- Professional Development
- Medicine & Nursing
- Arts & Crafts
- Health & Wellbeing
- Personal Development
980 Electronic courses
Electrical Engineering & Electronics for Electrician
By Compliance Central
***Beyond the Wires: Mastering the Science Behind Electrical Systems*** The world is becoming increasingly reliant on electricity, and electrical engineering principles are at the heart of it all. From the power grids that light our cities to the intricate circuits within our smartphones, a strong understanding of electrical engineering is crucial for a successful career as an electrician. This comprehensive Electrical Engineering & Electronics for Electrician course bundle offers a theoretical foundation in electrical engineering, equipping you with the knowledge and expertise to excel in various electrical applications. This Electrical Engineering & Electronics for Electrician Bundle Includes: Course 01: Basic Electricity Course Course 02: Electricity & Circuit Analysis Level 3 Course 03: Pat Testing: Electrical & Electronics Equipment Testing Training Course 04: PUWER Course 05: Electrical Safety Course 06: Fire Safety & Prevention Learning Outcomes By the end of this Electrical Engineering & Electronics for Electrician course, you'll be able to: Master electrical fundamentals (voltage, current, resistance, power) in electrical engineering. Analyze electrical circuits using electrical engineering techniques for troubleshooting and optimization. Understand and implement electrical engineering safety regulations. Master Portable Appliance Testing (PAT) for equipment safety. Apply PUWER regulations in electrical engineering installations. Grasp fire safety principles to minimize electrical fire risks. Key Highlight of Electrical Engineering & Electronics for Electrician bundle CPD QS Accredited Proficiency with this Electrical Engineering bundle After successfully completing the Electrical Engineering bundle, you will receive a FREE PDF Certificate from REED as evidence of your newly acquired abilities. Lifetime access to the whole collection of learning materials of this Electrical Engineering bundle The online test with immediate results You can study and complete the Electrical Engineering bundle at your own pace. Study for the electrical Engineering bundle using any internet-connected device, such as a computer, tablet, or mobile device. This Electrical Engineering & Electronics for Electrician course bundle is meticulously designed to provide electricians with a solid theoretical grounding in electrical principles and safety practices. Course 01: Basic Electricity Course lays the groundwork by introducing you to the fundamental concepts of electricity. You'll explore topics like voltage, current, resistance, power, and electrical components. Course 02: Electricity & Circuit Analysis Level 3 delves deeper into electrical circuits, equipping you with the ability to analyze them using various techniques. This will empower you to troubleshoot electrical problems and optimize circuit performance. Course 03: Pat Testing: Electrical & Electronics Equipment Testing Training focuses on Portable Appliance Testing (PAT). You'll gain the knowledge and skills necessary to conduct PAT inspections, ensuring the safety of electrical equipment. Course 04: PUWER explores the Provision and Use of Work Equipment Regulations (PUWER) and their application in electrical installations. This module equips you to comply with these essential safety regulations. Course 05: Electrical Safety emphasizes the importance of electrical safety in the workplace. You'll learn about electrical hazards, safety protocols, and best practices to minimize the risk of accidents. Course 06: Fire Safety & Prevention provides valuable insights into fire safety principles specifically related to electrical systems. This knowledge helps you identify and mitigate potential fire risks associated with electrical installations. CPD 60 CPD hours / points Accredited by CPD Quality Standards Who is this course for? This Electrical Engineering & Electronics for Electrician course bundle is essential for: Aspiring & qualified electricians seeking an electrical engineering foundation. Those interested in electrical engineering careers (maintenance, installations). DIYers & homeowners wanting to understand electrical engineering for projects or maintenance. Facilities personnel responsible for electrical equipment safety. Individuals seeking career advancement in the electrical engineering field. Requirements There are no prior qualifications required for this Electrical Engineering & Electronics for Electrician course. However, a basic understanding of mathematics will be beneficial for this Electrical Engineering course. Career path Electrical Engineering & Electronics for Electrician offers a diverse and rewarding career paths you can explore after completing this Electrical Engineering course: Electrician Maintenance electrician Industrial electrician Building services electrician Domestic electrician Smart home electrician Design Engineer This course bundle emphasizes Electrical Engineering in a theoretical context. Certificates Certificate of completion Digital certificate - Included Get 6 CPD accredited PDF certificate for Free. Each CPD Accredited Hardcopy Certificate Hard copy certificate - £10.79 Delivery Charge: Inside the UK: Free Outside the UK: £10.79

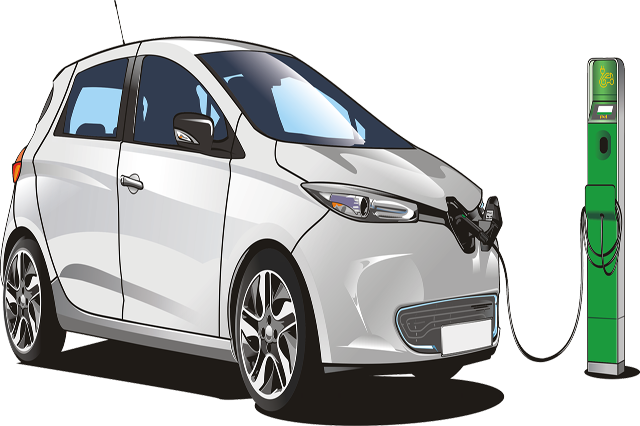
