- Professional Development
- Medicine & Nursing
- Arts & Crafts
- Health & Wellbeing
- Personal Development
Data Science for Business Professionals
By Mpi Learning - Professional Learning And Development Provider
The ability to identify and respond to changing trends is a hallmark of a successful business. Whether those trends are related to customers and sales, or to regulatory and industry standards, businesses are wise to keep track of the variables that can affect the bottom line. In today's business landscape, data comes from numerous sources and in diverse forms.
Internet of Things - IOT for leaders
By Mpi Learning - Professional Learning And Development Provider
The Internet of Things (IoT) promises a wide range of benefits for industry, energy and utility companies, municipalities, healthcare, and consumers. Data can be collected in extraordinary volume and detail regarding almost anything worth measuring, such as public health and safety, the environment, industrial and agricultural production, energy, and utilities.

This Leadership Skills Training Course covers all essential techniques of effective communication, building strong teams, leading with influence and all other necessary leadership skills to become a successful leader in your chosen profession or work setting

Data Ethics for Business Professionals
By Mpi Learning - Professional Learning And Development Provider
Data Ethics for Business Professionals is designed for individuals who are seeking to demonstrate an understanding of the ethical uses of data in business settings.

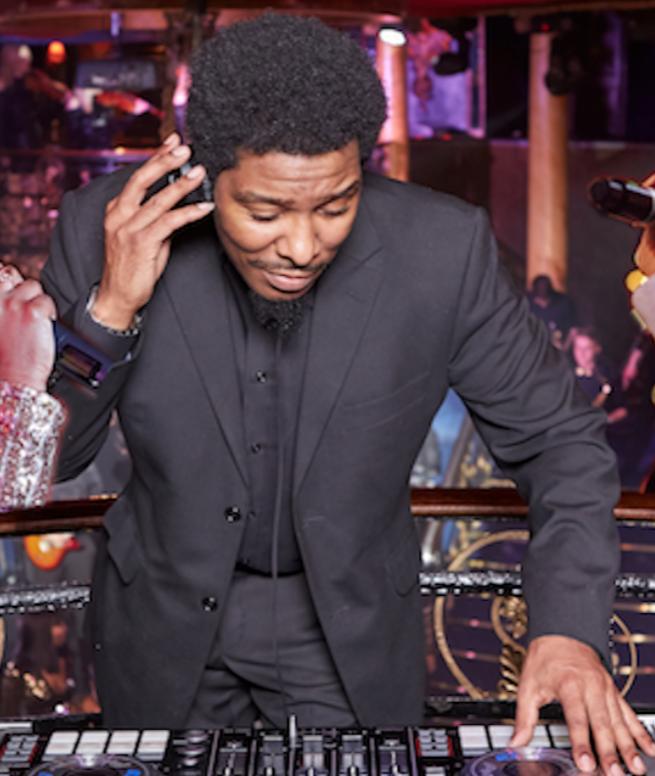
45 min One to One Dj Lesson
By Supa Dj School
Learn the basics of listening, mixing and hosting techniques. Get creative behind the decks and benefit from the skills and experience of almost 3 decades with professional DJ Supa.

