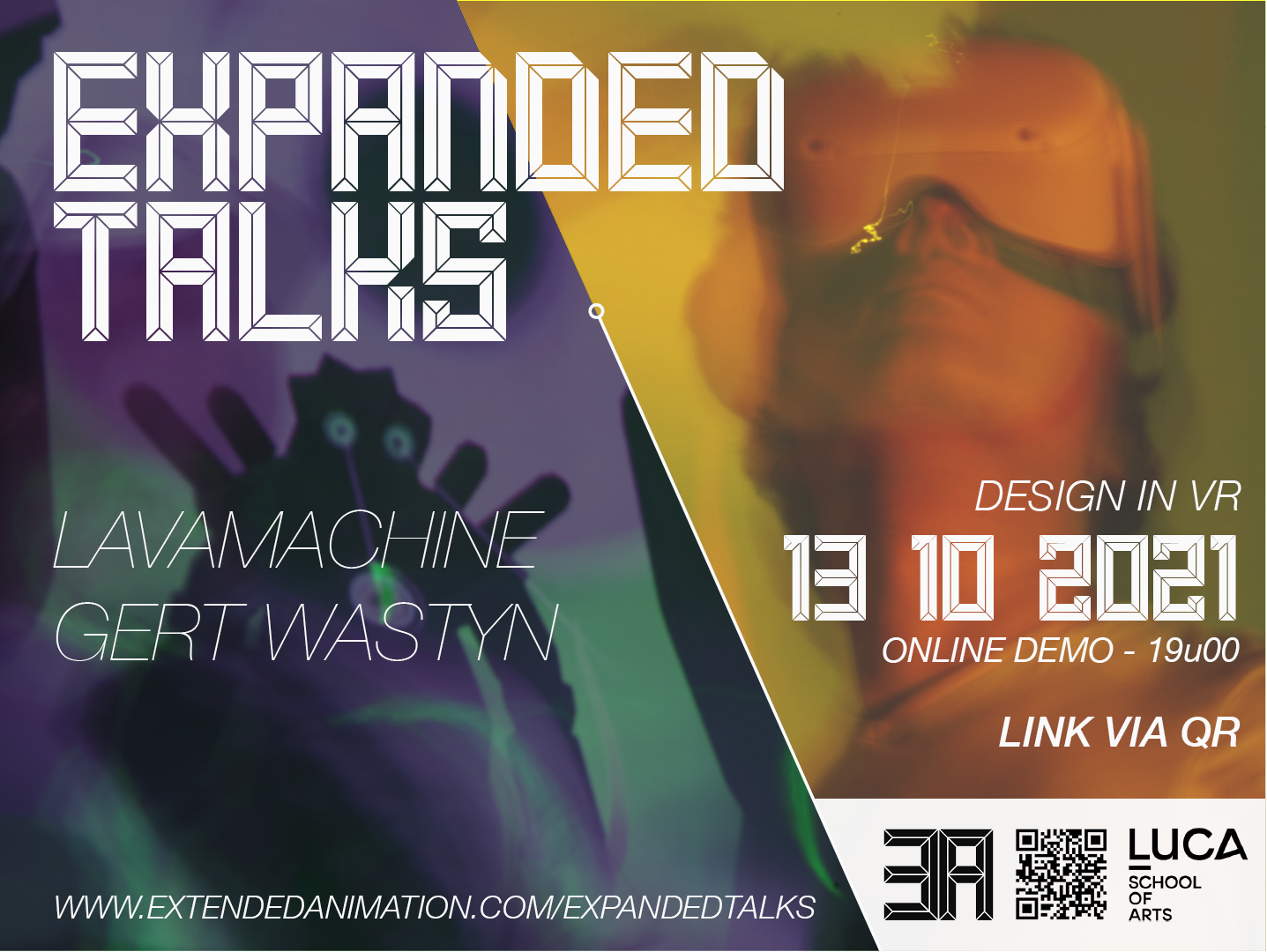
Expanded Talks: Design in VR w/ animation studio Lavamachine
By LUCA School of Arts
Expanded Talks webinar about design in with VR on 13/10 at 19h CET. Live demo with studio Lavamachine Design in VR with Multibrush and other VR tools.
