- Professional Development
- Medicine & Nursing
- Arts & Crafts
- Health & Wellbeing
- Personal Development
262 Pha courses delivered Live Online
Tableau Desktop Training - Analyst
By Tableau Training Uk
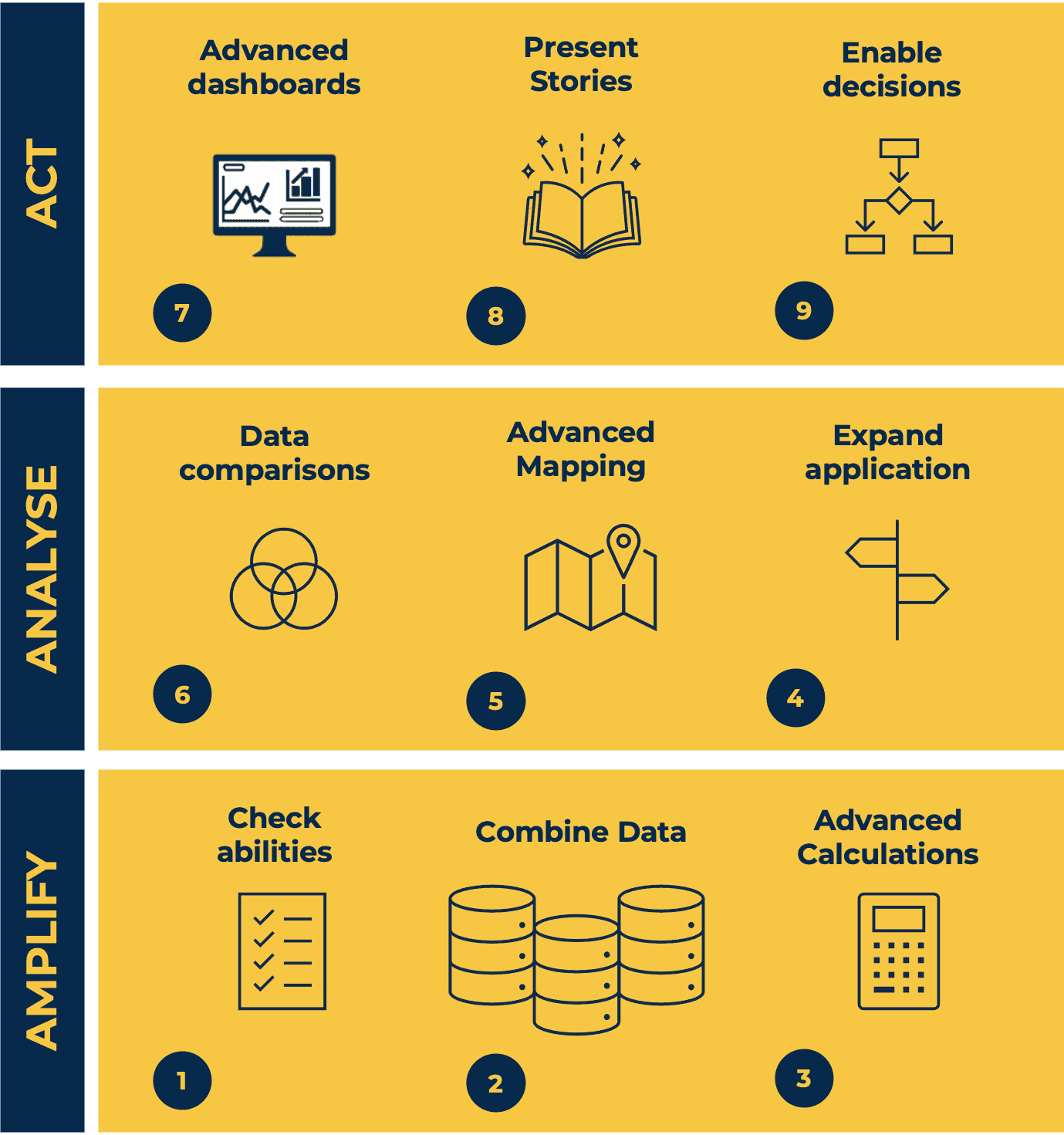
This Tableau Desktop Training intermediate course is designed for the professional who has a solid foundation with Tableau and is looking to take it to the next level. For Private options, online or in-person, please send us details of your requirements: This Tableau Desktop training intermediate course is designed for the professional who has a solid foundation with Tableau and is looking to take it to the next level. Attendees should have a good understanding of the fundamental concepts of building Tableau worksheets and dashboards typically achieved from having attended our Tableau Desktop Foundation Course. At the end of this course you will be able to communicate insights more effectively, enabling your organisation to make better decisions, quickly. The Tableau Desktop Analyst training course is aimed at people who are used to working with MS Excel or other Business Intelligence tools and who have preferably been using Tableau already for basic reporting. The course is split into 3 phases and 9 modules: Phase 1: AMPLIFY MODULE 1: CHECK ABILITIES Revision – What I Should Know What is possibleHow does Tableau deal with dataKnow your way aroundHow do we format chartsHow Tableau deals with datesCharts that compare multiple measuresCreating Tables MODULE 2: COMBINE DATA Relationships Joining Tables – Join Types, Joining tables within the same database, cross database joins, join calculations Blending – How to create a blend with common fields, Custom defined Field relationships and mismatched element names, Calculated fields in blended data sources Unions – Manual Unions and mismatched columns, Wildcard unions Data Extracts – Creating & Editing Data extracts MODULE 3: ADVANCED CALCULATIONS Row Level v Aggregations Aggregating dimensions in calculations Changing the Level of Detail (LOD) of calculations – What, Why, How Adding Table Calculations Phase 2: ANALYSE MODULE 4: EXPAND APPLICATION Making things dynamic with parameters Sets Trend Lines How do we format charts Forecasting MODULE 5: ADVANCED MAPPING Using your own images for spatial analysis Mapping with Spatial files MODULE 6: DATA COMPARISONS Advanced Charts Bar in Bar charts Bullet graphs Creating Bins and Histograms Creating a Box & Whisker plot Phase 3: ACT MODULE 7: ADVANCED DASHBOARDS Using the dashboard interface and Device layout Dashboard Actions and Viz In tooltips Horizontal & Vertical containers Navigate between dashboards MODULE 8: PRESENT STORIES Telling data driven stories MODULE 9: ENABLE DECISIONS What is Tableau Server Publishing & Permissions How can your users engage with content This training course includes over 25 hands-on exercises and quizzes to help participants “learn by doing” and to assist group discussions around real-life use cases. Each attendee receives a login to our extensive training portal which covers the theory, practical applications and use cases, exercises, solutions and quizzes in both written and video format. Students must bring their own laptop with an active version of Tableau Desktop 2018.2 (or later) pre-installed. What People Are Saying About This Course “Course was fantastic, and completely relevant to the work I am doing with Tableau. I particularly liked Steve’s method of teaching and how he applied the course material to ‘real-life’ use-cases.”Richard W., Dashboard Consulting Ltd “This course was extremely useful and excellent value. It helped me formalise my learning and I have taken a lot of useful tips away which will help me in everyday work.” Lauren M., Baillie Gifford “I would definitely recommend taking this course if you have a working knowledge of Tableau. Even the little tips Steve explains will make using Tableau a lot easier. Looking forward to putting what I’ve learned into practice.”Aron F., Grove & Dean “Steve is an excellent teacher and has a vast knowledge of Tableau. I learned a huge amount over the two days that I can immediately apply at work.”John B., Mporium “Steve not only provided a comprehensive explanation of the content of the course, but also allowed time for discussing particular