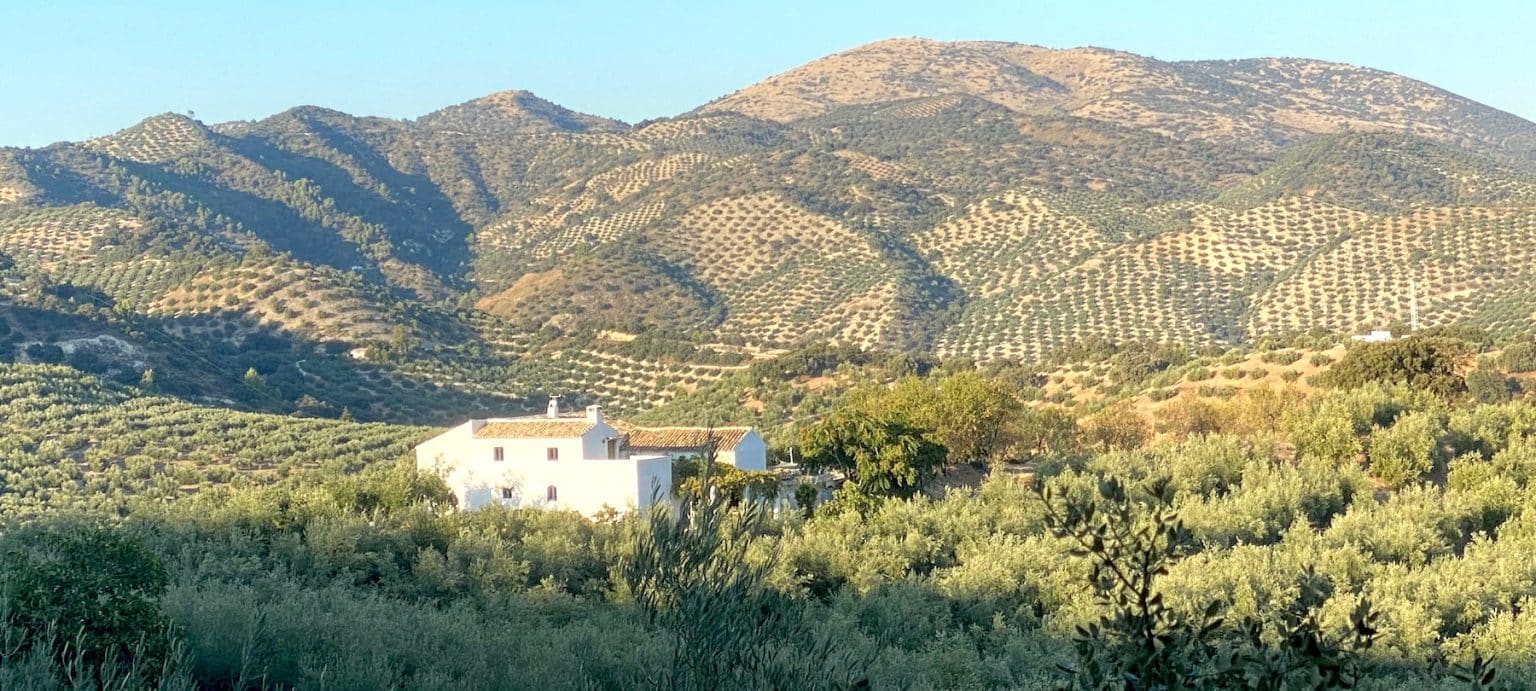
WYLLIE FOX ART TUITION
By Wyllie Fox Tuition
Francesca Wyllie (BA Hons Fine Art) has an amazing north-facing art studio at El Retiro in Andalucia, which was purpose-built to accommodate painting groups. Bespoke painting and sculpture workshops can be arranged or Francesca can travel locally to guide you in your own studios or locations.

Effective technical writing (In-House)
By The In House Training Company
The aim of this programme is to help attendees create better quality technical documents in an organised and efficient manner. It will give those new to the topic an appreciation of how to approach the task professionally whilst those with more experience will be able to refresh and refine their skills. The programme comprises three complementary one-day modules: The programme presents a structured methodology for creating technical documents and provides a range of practical techniques that help delegates put principles into practice. Although not essential, it is strongly advised that delegates for modules 2 and 3 have already attended module 1, or another equivalent course. Note: the content of each module as shown here is purely indicative and can be adapted to suit your particular requirements. This course will: Explain the qualities and benefits of well written technical documents Present a structured approach for producing technical documents Review the essential skills of effective technical writing Demonstrate practical methods to help create better documents Provide tools and techniques for specification and report writing Review how technical documents should be issued and controlled Note: the content of each module as shown here is purely indicative and can be adapted to suit your particular requirements. Module 1: Essential skills for technical writers 1 Introduction to the programme Aims and objectives of the module Introductions and interests of participants 2 Creating effective technical documents What is technical writing? how does it differ from other writing? Key qualities of an effective technical document Communication essentials and the challenges faced by technical writers The lessons of experience: how the best writers write The five key steps : prepare - organise - write - edit - release (POWER) 3 Preparing to write Defining the document aims and objectives; choosing the title Understanding technical readers and their needs Getting organised; planning and managing the process Integrating technical and commercial elements The role of intellectual property rights (IPR), eg, copyright 4 Organising the content The vital role of structure in technical documents Deciding what to include and how to organise the information Categorising information: introductory, key and supporting Tools and techniques for scoping and structuring the document Creating and using document templates - pro's and con's 5 Writing the document Avoiding 'blinding them with science': the qualities of clear writing Problem words and words that confuse; building and using a glossary Using sentence structure and punctuation to best effect Understanding the impact of style, format and appearance Avoiding common causes of ambiguity; being concise and ensuring clarity Using diagrams and other graphics; avoiding potential pitfalls 6 Editing and releasing the document Why editing is difficult; developing a personal editing strategy Some useful editing tools and techniques Key requirements for document issue and control Module 2: Creating better specifications 1 Introduction Aims and objectives of the day Introductions and interests of participants The 'POWER' writing process for specifications 2 Creating better specifications The role and characteristics of an effective specification Specifications and contracts; the legal role of specifications Deciding how to specify; understanding functional and design requirements Developing the specification design; applying the principles of BS 7373 Getting organised: the key stages in compiling an effective specification 3 Preparing to write a specification Defining the scope of the specification; deciding what to include and what not Scoping techniques: scope maps, check lists, structured brainstorming The why/what/how pyramid; establishing and understanding requirements Clarifying priorities; separating needs and desires: the MoSCoW method Useful quantitative techniques: cost benefit analysis, QFD, Pareto analysis Dealing with requirements that are difficult to quantify 4 Organising the content The role of structure in specifications Typical contents and layout for a specification What goes where: introductory, key and supporting sections Creating and using model forms: the sections and sub sections Detailed contents of each sub-section Exercise: applying the tools and techniques 5 Writing the specification Identifying and understanding the specification reader Key words: will, shall, must; building and using a glossary Writing performance targets that are clear and unambiguous Choosing and using graphics Exercise: writing a specification 6 Editing and releasing the document Key editing issues for specifications Issue and control of specifications Module 3: Writing better reports 1 Introduction Aims and objectives of the day Introductions and interests of participants The 'POWER' technical writing process for technical reports 2 Creating better reports What is a technical report? types and formats of report The role and characteristics of an effective technical report Understanding technical report readers and their needs The commercial role and impact of technical reports Getting organised: the key stages in compiling a technical report 3 Preparing to write reports Agreeing the terms of reference; defining aims and objectives Being clear about constraints; defining what is not to be included Legal aspects and intellectual property rights (IPR) for reports Preparing the ground; gathering information and reference documents Keeping track of information: note making, cataloguing and cross referencing Tools and techniques for developing a valid and convincing argument 4 Organising the content The role of structure reviewed; some typical report structures Who needs what: identifying the varied needs of the readership What goes where: introductory, key and supporting sections Creating and using model forms: the sections and sub sections Detailed contents of each sub-section Exercise: applying the tools and techniques 5 Writing the report Planning the storyline: the report as a journey in understanding Recognising assumptions about the reader; what they do and don't know Converting complex concepts into understandable statements Presenting technical data and its analysis; the role of graphics Presenting the case simply whilst maintaining technical integrity Exercise: writing a technical report 6 Editing and releasing the report Key editing issues for technical reports Issue and control of technical reports

