- Professional Development
- Medicine & Nursing
- Arts & Crafts
- Health & Wellbeing
- Personal Development
34346 OV courses
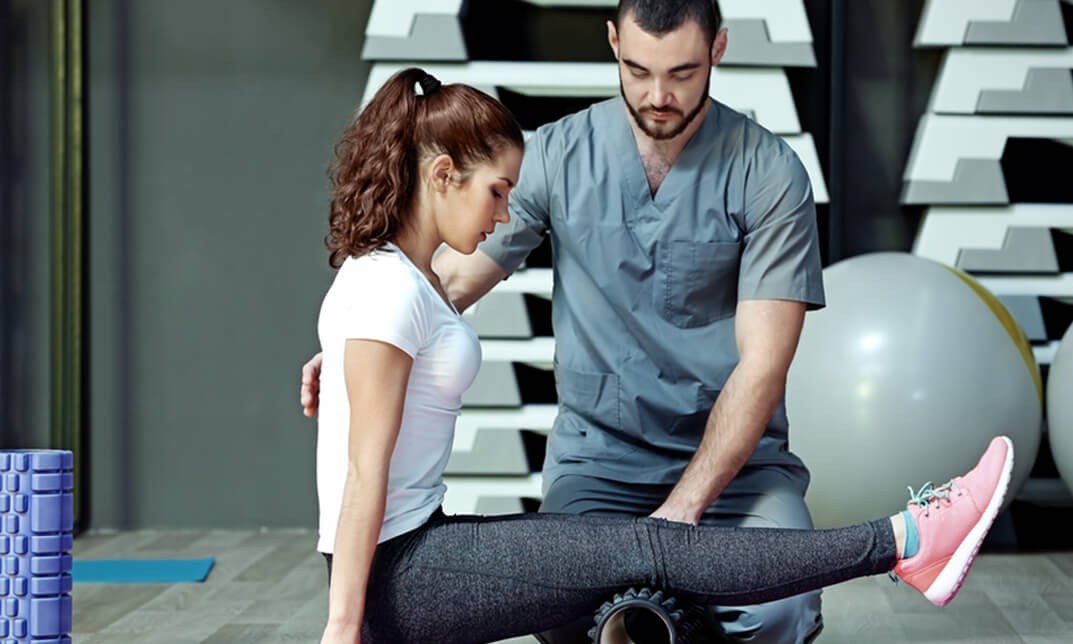
Follow your dreams by enrolling on the Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods course today and develop the experience, skills and knowledge you need to enhance your professional development. Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods will help you arm yourself with the qualities you need to work towards your dream job. Study the Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods training course online with Janets through our online learning platform and take the first steps towards a successful long-term career. The Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods course will allow you to enhance your CV, impress potential employers, and stand out from the crowd. This Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods course consists of a number of easy to digest, in-depth modules, designed to provide you with a detailed, expert level of knowledge. Study the Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods course through a mixture of instructional video lessons and online study materials. Receive online tutor support as you study the Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods course, to ensure you are supported every step of the way. Get a digital certificate as proof of your Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods course completion. Janets is one of the top online training course providers in the UK, and we want to make education accessible to everyone! Learn the essential skills you need to succeed and build a better future for yourself with the Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods course. The Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods course is designed by industry experts and is tailored to help you learn new skills with ease. The Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods is incredibly great value and allows you to study at your own pace. With full course access for one year, you can complete the Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods when it suits you. Access the Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods course modules from any internet-enabled device, including computers, tablets, and smartphones. The Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods course is designed to increase your employability and equip you with everything you need to be a success. Enrol on the Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods now and start learning instantly! Please note that this course does not entitle you to join the HCPC register or recognised as physiotherapist. Through this course you will come across all the basic guidelines of physiotherapy to boost and shine your knowledge in this particular field of Physiotherapy and it will add your CPD points. What You Get Out Of Studying Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods With Janets: Receive a digital Certificate upon successful completion of the Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods course Get taught by experienced, professional instructors Study at a time and pace that suits your learning style Get instant feedback on assessments 24/7 help and advice via email or live chat Get full tutor support on weekdays (Monday to Friday) Description The Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods training course is delivered through Janets' online learning platform. Access the Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods content from any internet-enabled device whenever or wherever you want to. The Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods course has no formal teaching deadlines, meaning you are free to complete the course at your own pace. Method of Assessment To successfully complete the Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods course, students will have to take an automated multiple-choice exam. This exam will be online and you will need to score 60% or above to pass the Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods course. After successfully passing the Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods course exam, you will be able to apply for a CPD-accredited certificate as proof of your Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods qualification. Certification All students who successfully complete the Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods course can instantly download their digital certificate. You can also purchase a hard copy of the Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods course certificate, which will be delivered by post for £9.99. Who Is This Course For: The Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods is ideal for those who already work in this sector or are an aspiring professional. This Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods course is designed to enhance your expertise and boost your CV. Learn key skills and gain a professional qualification to prove your newly-acquired knowledge. Requirements: The Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods is open to all students and has no formal entry requirements. To study the Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods course, all your need is a passion for learning, a good understanding of English, numeracy, and IT skills. You must also be over the age of 16. Career Path: The Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods is ideal for anyone who wants to pursue their dream career in a relevant industry. Learn the skills you need to boost your CV and go after the job you want. Complete the Physiotherapy Training and Treatment Methods and gain an industry-recognised qualification that will help you excel in finding your ideal job.