business issues that participants may be facing. That was really useful as part of my learning process.”Juan C., Financial Conduct Authority “Course was fantastic, and completely relevant to the work I am doing with Tableau. I particularly liked Steve’s method of teaching and how he applied the course material to ‘real-life’ use-cases.”Richard W., Dashboard Consulting Ltd “This course was extremely useful and excellent value. It helped me formalise my learning and I have taken a lot of useful tips away which will help me in everyday work.” Lauren M., Baillie Gifford “I would definitely recommend taking this course if you have a working knowledge of Tableau. Even the little tips Steve explains will make using Tableau a lot easier. Looking forward to putting what I’ve learned into practice.”Aron F., Grove & Dean “Steve is an excellent teacher and has a vast knowledge of Tableau. I learned a huge amount over the two days that I can immediately apply at work.”John B., Mporium
Doctor of Business Administration (DBA)
By School of Business and Technology London
Getting Started Enhance your career and earn the highest qualification available in business and management. The Doctor of Business Administration taught and awarded by the University of Central Lancashire is designed for senior managers and consultants who wish to learn and earn an advanced administration level while working full-time. DBA is a demanding research-based programme suitable for candidates pursuing higher-level business administration qualifications after an MBA. This programme provides a solid foundation in various aspects of business, including management, marketing, finance, and operations. Students can expect to gain practical insights into real-world business scenarios, enabling them to make informed decisions and solve complex problems effectively. You're learning journey will include: Lectures and guided reading. Active group work. Case studies. Videos. Reviews of current events and student presentations. You'll develop applied research skills as you evaluate industry-related problems critically. Throughout the programme, students receive support from experienced academics and industry professionals who provide guidance and feedback on their research projects. The programme is delivered through online webinars and independent study, allowing students to balance their studies with work and personal commitments. Doctor of Business Administration is awarded and delivered by the University of Central Lancashire. School of Business and Technology London partners with Chestnut Education Group to promote this Doctor of Business Administration programme. About Awarding Body Founded in 1828, the University of Central Lancashire is a public university based in Preston, Lancashire, England. Today, UCLAN is one of the largest in the United Kingdom, with a student and staff community of nearly 38,000. At present, the University has academic partners in all regions of the globe, and it is on a world stage that the first-class quality of its education was first recognised. In 2010, UCLAN became the first UK modern Higher Education institution to appear in the QS World University Rankings. In 2018, the Centre for World University Rankings estimated Central Lancashire to be in the top 3.7 per cent of all global universities, highlighting the growth the University has made in offering students real-world learning experiences and reflecting the University's extensive pool of academic talent. Ranked in the top 7% of universities worldwide. Student Communities from more than 100 countries WES Recognised Qualifi is a UK Government (Ofqual.gov.uk) regulated awarding organisation and has developed a reputation for supporting relevant skills in a range of job roles and industries, including Leadership, Enterprise and Management, Hospitality and catering, Health and Social Care, Business Process Outsourcing and Public Services. Qualifi is also a signatory to BIS international commitments of quality. The following are the key facts about Qualifi. Regulated by Ofqual.gov.uk World Education Services (WES) Recognised Assessment Assignments and Project No examination Entry Requirements Applicants should normally have a Master's degree or equivalent and work in or have recently worked with in business administration. If