Specification writing (introduction) (In-House)
By The In House Training Company
This intensive one-day training programme has been developed to help those involved in producing specifications create high quality documents in an organised and effective way. The programme explains the primary purpose of specifications and the importance of understanding the context in which they are used. It focuses particularly on how to develop and structure content and write requirements that are clear and concise. The methods and techniques presented will provide a practical foundation course for those new to the topic whilst offering new insights to those with more experience. The objectives of the workshop are to: Review and discuss the role and purpose of specifications Present a structured approach for organising and producing specifications Explain each of the key steps involved in creating effective specifications Review some methods for assisting in defining requirements Explain how to define the scope and develop the structure for a specification Present methods to assist the writing and editing of specifications Review how specifications should be issued and controlled 1 Introduction Course objectives Review of participants' needs and objectives 2 Specifications in perspective The role and purpose of specifications The impact of specifications on commercial performance The qualities of an effective specification The five key steps of 'POWER' writing: prepare-organise-write-edit-release 3 Step 1: Preparing to write Defining the purpose the specification; integrating the specification and contract Deciding how to specify: when to specify in functional and technical terms Getting the right people involved at the right time; engaging stakeholders Applying procedures for writing, issuing and controlling specifications 4 Step 2: Organising the specification content Scoping the document: scope maps, check lists, structured brainstorming Clarifying requirements; separating needs and desires Dealing with requirements that are difficult to quantify Useful techniques: cost benefit analysis, Pareto analysis Deciding what goes where; typical contents and layout for a specification Creating and using model forms: typical sections and sub sections 5 Step 3: Writing the specification Identifying and understanding the readers needs Choosing and using the right words; dealing with jargon Important words; will, shall, must; building a glossary Using sentence structure and punctuation to best effect Understanding the impact of style, format and appearance Avoiding common causes of ambiguity; being concise and ensuring clarity 6 Step 4: Editing the specification Why editing is difficult; how to develop a personal editing strategy Key areas to review: structure, content, accuracy, clarity, style and grammar Editing tools and techniques 7 Step 5: Releasing and controlling the specification Key requirements for document issue and control Final formatting and publication issues; document approval Requirements management: managing revisions and changes 8 Course review and action planning What actions should be implemented to improve specifications? Conclusion

Creating effective specifications (In-House)
By The In House Training Company
High quality specifications are of paramount importance in achieving the right technical performance and value for money. This long-established training programme has been developed to help those involved in producing specifications to create high quality documents in an organised and effective way. It provides a sound foundation for those new to the topic whilst at the same time offering new insights to those with more experience. The programme emphasises the need for a clear definition of requirements combined with the ability to communicate those requirements effectively to third parties. A structured method of preparing specifications is provided, and a range of practical techniques is presented, to enable participants to put the principles into practice. The commercial and contractual role of specifications is also addressed. The objectives of the workshop are to: Provide a clear understanding of the role and purpose of specifications Present a framework for organising and producing specifications Define the key steps involved in creating effective specifications Demonstrate methods for assisting in defining requirements Provide tools and techniques for scoping and structuring specifications Show the role of specifications in managing variations and changes to scope Present methods to assist the writing and editing of specifications Review how specifications should be issued and controlled DAY ONE 1 Introduction Review of course objectives Review of participants' needs and objectives 2 Creating effective specifications The role of specifications in communicating requirements The costs, benefits and qualities of effective specifications Understanding the differences between verbal and written communication The five key steps of 'POWER' writing: prepare-organise-write-edit-release Exercise: qualities of an effective specification 3 Step 1: Preparing to write - defining readership and purpose; the specification and the contract Designing the specifications required; applying BS 7373 Defining the purpose, readership and title of each document Effective procedures for writing, issuing and controlling specifications The roles and responsibilities of the key players Understanding contracts; the contractual role of the specification Integrating and balancing the technical and commercial requirements Writing specifications to achieve the appropriate contract risk strategy Deciding how to specify: when to use functional and technical specifications The role of specifications in managing