Follow your dreams by enrolling on the HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management course today and develop the experience, skills and knowledge you need to enhance your professional development. HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management will help you arm yourself with the qualities you need to work towards your dream job. Study the HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management training course online with Janets through our online learning platform and take the first steps towards a successful long-term career. The HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management course will allow you to enhance your CV, impress potential employers, and stand out from the crowd. This HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management course consists of a number of easy to digest, in-depth modules, designed to provide you with a detailed, expert level of knowledge. Study the HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management course through a mixture of instructional video lessons and online study materials. Receive online tutor support as you study the HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management course, to ensure you are supported every step of the way. Get a digital certificate as proof of your HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management course completion. Janets is one of the top online training course providers in the UK, and we want to make education accessible to everyone! Learn the essential skills you need to succeed and build a better future for yourself with the HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management course. The HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management course is designed by industry experts and is tailored to help you learn new skills with ease. The HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management is incredibly great value and allows you to study at your own pace. With full course access for one year, you can complete the HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management when it suits you. Access the HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management course modules from any internet-enabled device, including computers, tablets, and smartphones. The HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management course is designed to increase your employability and equip you with everything you need to be a success. Enrol on the HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management now and start learning instantly! What You Get Out Of Studying HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management With Janets: Receive a digital Certificate upon successful completion of the HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management course Get taught by experienced, professional instructors Study at a time and pace that suits your learning style Get instant feedback on assessments 24/7 help and advice via email or live chat Get full tutor support on weekdays (Monday to Friday) Description The HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management training course is delivered through Janets' online learning platform. Access the HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management content from any internet-enabled device whenever or wherever you want to. The HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management course has no formal teaching deadlines, meaning you are free to complete the course at your own pace. Method of Assessment To successfully complete the HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management course, students will have to take an automated multiple-choice exam. This exam will be online and you will need to score 60% or above to pass the HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management course. After successfully passing the HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management course exam, you will be able to apply for a CPD-accredited certificate as proof of your HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management qualification. Certification All students who successfully complete the HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management course can instantly download their digital certificate. You can also purchase a hard copy of the HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management course certificate, which will be delivered by post for £9.99. Who Is This Course For: The HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management is ideal for those who already work in this sector or are an aspiring professional. This HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management course is designed to enhance your expertise and boost your CV. Learn key skills and gain a professional qualification to prove your newly-acquired knowledge. Requirements: The HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management is open to all students and has no formal entry requirements. To study the HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management course, all your need is a passion for learning, a good understanding of English, numeracy, and IT skills. You must also be over the age of 16. Career Path: The HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management is ideal for anyone who wants to pursue their dream career in a relevant industry. Learn the skills you need to boost your CV and go after the job you want. Complete the HR, Bookkeeping and Payroll Management and gain an industry-recognised qualification that will help you excel in finding your ideal job.