English is not your first language, you will be expected to demonstrate a certificated level of proficiency of at least IELTS 6.5 (Academic level) or equivalent English Language qualification. Progression Upon completing the doctorate programme, learners will possess the necessary skills and knowledge to pursue various career opportunities in administration, management research, etc. One can choose from various positions upon successfully completing a DBA. Some of the most notable career paths are Professor and Postdoctoral Researcher, Market Research Analyst, Economic Analyst, etc. Learners must request before enrolment to interchange unit(s) other than the preselected units shown in the SBTL website because we need to make sure the availability of learning materials for the requested unit(s). SBTL will reject an application if the learning materials for the requested interchange unit(s) are unavailable. Learners are not allowed to make any request to interchange unit(s) once enrolment is complete. Structure Phase 1: Qualifi Level 8 Diploma in Strategic Management and Leadership Programme Structure The course is structured around eight mandatory units, encompassing various topics aligned with learning outcomes. Each unit holds a value of 20 credits. Learners can participate in lectures and workshops to familiarize themselves with the subject. Attaining a total of 160 credits by completing all units is a prerequisite for the issuance of the Diploma. Unit 800: Leadership Qualities and Practice Unit code: A/506/9126 This unit delves into the connections between leadership and management within strategic operations. It scrutinizes various leadership styles, their underlying principles, and associated concepts. The unit also investigates methods to assess and enhance team performance to achieve strategic business and operational goals. Additionally, it encompasses the interplay between strategic management and leadership, containing crucial leadership principles, theories, and their alignment with organizational strategy. Unit 701: Research Methods Unit code: Y/506/9134 The objective of this unit is to enhance the learner's knowledge and comprehension of academic practices and research methodologies. It employs a problem-based learning approach to cultivate practical proficiency in areas relevant to educational practice and research in business and management. Unit 801: Personal Leadership Development as a Strategic Manager Unit code: F/506/9127 This unit focuses on the strategic leadership skills essential for directors and senior managers to effectively guide international organizational strategic initiatives, collaborating with partners, buyers, suppliers, customers, and competitors. Unit 802: Strategy Development in Cross Border and Global Organisations Unit code: F/506/9130 This unit tackles formulating strategies for cross-border or global organizations, which encounter complexities stemming from political, religious, cultural, and social differences, as well as the management of organizations operating within specific country boundaries. Unit 803: Strategic Planning for Cross Border and Global Organisations Unit code: L/506/9132 This unit scrutinises the diverse influences and effects on cross-border or global organisations and how they contribute to the development of successful strategies and the mitigation of risks. Unit 804: Strategic Direction in Cross Border and Global Organisations Unit code: R/506/9133 This unit provides senior strategic managers with the opportunity to delve into the influences and effects of cross-border and global policy and strategy. It aims to facilitate enhancements in establishing direction, shaping the approach, and forecasting the success of cross-border or worldwide policy and procedure. Unit 805: Strategic Communication Unit code: L/506/9129 The unit aims to develop the ability to critically assess and appreciate the impact of media on international organisations. It considers stakeholders, political and pressure groups, as well as the part played by media owners. Unit 806: Culture and its Impact on Strategy Unit code: J/506/9128 This unit strives to foster a profound comprehension of the intricacies faced by internationally operating organizations and how this impacts the strategy development process. It employs