variations and changes to scope 4 Case study 1 Teams review a typical project scenario and identify the implications for the specification Feedback and discussion 5 Step 2: Organising the specification content Defining the need and establishing user requirements Deciding what issues the specification should cover Scoping techniques: scope maps, check lists, structured brainstorming Clarifying priorities: separating needs and desires Dealing with requirements that are difficult to quantify Useful techniques: cost benefit analysis, QFD, Pareto analysis 6 Case study 2 Teams apply the scoping techniques to develop the outline contents for a specification Feedback and discussion DAY TWO 7 Step 2: Organising the specification content (cont) Deciding what goes where; typical contents and layout for a specification The three main segments: introductory, key and supporting Creating and using model forms: the sections and sub-sections Detailed contents of each sub-section Tools and techniques for outlining and structuring specifications 8 Case study 3 Teams develop the detailed specification contents using a model form Feedback and discussion 9 Step 3: Writing the specification The challenges of written communication Identifying and understanding the readers needs Choosing and using the right words; dealing with jargon Problem words; will, shall, must, etc; building a glossary Using sentence structure and punctuation to best effect Understanding the impact of style, format and appearance Avoiding common causes of ambiguity Being concise and ensuring clarity Choosing and using graphics to best effect Exercises and examples 10 Step 4: Editing the specification Why editing is difficult; how to develop a personal editing strategy Key areas to review: structure, content, accuracy, clarity, style and grammar Editing tools and techniques 11 Step 5: Releasing and controlling the specification Key requirements for document issue and control Final formatting and publication issues; document approval Requirements management: managing revisions and changes 12 Course review and action planning What actions should be implemented to improve specifications? Conclusion

Communication skills (In-House)
By The In House Training Company
Effective communication is a skill. This half-day workshop is very interactive - participants can practise their communication skills in a positive, supportive environment. 1 Welcome, introductions and objectives The definition of effective communication Exercise: sending a message 2 Verbal communications Effective communicators - who are they? What skills or attributes do they have? Listening skills, clear use of words, presence, eye contact, body language 3 How good a listener are you? Exercise: listening skills questionnaire and evaluation 4 Impact versus intent - what did you really mean to say? Attitudes influence behaviour and behaviour breeds behaviour Exercise: 'I never said she stole money' The need to avoid misunderstanding or misinterpretation 5 The 5 key principles to effective communication Exercise: 'What would you say?' 6 Written communication What makes an effective written communication? Kipling's 6 Honest Men: who, what, where, when, why and how Planning to write an email 7 Fuzzy meanings Probabilities for misunderstandings and misinterpretations 8 Practical exercise Hone written communication skills and put into practice hints and tips from the session 9 Review of key learning points and objectives

Business writing skills (In-House)
By The In House Training Company
This very practical workshop is designed to enable participants to improve the impact, clarity and accuracy of their business documents - both internal and external.: This workshop will help participants: Identify the purpose of writing their documents - to themselves and to their readers Recognise and meet the needs of their readers Plan documents systematically and improve the layout, flow and structure Express the content more clearly, concisely and correctly Adapt the tone and style of writing to the circumstances Proof-read and edit work effectively, using formal marks and techniques Improve visual layout, format and appearance 1 Course objectives Welcome and Introductions The problems now - group discussion 2 Writing better business documents What points to highlight / exclude Starting off Introductions Conclusions Executive summaries 3 Rules and standards George Orwell's famous maxim Why write? - clarifying your aims and objectives A seven-step method for better preparation The three-stage process for writing well Grouping information for your reader 4 Proof-reading and editing The difference between proof-reading and editing Proof-reading methods and strategies Proof-reading marks and techniques Training your eye for detail Knowing what to look for 5 Effective editing Grammar and English standards Words - usage and spelling Sentences - units of thought Paragraphs - themes Punctuation - spotting and correcting common errors Say what you mean - active v passive language 6 How's your English? Grammar quizzes and punctuation test Spotting spelling errors Rephrasing jargons and clicheÌs Common error's and mistakes 7 Document layout House style Use of white space Fonts and effects 8 One-to-one workshops These are practical sessions with one-to-one consultation with colleagues and the trainer They are held at key points to consolidate the learning from different sessions 9 Course summary Summary of key points Action plans

Smart sales prospecting (In-House)
By The In House Training Company