Follow your dreams by enrolling on the Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding course today and develop the experience, skills and knowledge you need to enhance your professional development. Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding will help you arm yourself with the qualities you need to work towards your dream job. Study the Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding training course online with Janets through our online learning platform and take the first steps towards a successful long-term career. The Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding course will allow you to enhance your CV, impress potential employers, and stand out from the crowd. This Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding course consists of a number of easy to digest, in-depth modules, designed to provide you with a detailed, expert level of knowledge. Study the Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding course through a mixture of instructional video lessons and online study materials. Receive online tutor support as you study the Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding course, to ensure you are supported every step of the way. Get a digital certificate as proof of your Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding course completion. Janets is one of the top online training course providers in the UK, and we want to make education accessible to everyone! Learn the essential skills you need to succeed and build a better future for yourself with the Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding course. The Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding course is designed by industry experts and is tailored to help you learn new skills with ease. The Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding is incredibly great value and allows you to study at your own pace. With full course access for one year, you can complete the Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding when it suits you. Access the Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding course modules from any internet-enabled device, including computers, tablets, and smartphones. The Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding course is designed to increase your employability and equip you with everything you need to be a success. Enrol on the Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding now and start learning instantly! Please note that this course does not entitle you to join the HCPC register or recognised as psychologist. Through this course you will come across all the basic guidelines of psychology to boost and shine your knowledge in this particular field of Psychology and it will add your CPD points. What You Get Out Of Studying Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding With Janets: Receive a digital Certificate upon successful completion of the Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding course Get taught by experienced, professional instructors Study at a time and pace that suits your learning style Get instant feedback on assessments 24/7 help and advice via email or live chat Get full tutor support on weekdays (Monday to Friday) Description The Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding training course is delivered through Janets' online learning platform. Access the Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding content from any internet-enabled device whenever or wherever you want to. The Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding course has no formal teaching deadlines, meaning you are free to complete the course at your own pace. Method of Assessment To successfully complete the Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding course, students will have to take an automated multiple-choice exam. This exam will be online and you will need to score 60% or above to pass the Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding course. After successfully passing the Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding course exam, you will be able to apply for a CPD-accredited certificate as proof of your Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding qualification. Certification All students who successfully complete the Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding course can instantly download their digital certificate. You can also purchase a hard copy of the Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding course certificate, which will be delivered by post for £9.99. Who Is This Course For: The Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding is ideal for those who already work in this sector or are an aspiring professional. This Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding course is designed to enhance your expertise and boost your CV. Learn key skills and gain a professional qualification to prove your newly-acquired knowledge. Requirements: The Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding is open to all students and has no formal entry requirements. To study the Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding course, all your need is a passion for learning, a good understanding of English, numeracy, and IT skills. You must also be over the age of 16. Career Path: The Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding is ideal for anyone who wants to pursue their dream career in a relevant industry. Learn the skills you need to boost your CV and go after the job you want. Complete the Diploma in Psychology and NLP Understanding and gain an industry-recognised qualification that will help you excel in finding your ideal job.

Follow your dreams by enrolling on the Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development course today and develop the experience, skills and knowledge you need to enhance your professional development. Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development will help you arm yourself with the qualities you need to work towards your dream job. Study the Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development training course online with Janets through our online learning platform and take the first steps towards a successful long-term career. The Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development course will allow you to enhance your CV, impress potential employers, and stand out from the crowd. This Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development course consists of a number of easy to digest, in-depth modules, designed to provide you with a detailed, expert level of knowledge. Study the Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development course through a mixture of instructional video lessons and online study materials. Receive online tutor support as you study the Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development course, to ensure you are supported every step of the way. Get a digital certificate as proof of your Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development course completion. Janets is one of the top online training course providers in the UK, and we want to make education accessible to everyone! Learn the essential skills you need to succeed and build a better future for yourself with the Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development course. The Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development course is designed by industry experts and is tailored to help you learn new skills with ease. The Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development is incredibly great value and allows you to study at your own pace. With full course access for one year, you can complete the Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development when it suits you. Access the Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development course modules from any internet-enabled device, including computers, tablets, and smartphones. The Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development course is designed to increase your employability and equip you with everything you need to be a success. Enrol on the Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development now and start learning instantly! Please note that this course does not entitle you to join the HCPC register or recognised as psychologist. Through this course you will come across all the basic guidelines of psychology to boost and shine your knowledge in this particular field of Psychology and it will add your CPD points. What You Get Out Of Studying Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development With Janets: Receive a digital Certificate upon successful completion of the Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development course Get taught by experienced, professional instructors Study at a time and pace that suits your learning style Get instant feedback on assessments 24/7 help and advice via email or live chat Get full tutor support on weekdays (Monday to Friday) Description The Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development training course is delivered through Janets' online learning platform. Access the Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development content from any internet-enabled device whenever or wherever you want to. The Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development course has no formal teaching deadlines, meaning you are free to complete the course at your own pace. Method of Assessment To successfully complete the Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development course, students will have to take an automated multiple-choice exam. This exam will be online and you will need to score 60% or above to pass the Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development course. After successfully passing the Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development course exam, you will be able to apply for a CPD-accredited certificate as proof of your Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development qualification. Certification All students who successfully complete the Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development course can instantly download their digital certificate. You can also purchase a hard copy of the Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development course certificate, which will be delivered by post for £9.99. Who Is This Course For: The Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development is ideal for those who already work in this sector or are an aspiring professional. This Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development course is designed to enhance your expertise and boost your CV. Learn key skills and gain a professional qualification to prove your newly-acquired knowledge. Requirements: The Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development is open to all students and has no formal entry requirements. To study the Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development course, all your need is a passion for learning, a good understanding of English, numeracy, and IT skills. You must also be over the age of 16. Career Path: The Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development is ideal for anyone who wants to pursue their dream career in a relevant industry. Learn the skills you need to boost your CV and go after the job you want. Complete the Diploma in Psychology and Personal Development and gain an industry-recognised qualification that will help you excel in finding your ideal job.