well-reasoned and thoroughly researched perspectives to cultivate alternative viewpoints. Phase 2 - Doctor of Business Administration Programme Structure Stage 1 - Taught component The Reflexive Practitioner Management, Rhetoric, Policy and Practice Research Methodologies and Design Qualitative Research Methods Quantitative Research Methods Accordion Title Stage 2 - Research component The Reflexive Practitioner Delivery Methods The Doctor of Business Administration is awarded and delivered by the University of Central Lancashire. This doctorate from the University of Central Lancashire is offered as a block teaching and research programme. The DBA will run at the Preston Campus of the University. You'll have full access to the Library and information resources of the University throughout the DBA and may use all social, cultural and sports facilities of the University. Stage 1 - Taught component The DBA Taught Programme consists of six taught modules, each being completed through a four-day intensive workshop plus a period of private study both before and after the workshop. During Stage 1 you will develop critical and reflective skills at doctoral level, through the requirement to think conceptually, apply critical thinking, and reasoning skills and to challenge orthodoxy relating to the body of knowledge and research relating to Management and Organisation. Action learning is incorporated within the study sessions and is an important and distinctive feature of our DBA. You will work in sets or small development groups with fellow participants throughout the programme and also develop your skills as a critical and reflective learner. Stage 2 - Research component The DBA Research Programme - as part of the development process of your DBA project, you will have worked with the DBA staff to agree a suitable supervisory team, including a Director of Studies. This team will work with you throughout Stage 2 helping you to design and implement your own particular DBA project. This will normally take two years working on a part-time basis although you may choose to work at a pace that requires more time and you may therefore take up to five years. Resources and Support School of Business & Technology London is dedicated to offering excellent support on every step of your learning journey. School of Business & Technology London occupies a centralised tutor support desk portal. Our support team liaises with both tutors and learners to provide guidance, assessment feedback, and any other study support adequately and promptly. Once a learner raises a support request through the support desk portal (Be it for guidance, assessment feedback or any additional assistance), one of the support team members assign the relevant to request to an allocated tutor. As soon as the support receives a response from the allocated tutor, it will be made available to the learner in the portal. The support desk system is in place to assist the learners adequately and streamline all the support processes efficiently. Quality learning materials made by industry experts is a significant competitive edge of the School of Business & Technology London. Quality learning materials comprised of structured lecture notes, study guides, practical applications which includes real-world examples, and case studies that will enable you to apply your knowledge. Learning materials are provided in one of the three formats, such as PDF, PowerPoint, or Interactive Text Content on the learning portal. How does the Online Learning work at SBTL? We at SBTL follow a unique approach which differentiates us from other institutions. Indeed, we have taken distance education to a new phase where the support level is incredibly high.Now a days, convenience, flexibility and user-friendliness outweigh demands. Today, the transition from traditional classroom-based learning to online platforms is a significant result of these specifications. In this context, a crucial role played by online learning by leveraging the opportunities for convenience and easier access. It benefits the people who want to enhance their career, life and education in parallel streams. SBTL's simplified online learning facilitates an individual to progress towards the accomplishment of higher career growth without stress and dilemmas. How will you study