Description Fundamentals of Electric Vehicles Introducing the Fundamentals of Electric Vehicles Diploma, a comprehensive online course designed to equip learners with essential knowledge and skills in the rapidly growing field of electric vehicles (EVs). This course provides a thorough understanding of the critical components, systems, and technologies that make electric vehicles an increasingly attractive and sustainable transportation option. The Fundamentals of Electric Vehicles Diploma is tailored for individuals seeking a solid foundation in the various aspects of electric vehicle technology. Whether an automotive enthusiast, an engineering professional, or someone interested in pursuing a career in the EV industry, this course offers valuable insights and practical knowledge to help stay ahead in this dynamic and evolving sector. Starting with an Introduction to Electric Vehicles, learners will gain an overview of the history, types, and benefits of electric vehicles, as well as the key components and subsystems that enable their operation. The course will also delve into the Battery Technology for Electric Vehicles, providing an in-depth understanding of the different types of batteries, their chemistry, and the factors influencing their performance and lifespan. Electric Motors for Electric Vehicles is another essential topic covered in the Fundamentals of Electric Vehicles Diploma. Participants will explore various electric motor types, their working principles, and their applications in EVs. The course also covers Power Electronics for Electric Vehicles, addressing the critical role of power electronics in controlling and converting electrical energy in electric vehicle systems. A robust Charging Infrastructure for EVs is fundamental to their widespread adoption. This course thoroughly examines different charging technologies, their compatibility with various electric vehicles, and the challenges and opportunities in developing a comprehensive EV charging network. Furthermore, the course delves into Energy Management in Electric Vehicles, discussing strategies to optimise energy consumption and extend the driving range of EVs. The Fundamentals of Electric Vehicles Diploma also covers Thermal Management in Electric Vehicles, a crucial aspect of ensuring battery and motor performance, reliability, and longevity. Participants will learn about various thermal management techniques and their applications in electric vehicles. Vehicle Dynamics and Control in Electric Vehicles is another key topic, focusing on the unique challenges and opportunities in ensuring stability, handling, and ride comfort in electric vehicles. Design and Integration of Electric Drivetrains is an important aspect of developing efficient and high-performance electric vehicles. The course provides insights into the design and integration of drivetrain components, as well as their influence on overall vehicle performance. Finally, the Fundamentals of Electric Vehicles Diploma addresses Future Trends and Developments in Electric Vehicles, offering a forward-looking perspective on emerging technologies, market trends, and potential advancements in the EV industry. By completing the Fundamentals of Electric Vehicles Diploma, learners will have acquired a well-rounded understanding of electric vehicle technology, enabling them to contribute effectively to the EV industry or pursue further studies in this fascinating domain. Enrol today to start your journey towards becoming an expert in electric vehicle technology and help shape the future of sustainable transportation. What you will learn 1:Introduction to Electric Vehicles 2:Battery Technology for Electric Vehicles 3: Electric Motors for Electric Vehicles 4:Power Electronics for Electric Vehicles 5:Charging Infrastructure for EV 6:Energy Management in Electric Vehicles 7:Thermal Management in Electric Vehicles 8:Vehicle Dynamics and Control in Electric Vehicles 9:Design and Integration of Electric Drivetrains 10:Future Trends and Developments in Electric Vehicles Course Outcomes After completing the course, you will receive a diploma certificate and an academic transcript from Elearn college. Assessment Each unit concludes with a multiple-choice examination. This exercise will help you recall the major aspects covered in the unit and help you ensure that you have not missed anything important in the unit. The results are readily available, which will help you see your mistakes and look at the topic once again. If the result is satisfactory, it is a green light for you to proceed to the next chapter. Accreditation Elearn College is a registered Ed-tech company under the UK Register of Learning( Ref No:10062668). After completing a course, you will be able to download the certificate and the transcript of the course from the website. For the learners who require a hard copy of the certificate and transcript, we will post it for them for an additional charge.