Register on the CompTIA A+ (220-1001) today and build the experience, skills and knowledge you need to enhance your professional development and work towards your dream job. Study this course through online learning and take the first steps towards a long-term career. The course consists of a number of easy to digest, in-depth modules, designed to provide you with a detailed, expert level of knowledge. Learn through a mixture of instructional video lessons and online study materials. Receive online tutor support as you study the course, to ensure you are supported every step of the way. Get an e-certificate as proof of your course completion. The CompTIA A+ (220-1001) is incredibly great value and allows you to study at your own pace. Access the course modules from any internet-enabled device, including computers, tablet, and smartphones. The course is designed to increase your employability and equip you with everything you need to be a success. Enrol on the now and start learning instantly! What You Get With The CompTIA A+ (220-1001) Receive a e-certificate upon successful completion of the course Get taught by experienced, professional instructors Study at a time and pace that suits your learning style Get instant feedback on assessments 24/7 help and advice via email or live chat Get full tutor support on weekdays (Monday to Friday) Course Design The course is delivered through our online learning platform, accessible through any internet-connected device. There are no formal deadlines or teaching schedules, meaning you are free to study the course at your own pace. You are taught through a combination of Video lessons Online study materials Certification Upon successful completion of the course, you will be able to obtain your course completion e-certificate free of cost. Print copy by post is also available at an additional cost of £9.99 and PDF Certificate at £4.99. Who Is This Course For: The course is ideal for those who already work in this sector or are an aspiring professional. This course is designed to enhance your expertise and boost your CV. Learn key skills and gain a professional qualification to prove your newly-acquired knowledge. Requirements: The online training is open to all students and has no formal entry requirements. To study the CompTIA A+ (220-1001), all your need is a passion for learning, a good understanding of English, numeracy, and IT skills. You must also be over the age of 16.

Follow your dreams by enrolling on the Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK course today and develop the experience, skills and knowledge you need to enhance your professional development. Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK will help you arm yourself with the qualities you need to work towards your dream job. Study the Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK training course online with Janets through our online learning platform and take the first steps towards a successful long-term career. The Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK course will allow you to enhance your CV, impress potential employers, and stand out from the crowd. This Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK course consists of a number of easy to digest, in-depth modules, designed to provide you with a detailed, expert level of knowledge. Study the Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK course through a mixture of instructional video lessons and online study materials. Receive online tutor support as you study the Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK course, to ensure you are supported every step of the way. Get a digital certificate as proof of your Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK course completion. Janets is one of the top online training course providers in the UK, and we want to make education accessible to everyone! Learn the essential skills you need to succeed and build a better future for yourself with the Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK course. The Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK course is designed by industry experts and is tailored to help you learn new skills with ease. The Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK is incredibly great value and allows you to study at your own pace. With full course access for one year, you can complete the Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK when it suits you. Access the Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK course modules from any internet-enabled device, including computers, tablets, and smartphones. The Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK course is designed to increase your employability and equip you with everything you need to be a success. Enrol on the Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK now and start learning instantly! What You Get Out Of Studying Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK With Janets: Receive a digital Certificate upon successful completion of the Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK course Get taught by experienced, professional instructors Study at a time and pace that suits your learning style Get instant feedback on assessments 24/7 help and advice via email or live chat Get full tutor support on weekdays (Monday to Friday) Description The Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK training course is delivered through Janets' online learning platform. Access the Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK content from any internet-enabled device whenever or wherever you want to. The Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK course has no formal teaching deadlines, meaning you are free to complete the course at your own pace. Method of Assessment To successfully complete the Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK course, students will have to take an automated multiple-choice exam. This exam will be online and you will need to score 60% or above to pass the Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK course. After successfully passing the Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK course exam, you will be able to apply for a CPD-accredited certificate as proof of your Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK qualification. Certification All students who successfully complete the Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK course can instantly download their digital certificate. You can also purchase a hard copy of the Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK course certificate, which will be delivered by post for £9.99. Who Is This Course For: The Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK is ideal for those who already work in this sector or are an aspiring professional. This Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK course is designed to enhance your expertise and boost your CV. Learn key skills and gain a professional qualification to prove your newly-acquired knowledge. Requirements: The Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK is open to all students and has no formal entry requirements. To study the Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK course, all your need is a passion for learning, a good understanding of English, numeracy, and IT skills. You must also be over the age of 16. Career Path: The Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK is ideal for anyone who wants to pursue their dream career in a relevant industry. Learn the skills you need to boost your CV and go after the job you want. Complete the Real Estate and Key Legislations in the UK and gain an industry-recognised qualification that will help you excel in finding your ideal job.