online? With the School of Business & Technology London, you can study wherever you are. You finish your program with the utmost flexibility. You will be provided with comprehensive tutor support online through SBTL Support Desk portal. How will I get tutor support online? School of Business & Technology London occupies a centralised tutor support desk portal, through which our support team liaise with both tutors and learners to provide guidance, assessment feedback, and any other study support adequately and promptly. Once a learner raises a support request through the support desk portal (Be it for guidance, assessment feedback or any additional assistance), one of the support team members assign the relevant to request to an allocated tutor. As soon as the support receive a response from the allocated tutor, it will be made available to the learner in the portal. The support desk system is in place to assist the learners adequately and to streamline all the support process efficiently. Learners should expect to receive a response on queries like guidance and assistance within 1 - 2 working days. However, if the support request is for assessment feedback, learners will receive the reply with feedback as per the time frame outlined in the Assessment Feedback Policy.

Introduction to contract negotiation (In-House)
By The In House Training Company
This intensive one-day IACCM-approved programme helps participants develop the skills, knowledge and competencies required to plan for and carry out effective negotiations in a range of different environments. By the end of the programme participants will be able to: Understand the basic concepts of negotiation and how it adds value to the organisation Recognise the stages of negotiation and the skills required at each stage Make use of tried-and-tested negotiation planning tools Apply a range of negotiation tools and techniques to support the organisation in obtaining value for money, quality and fit-for-purpose outcomes Set negotiation objectives Appreciate the importance of interpersonal skills in maximising the opportunities for reaching win/win agreements 1 Welcome Introductions Aims and objectives Plan for the day 2 Why negotiate? Understanding the negotiation context Negotiating with suppliers Negotiating with stakeholders 3 Understanding the process The phases of negotiation and what to do in each phase Before During After 4 Planning Appreciating the importance of planning Different approaches Identifying the key variables Setting objectives for each of them Practical negotiation planning exercise 5 Doing The key skills required, Communication Numeracy empathy Applying these skills in a role play: practical exercise 6 Close Review of key learning points Personal action planning

CDM 2015 - in-depth (In-House)
By The In House Training Company
The learning objectives that we believe you require to be covered within the training include: A detailed understanding of the CDM 2015 Regulations and how they should work in practice An understanding of the key roles (Designer, Principal designer, contractor, principal contractor and client) under CDM 2015 What constitutes design and when you may be acting as a designer The requirements for notification Pre construction information, the construction phase plan and the H&S file An opportunity for delegates to ask questions and gain clarification on specific project requirements 1 Introduction Why manage health and safety? The costs of accidents Construction industry statistics Why CDM 2015? 2 Overview of health and safety law and liabilities Criminal and civil law Liability Enforcement and prosecution Compliance - how far do we go? Statutory duties 3 Health and safety law in construction - the current framework Framework of relevant legislationHealth and Safety at Work etc Act 1974Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999Construction (Design and Management) Regulations 2015Work at Height Regulations 2005 Who is responsible for the risks created by construction work? Shared workplaces/shared responsibilities Control of contractors - importance of contract law 4 CDM 2015 - the principles and current best practice Scope - what is construction? Application - when do the Regulations apply? The CDM management systemDutyholders (client, designer, principal