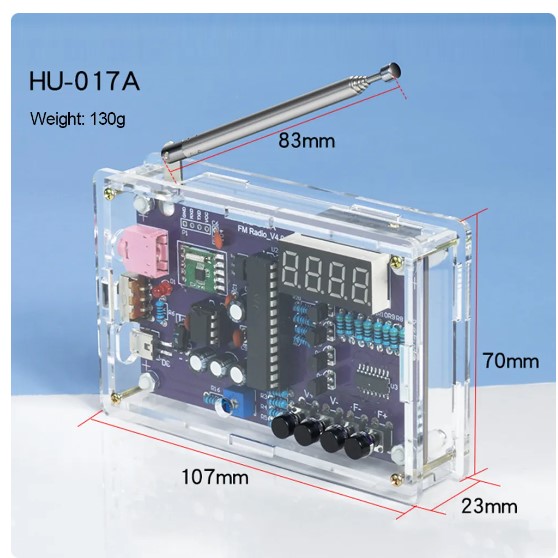
Solder an FM Radio!
By CNC Woodworking and Electronics Workshops - SteveMpotter.tech
Learn to Solder an FM Radio!

A Beginner's Guide to a Microservices Architecture
By Packt
Learn the Microservices overall Architecture, Building Blocks, Key Advantages, Challenges and Industry Case Studies

24 Hours Left! Don't Let Year-End Deals Slip Away - Enrol Now! Harness the power of engineering and management to grow your professional career with our CPD-accredited Engineering Management bundle. This exclusive package combines 20 expertly designed courses to provide a complete exploration of various engineering disciplines. We will ensure you have the knowledge and skills to succeed in today's fast-paced industry. From the fundamentals of Energy and Electrical Engineering to the complexities of Automotive Engineering, Hybrid Vehicle Expert Training, and Power Electronics, this bundle covers it all. Dive into Sustainable Energy, HVAC Technician Training, and Quality Management, all while earning a recognised CPD certification that significantly boosts your professional profile. Plus, with courses like Project Management, Operations Management, Emergency First Aid and Incident Management at Work, you'll develop a deep understanding of engineering management that will set you apart in the workforce. You will be the one with complete knowledge of every sector. And the best part? After completing each course, you'll receive a free CPD PDF certificate, solidifying your achievements and commitment to continuous learning. In total, for 20 courses you will get 20 free CPD Certificates. Don't miss this golden opportunity to invest in yourself and unlock new possibilities in your career. Enrol in the Engineering Management bundle today and take the first step towards a brighter and more successful future. *** Course Curriculum *** Here is the curriculum breakdown of the Engineering Management - CPD Accredited Bundle: Course 01: Energy Engineer Course Course 02: Solar Energy Course 03: Essential Hydro Electric Power Plant Training Course 04: Electrical Engineering DC Circuit Analysis Course 05: Electrical Power System and High Voltage Engineering Course 06: Basic Automotive Engineering: Onboard Diagnostics Course 07: Hybrid Vehicle Expert Training Course 08: Supercharger Automobile Engineering Course 06: Power Electronics for Electrical Engineering Course 10: Power Engineering: Power System Analysis Course 11: Energy Saving in Electric Motors Course 12: Heating, Ventilation & Air Conditioning (HVAC) Technician Course 13: Sustainable Energy and Development Diploma Course 14: Level 5 CAD Designer Training Course 15: Project Management Course Course 16: Operations Management Course 17: Diploma in Lean Process and Six Sigma Course 18: Quality Management Course 19: Large Goods Vehicle (LGV) Course 20: Emergency First Aid and Incident Management at Work Learning Outcomes Upon completion of the courses in this Engineering Management bundle, you will be able to: Acquire a comprehensive understanding of energy engineering, including solar and hydroelectric power. Master the fundamentals and advanced concepts of electrical engineering and automotive engineering. Gain expert knowledge in hybrid vehicle technology and supercharger automobile engineering. Develop proficiency in power electronics, power system analysis, and energy saving in electric motors. Cultivate essential skills in project management, operations management, and lean process and Six Sigma. Enhance your expertise in quality management and large goods vehicle operations. Learn critical emergency first aid techniques and incident management strategies for the workplace. Earn 20 CPD-certified accreditations to boost your professional profile. Unleash your potential and boost your career with our Engineering Management - CPD Accredited bundle. This complete package offers knowledge of many engineering and management disciplines, providing you with the essential knowledge and skills needed to succeed in today's dynamic industry. With 20 CPD-certified courses, from energy engineering to project management, you'll be well-equipped to tackle any challenge that comes your way. Plus, with free PDF