Mastery: How to Make It Happen? Take Charge over Life Changes.
By believe-IN. Make It Happen!®
believe-IN Webinar Series: Plan the Way Out of Life Changes Webinar 4 – Mastery: How to Make It Happen? Take Charge over Life Changes.

Upcycled Denim Competition
By Refashion My Town
Welcome to Refashion My Town’s upcycled Denim Design competition! Refashion My Town is a social enterprise based in Chippenham. Our mission is to help and encourage young people to make a positive social and environmental impact through fashion. Our goal is to highlight the impact that fast fashion has on the environment and while doing so, we aim to help young people reduce, reuse, refashion and mend more. And what better way to start is by participating and joining our Upcycled Denim Design Competition! Why Denim? Denim has become an integral part of everyday life, but it wasn’t always like that. Denim was long known to be worn by working class individuals such as miners, railroad workers and even labourers, before booming into a fashion trend that had not ceased to stop. Now you see denim worn by nearly everyone across the globe due to its easy and comfortable wear. However, denim has done more than become a global fashion trend, it has also contributed to the slow destruction of the environment. Most demin products are made with an overwhelmingly large number of dyes that are highly toxic and damaging. Denim also relies on cotton that needs lots of water and pesticides to grow. Pesticides are harmful to human health and can become an environmental risk but that is just one part of the problem. The production of one pair of jeans could require up to 80 gallons of water which is around 360 litres. This is a lot! This is why here at Refashion my Town, we want young people to reduce, reuse, refashion and mend more to combat the issues the fashion industry has on society and environment. Our upcycled Denim design competition is open to 14-18 year olds on Friday 22nd April 2022 and submissions will close on Monday 5th September 2022. This competition requires you to EITHER: A. A 3-minute video explaining the concept, inspiration, and idea of your upcycled denim design. We would like to see a mock-up of your design within your presentation, as well as before and after of the material used. You can also include a completed final product or garment but this is optional. Or B. 1 x A3 sheet with design concept 1 x A3 sheet with design development 1 x A3 sheet with final design including before and after Mock-up of final design ( Final product - optional ). Please note: this is a design ( NOT sewing ) competition, so entries will mainly be judged based on creative flair and out of the box thinking, rather than technical sewing skills. So play and have fun developing your ideas. There will be FIVE judges of the competition: • Liz Alstrom - Mayor of Chippenham • Rachel Sheila Kan - Founder, Circular earth • Yvonne Skelton - Head of textiles, Bath College • Melissa Barnett - Curator, Chippenham Museum • Tricia Morris - Mending and Upcycling Expert, Morrissews. All entrants have access to materials and trimmings from Refashion My Town. Refashion My Town will also have FREE drop-in sessions every Friday at 3.30 - 5 pm, starting 29th April, to help entrants develop their ideas and if necessary, learn new skills to complete their entries.