designer, principal contractor, contractor)Documents (pre construction information, Notification, construction phase Plan, H&S File)Management process The 2015 HSE guidance / industry best practice Clarification of roles and responsibilities 5 Competence under CDM 2015 What is 'Competence'? The criteria to be used in construction Achieving continuous improvement 6 Part 4 Construction Health Safety and Welfare Overview of Part 4 Responsibilities Welfare arrangements 7 Risk assessment and the role of the designer Principles of risk assessment Loss prevention / hazard management What is a suitable risk assessment?Design v construction risk assessmentThe client is a designer?Whose risk is it? 8 Risk assessment exercise Understanding the principles of design risk assessment Identifying hazards under the control of clients and designers Quantifying the risk 9 Questions, discussion and review

CDM 2015 - Understanding and achieving best practice (In-House)
By The In House Training Company
This course provides participants with a comprehensive understanding of the requirements of the CDM Regulations 2015 and how these should be implemented in practice. The Regulations are put in context with other key health and safety legislation. The programme sets out clearly the roles and responsibilities of the principal duty holders and explores with the participants how these roles may vary on different types of project and procurement routes. The programme examines the content and appropriate level of information that should be included in the Pre-Construction Information and the Construction Phase Plan. The trainer will discuss best practice in implementing CDM through the new 2015 Regulations and Guidance. This course is essential for anyone who is involved in the procurement, planning, design or implementation of construction work. The course will provide you with: An overview of construction health and safety law, liability and enforcement A detailed understanding of the 2015 CDM Regulations and the part they play with other key legislation An explanation of the roles and responsibilities of all duty holders and the requirements for the CDM documentation Clear advice on current best practice for complying with the principles of the CDM Regulations and the changes introduced by the 2015 Regulations An understanding of how risk assessment should be applied practically throughout the design and how this responsibility is then transferred to contractors 1 Introduction Why manage health and safety? The costs of accidents Construction industry statistics Why CDM? Health and safety culture in the construction industry 2 Overview of health and safety law and liabilities Criminal and civil law Liability Enforcement and prosecution Compliance - how far do we go? Statutory duties 3 Health and safety law in construction Framework of relevant legislation Health and Safety at Work etc Act 1974 Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999 Construction (Design and Management) Regulations 2015 Who is responsible for the risks created by construction work? Shared workplaces/shared responsibilities Control of contractors - importance of contract law 4 Construction (Design and Management) Regulations 2015 Scope - What is construction? Application - When do they apply? The CDM Management System Duty holders (Client, Domestic Client, Designer, Principal Designer, Principal Contractor, Contractor) Documents (HSE Notification, Pre-Construction Information, Construction Phase Health & Safety Plan, H&S File) Management process The 2015 Guidance 5 Best practice - key issues in the CDM process The client and client management arrangements Competence and resource under CDM 2015 The role of the Principal Designer in practice Design risk assessment and the role of the Designer The CDM Documents (PCI, PCI Pack, Plan and File) Construction health, safety and welfare Making CDM work in practice 6 Questions, discussion and review

CDM 2015 - Understanding and achieving best practice (In-House)
By The In House Training Company