certificates included for each course, your achievements will be recognised and valued by employers worldwide. Enrol now and take the first step towards success! Why Choose Our Engineering Management Courses: Get instant access to the Engineering Management courses. Learn Engineering Management from anywhere in the world This Engineering Management bundle is affordable and simple to understand The Engineering Management bundle is entirely online and has interactive lessons with voiceover audio Lifetime access to the Engineering Management course materials The Engineering Management bundle comes with 24/7 tutor support After enrolling in the Engineering Management bundle, you can get free career guidance and expert consultation. Get 20 valuable CPD certifications after completing Engineering Management courses. CPD 200 CPD hours / points Accredited by CPD Quality Standards Who is this course for? This bundle is ideal for: Students seeking mastery in this field Professionals seeking to enhance their skills Anyone who is passionate about this topic Career path Engineering Manager: £40,000 - £70,000 per year Energy Engineer: £25,000 - £70,000 per year Electrical Engineer: £28,000 - £60,000 per year Project Manager: £30,000 - £80,000 per year Operations Manager: £35,000 - £100,000 per year Quality Manager: £30,000 - £75,000 per year Automotive Engineer: £30,000 - £70,000 per year HVAC Technician: £25,000 - £50,000 per year Certificates CPD Accredited Hard Copy Certificate Hard copy certificate - Included If you are an international student, then you have to pay an additional 10 GBP for each certificate as an international delivery charge. CPD Accredited Digital Certificate Digital certificate - Included

Digital Electronics and Circuit Design
By Course Cloud
The comprehensive Digital Electronics and Circuit Design has been designed by industry experts to provide learners with everything they need to enhance their skills and knowledge in their chosen area of study. Enrol on the Digital Electronics and Circuit Design today, and learn from the very best the industry has to offer! This best selling Digital Electronics and Circuit Design has been developed by industry professionals and has already been completed by hundreds of satisfied students. This in-depth Digital Electronics and Circuit Design is suitable for anyone who wants to build their professional skill set and improve their expert knowledge. The Digital Electronics and Circuit Design is CPD-accredited, so you can be confident you're completing a quality training course will boost your CV and enhance your career potential. The Digital Electronics and Circuit Design is made up of several information-packed modules which break down each topic into bite-sized chunks to ensure you understand and retain everything you learn. After successfully completing the Digital Electronics and Circuit Design, you will be awarded a certificate of completion as proof of your new skills. If you are looking to pursue a new career and want to build your professional skills to excel in your chosen field, the certificate of completion from the Digital Electronics and Circuit Design will help you stand out from the crowd. You can also validate your certification on our website. We know that you are busy and that time is precious, so we have designed the Digital Electronics and Circuit Design to be completed at your own pace, whether that's part-time or full-time. Get full course access upon registration and access the course materials from anywhere in the world, at any time, from any internet-enabled device. Our experienced tutors are here to support you through the entire learning process and answer any queries you may have via email.

Search By Location
- Electronic Courses in London
- Electronic Courses in Birmingham
- Electronic Courses in Glasgow
- Electronic Courses in Liverpool
- Electronic Courses in Bristol
- Electronic Courses in Manchester
- Electronic Courses in Sheffield
- Electronic Courses in Leeds
- Electronic Courses in Edinburgh
- Electronic Courses in Leicester
- Electronic Courses in Coventry
- Electronic Courses in Bradford
- Electronic Courses in Cardiff
- Electronic Courses in Belfast
- Electronic Courses in Nottingham