How to speak in public with Karen Hale - Speak up and be heard
By The Motivation Clinic
An interactive workshop with Karen Hale. Learn how to gain the confidence, skills and techniques to speak up so you can be heard. "There are two types of speakers: Those who get nervous and those who are liars." - Mark Twain Is this you? Promotions not applied for, jobs roles not tried for, networking events not attended? Parties avoided, family ceremonies not spoken at, too much left unsaid? Do you have excellent ideas that get lost in time because you are fearful of voicing them. Have you missed opportunities because it involves showing up? Do you stay silent in meetings? Do you have a brilliant business idea that isn’t being pursued because you know it will involve some kind of networking or public speaking? If the answer to any/most of these is YES, then read on... This workshop is strange by its nature. Why would someone who disliked public speaking, go to a place where they would speak in public? This is why.... Because Karen has analysed what makes a good communicator when speaking informally to people; she has taken those aspects and developed a group of exercises that allows you to use these exact techniques when speaking at networking events and in public. Added to that, Karen provides a smorgasbord of methods on how to control nerves to ensure you communicate at your authentic best. Please note: everybody in the room will be there for the same reason as you! You will be supported and encouraged and will learn how to turn fear into empowerment! About Karen: An empowerment and public speaking coach with over 30 years experience in coaching and advising individuals and business leaders from a diverse range of sectors on effective communication skills. It takes a second to form a first impression about a person. Your body language, clothes, speech and personal presence convey messages about your background, skills and expertise. Karen works with her clients to ensure they make that first impression powerful and authentic so they get remembered for the right reasons. By creating a confident and authentic presence you increase your visibility and your credibility. “Karen is a truly special individual. She made me feel totally at ease and was able to help me stand and speak confidently for the first time and she did that all with huge warmth and a lot of humour.” She fulfils her greatest passion on a daily basis, helping people present themselves to the outside world in the very best way. She has enabled hundreds of people to move on in their life and careers and build their growth, confidence and image. Karen works across a huge spectrum - from CEOs in FTSE 100 companies to Foundation Class university students at UAL coaching presentation skills. She coaches senior individuals and consults to leading global banks, private banks and family offices, advising business leaders and their teams. She is Central School of Speech and Drama trained. Kind words about Karen... I have had the absolute pleasure of working with Karen numerous times over the past 16 years to assist me in my various corporate roles. Karen has always been the person I have turned to first and foremost when I have needed help with my personal brand, presence and communication, helping me develop confidence in public speaking and showing up in front of the camera. A HUGE thank you for Monday – you were wonderful. The feedback we have had has been unbelievable – I can honestly say in all my years in this industry I have never heard such positive comments on every aspect. Karen has an incredible gift of making you feel completely at ease and is able to bring the best out of a person with ease. She is friendly, approachable and warm and I now refer Karen to everybody I know who needs assistance with any type of public speaking, communication and confidence requirement. The results speak for themselves. Highly recommend! You can contact Karen at: https://www.linkedin.com/in/karen-hale-8925862b/ / 07956626740 For any questions regarding this event, please contact the organiser lara@themotivationclinic.co.uk / 07817247727 - thank you!

Small Biz Owners November Get-Together
By The Motivation Clinic
The Motivation Clinic - November Gathering Lunch and learn / networking at The Brew House, 155 Guildford High Street, Guildford House Gallery, Guildford, GU1 3AJ (Opposite Sainsbury/Bora) It can be a lonely world beavering away building your business alone and navigating the veritable rollercoaster! Love to see you for warm chats and networking to assure you that you are not alone and provide you with the support, encouragement and the motivation to keep going, even when times are tough. Meet and learn Yvette Masure, Medical Acupuncturist and Vibrational Therapist will be taking us through a quick overview of the wonderful world and powers of mushrooms (not the magic kind!) including adaptogenic coffee (and mushroom) blends. You also get a chance to view a lovely potential venue/workshop/talks space (The Brew House) you may want to use?! Feedback from October's Gathering "Informal atmosphere, great group of people, lovely environment" "a friendly, welcoming relaxed atmosphere real sense of community." "uplifted and felt encouraged to get involved more." "lovely session and some great conversations" "a lovely opportunity to meet fellow business owners." Can't wait to see you. Lara Doherty The Motivation Clinic 07817247727 / lara@themotivationclinic.co.uk

Search By Location
- OV Courses in London
- OV Courses in Birmingham
- OV Courses in Glasgow
- OV Courses in Liverpool
- OV Courses in Bristol
- OV Courses in Manchester
- OV Courses in Sheffield
- OV Courses in Leeds
- OV Courses in Edinburgh
- OV Courses in Leicester
- OV Courses in Coventry
- OV Courses in Bradford
- OV Courses in Cardiff
- OV Courses in Belfast
- OV Courses in Nottingham