This course provides participants with a comprehensive understanding of the requirements of the CDM Regulations 2015 and how these should be implemented in practice. The Regulations are put in context with other key health and safety legislation. The programme sets out clearly the roles and responsibilities of the principal duty holders and explores with the participants how these roles may vary on different types of project and procurement routes. The programme examines the content and appropriate level of information that should be included in the Pre-Construction Information and the Construction Phase Plan. The trainer will discuss best practice in implementing CDM through the new 2015 Regulations and Guidance. This course is essential for anyone who is involved in the procurement, planning, design or implementation of construction work. The course will provide you with: An overview of construction health and safety law, liability and enforcement A detailed understanding of the 2015 CDM Regulations and the part they play with other key legislation An explanation of the roles and responsibilities of all duty holders and the requirements for the CDM documentation Clear advice on current best practice for complying with the principles of the CDM Regulations and the changes introduced by the 2015 Regulations An understanding of how risk assessment should be applied practically throughout the design and how this responsibility is then transferred to contractors 1 Introduction Why manage health and safety? The costs of accidents Construction industry statistics Why CDM? Health and safety culture in the construction industry 2 Overview of health and safety law and liabilities Criminal and civil law Liability Enforcement and prosecution Compliance - how far do we go? Statutory duties 3 Health and safety law in construction Framework of relevant legislation Health and Safety at Work etc Act 1974 Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999 Construction (Design and Management) Regulations 2015 Who is responsible for the risks created by construction work? Shared workplaces/shared responsibilities Control of contractors - importance of contract law 4 Construction (Design and Management) Regulations 2015 Scope - What is construction? Application - When do they apply? The CDM Management System Duty holders (Client, Domestic Client, Designer, Principal Designer, Principal Contractor, Contractor) Documents (HSE Notification, Pre-Construction Information, Construction Phase Health & Safety Plan, H&S File) Management process The 2015 Guidance 5 Best practice - key issues in the CDM process The client and client management arrangements Competence and resource under CDM 2015 The role of the Principal Designer in practice Design risk assessment and the role of the Designer The CDM Documents (PCI, PCI Pack, Plan and File) Construction health, safety and welfare Making CDM work in practice 6 Questions, discussion and review

Discover the Exciting Field of Clinical Research
By John Huber
Learn more about entering the exciting field of Clinical Research, and how you can quickly start or grow your career! Tuesday, August 27 · 1 - 2am GMT+1 Join us to learn about Clinical Research--a growing field that offers a variety of career opportunities--and how you can acquire the skills to work in Clinical Research! Ask questions of experts working in the field. Discover the PCC Clinical Research program. In this 6 month, part-time class, you learn the foundational terms, concepts, and elements of designing and implementing clinical research, preparing you for a great job for an in-demand role. Most positions offer starting hourly rates ranging between $23-$36 per hour, and typically include benefits. Clinical research skills and knowledge are used in research sites such as medical centers and hospitals, pharmaceutical, device or biotechnology companies, or in contract research organizations. PCC's Foundations of Clinical Research curriculum was developed in partnership with local Oregon healthcare leaders including OHSU, Kaiser Permanente, Providence Health & Services, and Legacy Health. In the Foundations of Clinical Research non-credit certificate program at PCC's Institute for Health Professionals, you will learn will ethical, regulatory, historical and operational, recruitment, reporting, and other principles that support successful clinical trials. Seeking a new opportunity in a growing field? Already a CNA or Nurse and looking to transition to a role that doesn't have you running ragged all day? Check out PCC's IHP Clinical Research program!