As technology continues to develop and increasingly interact with our daily lives, so must our sales techniques to ensure we're leveraging advances in how people do business to our advantage. It is essential for all salespeople to understand how to navigate the various tools at our disposal and grow their skills and confidence to put them into action in order to build a solid business pipeline. We have developed this programme to be practical, fun and interactive, whilst ensuring that participants will learn how to utilise new technology to their advantage, self-generate new business leads and opportunities, gain additional business and referrals from existing contacts, and save time and effort using proven business development skills. This course will help participants: Understand the 'organized persistence' model of sales prospecting Develop skills in using video, online and social media to generate interest Understand how to write effective sales and outreach emails and using online tools Develop techniques for effectively managing telephone appointments Learn ways to use LinkedIn for connecting with customers and prospects Develop networking skills and learn how to source and develop referrals and professional introductions 1 Key principles of smart sales prospecting Set your sales prospecting goals and objectives Elevator pitch, core messages and your value proposition Targeting and segmenting your market 'Organised persistence' using your CRM effectively 2 Setting appointments by telephone - planning and preparation Why calling still works and the best times to call Creating a call prompt sheet: Opening a call and taking control Giving a reason to meet Key questions to ask Overcoming the cold calling blues 3 Setting appointments by telephone - advanced skills Giving a reason to meet and 'selling the appointment' Key questions to ask that will create interest and motivation to meet Voice tone, power words, phrasing, pausing, responding Getting past gatekeepers and getting through 4 Using LinkedIn for research and follow-up Why LinkedIn matters and how to use it Finding new contacts, connecting and Inmailing Short-cuts and advanced skills 5 Email strategies that work Using AIDA and other templates for sales emails Using personalized video emails to create interest Vertical targeting emails, with examples Building awareness with an email chain

Selling through service (In-House)
By The In House Training Company
In today's fast-moving competitive environment, sales are often made or lost on the strength of a telephone conversation or a brief email. This means that not only is customer service everyone's responsibility - so is sales. Customer service staff are failing the customer if they don't think about sales. And sales staff are failing customers if they don't think about service. And anyone failing a customer is failing both themselves and their employer. Too often, customer service staff feel neither capable nor empowered to recognise or capitalise upon a sales opportunity. Too often, sales people pursue the short-term opportunity at the expense of the bigger picture. The good news is - it doesn't have to be this way! Sales and customer service skills can be acquired, developed and polished just like any other skill. This tried-and-tested programme shows you how to do it. As a result of this course, participants will be able to: Take control of a customer conversation, with confidence Refresh and polish their customer service and sales performance Recognise and develop a sales opportunity Engage the customer and build rapport Identify a customer's needs Match the customer's needs to the organisation's products or services Handle objections confidently Ask for the order At the end of the workshop each participant will have developed their own action plan for developing and using their skills in the workplace. 1 Introduction Course overview, objectives and introductions 2 Serving or selling? Feelings and attitudes - How we can affect the outcome by our feelings and behaviour What is selling? - Selling is helping people to buy, identifying the opportunities that exist within the conversation to develop the customer's interest in our products or services 3 Developing the right skills Communication- The impact of body language, voice tone and words- How to make the best impression on the customer and create a 'buying environment' Rapport-building- What makes a good working relationship?- What do customers look for when they call us?- How can we match their expectations in terms of our own interpersonal skills? Relating to different types of people by identifying and matching their communication style on the telephone 4 Making it easy for the customer Starting it right- Opening the conversation positively- Building rapport- How to develop interest in our products or services Gaining and clarifying information- Questioning skills and questioning style- What do we need to know from the customer?- How can we use that information in the conversation? Active listening- The most under-rated skill of all- Picking up on the 'Golden Moments' when a customer shows they may be interested Presenting information confidently- Knowing the benefits of our products or services- How to tell the customer what they need to know in order to enable them to buy Closing on a positive note- When and how to ask for commitment Dealing with the customer's objections and concerns in a positive manner 5 Course summary and action plans Review of main learning points Presentation of personal action plans

Search By Location
- Word Courses in London
- Word Courses in Birmingham
- Word Courses in Glasgow
- Word Courses in Liverpool
- Word Courses in Bristol
- Word Courses in Manchester
- Word Courses in Sheffield
- Word Courses in Leeds
- Word Courses in Edinburgh
- Word Courses in Leicester
- Word Courses in Coventry
- Word Courses in Bradford
- Word Courses in Cardiff
- Word Courses in Belfast
- Word Courses in Nottingham