Leading technical teams (In-House)
By The In House Training Company
The work of a technical team is invariably challenging and often unpredictable. Definition of the work can be problematic, timescales can be hard to estimate and the right technical approach difficult to select. Staff involved in this type of work usually have very high levels of specialist knowledge in their field and have high expectations of those who lead them. In addition to the challenges of the work, the team leader often has to balance the need for professional excellence with financial and commercial considerations and to ensure that team goals are realistic by being an effective negotiator with other project and senior managers. These characteristics make technical team leadership a demanding and complex activity. This programme aims to help participants develop the skills needed to become an effective technical team leader. The objectives of this programme are to help participants: understand the significance of leadership skills and their impact on team performance review the key skills needed to be an effective, 'multi-dimensional' team leader and learn how to develop, adapt and apply them in practice learn how to identify the preferred leadership style for the context and organisational culture and how to develop personal style versatility understand the role of the project leader in building an effective team and the skills required to promote and sustain team performance gain a better understanding of the interpersonal skills needed to motivate individual team members and harness the full potential of the team DAY ONE 1 Technical teams and leadership What is a leader? How much can leadership be learned? The team environment and the impact of leadership skills The characteristics of high performance teams and their leaders Some useful models and theories of leadership explored Types of leadership; choosing how to use leadership power Evaluating personal leadership style; how to develop style flexibility 2 Essential skills for team leaders 3 key dimensions of effective leadership: inwards, outwards and upwards Developing and promoting a 'team vision': strategic thinking skills The vital role of communication skills and how to develop them Understanding others; emotional intelligence skills Being a visible leader; behavioural and influencing skills Building effective relationships; the importance of trust and respect DAY TWO 3 Leading inwards to build the team The role of leadership in developing team performance Understanding individuals in the team; recognising team role preferences Managing conflict and promoting positive team dynamics Setting standards, maintaining discipline and rewarding performance Harnessing team potential: building motivation within the team Promoting team learning; the team leader as coach / mentor 4 Leading outwards and upwards to support the team Negotiating realistic team goals; effective influencing skills Gaining empowerment and support from the key stakeholders Leading upwards: knowing when and how to take the initiative Building team credibility within the organisation; helping the team deliver Becoming an effective team player in leadership teams Building and maintaining rapport with influential stakeholders

Search By Location
- TEC Courses in London
- TEC Courses in Birmingham
- TEC Courses in Glasgow
- TEC Courses in Liverpool
- TEC Courses in Bristol
- TEC Courses in Manchester
- TEC Courses in Sheffield
- TEC Courses in Leeds
- TEC Courses in Edinburgh
- TEC Courses in Leicester
- TEC Courses in Coventry
- TEC Courses in Bradford
- TEC Courses in Cardiff
- TEC Courses in Belfast
- TEC Courses in Nottingham