Agile: an introduction (In-House)
By The In House Training Company
Agility has become a prized business attribute. Although Agile methods were once most associated with software development, they are now applied in a host of different areas. Agile continues to find new applications because it is primarily an attitude. This programme delivers a solid grounding in both the Agile mindset and Agile methods. It covers three methods, illustrates the benefits of each and shows how they can be integrated. It includes practical techniques as well as background knowledge. By the end of the session, participants will be able to: Apply Agile concepts to self-manage their work Understand the roles people take on in Agile teams Use a variety of techniques to help deliver customer satisfaction Focus on delivering against priorities Employ a range of estimating techniques 1 Introduction Overview of the programme Review of participants' needs and objectives 2 The basics of Agile What makes Agile different Agile Manifesto and Principles Using feedback to deliver what is needed 3 Agile teams Multi-disciplinary teams Team size and empowerment Agile values 4 Agile at the team level - Scrum Scrum roles Scrum 'events' Scrum 'artifacts' 5 Agile for teams juggling multiple demands - Kanban Taking control of the work Improving throughput Dealing with bottlenecks 6 Agile in projects - AgilePM The phases of an Agile project Managing change requests Delivering on time 7 Estimating T-shirt / Pebble sizing Yesterday's weather Planning poker 8 Pick 'n' mix - some useful techniques The daily stand-up User stories Retrospectives Work-in-process limits Burndown charts Minimum viable product A / B testing 9 Review and action planning Identify actions to be implemented individually Conclusion

Introduction to project management (In-House)
By The In House Training Company
This programme provides an intensive, one-day overview of the key concepts and techniques of project management. The project management methods presented can be applied to a wide range of projects and the course emphasises both the task and the team-related aspects of project management. The aims of the programme are to: Present the key concepts of project management Provide a structured approach for managing projects Demonstrate tools and techniques for planning and controlling project work Enable participants to apply the techniques to their own projects At the end of the programme, participants will: Recognise the benefits of a structured approach to project work Be able to apply a range of practical tools and techniques to improve their personal effectiveness in project work Have a means of determining the status of current projects and know what actions are needed to ensure success 1 Introduction Why this programme has been developed Review of participants' needs and objectives 2 Key concepts The characteristics of projects and project work The four key phases of a project Essential lessons from past projects Key success factors Achieving success through the 'Team-Action Model' Challenges of the multi-project situation 3 Setting project goals Understanding 'customer' requirements Managing project stakeholders and gaining commitment Using questioning skills to define goals and success criteria Defining and documenting the scope of the project 4 Project planning Defining what has to be done Creating a work breakdown Agreeing roles and responsibilities for the work Developing a programme using networks and bar charts Estimating timescales, costs and resource requirements Planning exercise: participants develop a project plan Identifying and managing project risks Using project planning software Managing and updating the plan 5 Project implementation and control Creating a pro-active monitoring and control process Techniques for monitoring progress Using latest estimates Managing project meetings Resolving problems effectively Managing multiple projects Personal time management 6 Course review and action planning Identify actions Sponsor-led review and discussion of proposals Conclusion

Negotiation skills (In-House)
By The In House Training Company
Any successful business manager will tell you that you never get the deal you deserve - you always get the deal you negotiate! This two-day workshop includes recent research and practical techniques from the Harvard Business School Negotiation Project and provides a unique opportunity to learn and practice these skills in a safe environment using up to date materials and life-like practice negotiation case studies. This course will help participants to: Understand the basics of negotiation Develop negotiating skills Increase their business acumen Develop their communication skills Learn the models, techniques and tools for an effective negotiation Identify the barriers to agreements Close the deal 1 What is negotiation? Key skills for negotiation Types of negotiation Win-lose negotiations versus Win-win negotiations Wise agreements and Principled Negotiation 2 Four key negotiating concepts BATNA - Best alternative to negotiated agreement Setting your reservation price ZOPA - Zone of possible agreement Creating and trading value 3 Business acumen Understanding pricing, gross margins and profit Knowing the key points on which to negotiate 4 A Four Phase Model for negotiation Nine steps to successful planning Discussing a deal - creating and claiming value Making and framing proposals Bargaining for the winning deal 5 Effective communication Effective questioning Active listening skills Understanding and interpreting body language Barriers to effective communication 6 Understanding influence and persuasion Influencing strategies Ten proven ways to influence people Six universal methods of persuasion Understanding why people do business with other people 7 Negotiating tactics Tactics for win-lose negotiations Tactics for win-win negotiations Effective team negotiating Understanding and using powerv What do you do when the other side has more power? 8 Barriers to agreement Common barriers to agreement The Negotiators Dilemma Dealing with die-hard negotiators Dealing with lack of trust 9 Potential barriers to cross-border agreements Understanding business methods and practice in other cultures Figuring out who has the power and who makes decisions Recognising and dealing with cultural differences What's OK here might not be OK there 10 Closing the deal Four steps to closing the winning deal
