- Professional Development
- Medicine & Nursing
- Arts & Crafts
- Health & Wellbeing
- Personal Development
1188 Courses in Cardiff delivered Live Online
M.D.D V.I.P RELATIONSHIP CRISIS DELIVERY (V.I.P)
4.9(27)By Miss Date Doctor Dating Coach London, Couples Therapy
Has something just happened? Did you just break up? Did you have an argument? Found out you were being cheating on or feeling extremely low whatever the problem your M.D.D date coach will come to your home with a gourmet meal, magazines and fresh fruit and will stay with you for 90 mins to discuss the issue and give you a relationship coaching session.(Available between 9- 7 pm appointment based.) £300 https://relationshipsmdd.com/product/m-d-d-v-i-p-relationship-crisis-delivery/

MHFA® Youth Mental Health Awareness Training
By Brightcore Consultancy
This introductory three hour session raises awareness of young people’s mental health. It covers: Some of the common mental health issues affecting young people, including depression, anxiety, eating disorders and psychosis Skills to work more effectively with young people living with mental health issues Ways to support young people with a mental health issue and relate to their experiences

Management of Risk (M_o_R) Foundation: In-House Training
By IIL Europe Ltd
Management of Risk (M_o_R®) Foundation: In-House Training This M_o_R® Foundation course prepares learners to demonstrate knowledge and comprehension of the four elements of the M_o_R framework: Principles, Approach, Processes, Embedding and Reviewing and how these elements support corporate governance. The M_o_R Foundation Course is also a prerequisite for the M_o_R Practitioner qualification. What you will Learn At the end of the M_o_R Foundation course, participants will gain competencies in and be able to: Describe the key characteristics of risk and the benefits of risk management List the eight M_o_R Principles List and describe the use of the key M_o_R Approach documents Create Probability and Impact scales Define and distinguish between risks and issues Create a Risk Register Create a Stakeholder map Identify the key roles in risk management Use the key techniques and describe specialisms in risk management Undertake the M_o_R Foundation examination Introduction Introduction to the M_o_R course What is a risk? What is risk management? Why is risk management so important? Basic risk definitions The development of knowledge about risk management Corporate governance and internal control Where and when should risk management be applied? M_o_R Principles The purpose of M_o_R principles Aligns with objectives Fits the context Engages stakeholders Provides clear guidance Informs decision-making Facilitates continual improvement Creates a supportive culture Achieves measurable value Risk management maturity models M_o_R Approach Relationship between the documents Risk management policy Risk management process guide Risk management strategy Risk register Issue register Risk response plan Risk improvement plan Risk communications plan M_o_R Process Common process barriers Identify contexts Identify the risks Assess estimate Assess evaluate Plan Implement Communication throughout the process M_o_R Perspectives Strategic perspective Program perspective Project perspective Operational perspective Risk Specialisms Business continuity management Incident and crisis management Health and Safety management Financial risk management Environmental risk management Reputational risk management Contract risk management

Management of Risk (M_o_R) Foundation: Virtual In-House Training
By IIL Europe Ltd
Management of Risk (M_o_R®) Foundation: Virtual In-House Training This M_o_R® Foundation course prepares learners to demonstrate knowledge and comprehension of the four elements of the M_o_R framework: Principles, Approach, Processes, Embedding and Reviewing and how these elements support corporate governance. The M_o_R Foundation Course is also a prerequisite for the M_o_R Practitioner qualification. What you will Learn At the end of the M_o_R Foundation course, participants will gain competencies in and be able to: Describe the key characteristics of risk and the benefits of risk management List the eight M_o_R Principles List and describe the use of the key M_o_R Approach documents Create Probability and Impact scales Define and distinguish between risks and issues Create a Risk Register Create a Stakeholder map Identify the key roles in risk management Use the key techniques and describe specialisms in risk management Undertake the M_o_R Foundation examination Introduction Introduction to the M_o_R course What is a risk? What is risk management? Why is risk management so important? Basic risk definitions The development of knowledge about risk management Corporate governance and internal control Where and when should risk management be applied? M_o_R Principles The purpose of M_o_R principles Aligns with objectives Fits the context Engages stakeholders Provides clear guidance Informs decision-making Facilitates continual improvement Creates a supportive culture Achieves measurable value Risk management maturity models M_o_R Approach Relationship between the documents Risk management policy Risk management process guide Risk management strategy Risk register Issue register Risk response plan Risk improvement plan Risk communications plan M_o_R Process Common process barriers Identify contexts Identify the risks Assess estimate Assess evaluate Plan Implement Communication throughout the process M_o_R Perspectives Strategic perspective Program perspective Project perspective Operational perspective Risk Specialisms Business continuity management Incident and crisis management Health and Safety management Financial risk management Environmental risk management Reputational risk management Contract risk management

Become a Mental Health First Aid Champion Mental Health First Aid (MHFA) is an internationally recognised training course, which teaches people how to spot the signs and symptoms of mental ill health and to provide help on a first aid basis. This course is designed for people who want to promote and positively affect attitudes on mental health in the workplace.

Leading People through Change: In-House Training
By IIL Europe Ltd
Leading People through Change: In-House Training Research shows that 70% of change initiatives fail in large organizations. The largest factor contributing to this failure rate is leadership - the inability to plan and lead people through change. In many change situations, tremendous focus is put on strategy, processes, and systems, while the issue of changing people's behavior is assumed it will 'just happen'. In this interactive course, you will learn why the people side of change is crucial. We will begin by understanding why and how people resist change, and how important it is to become strong and effective change champions. Next, we will focus on critical change management practices - creating our vision of the future state, planning for acceptance in our change audience and stakeholders, mitigating threats, and capitalizing on opportunities. We will use metrics to plan, show progress, and confirm success. Lastly, we will focus on the need to reinforce and sustain change, and to prevent relapse to old ways and methods. What you will Learn At the end of this program, you will be able to: Realize the nature of change and describe how resistance manifests in people Compare prevalent change models and categorize their similarities Identify and rate the skills, traits, and behaviors of effective change champions Envision the future state and assess stakeholders Plan for change communication, training, and risks Evaluate change effectiveness using feedback and metrics Develop reinforcement practices for benefits and communication Foundation Concepts What is Change? Resistance to Change Common Change Management Theories Becoming a Change Champion Plan Envisioning the future state Planning for people Change management plan Do Change communication Training Piloting Risks Study Feedback Metrics Variance analysis Act Benefits realization Change sustainment Reinforcement messaging and communications

M.D.D WHATS APP EMERGENCY DAY PASS (SINGLES)
4.9(27)By Miss Date Doctor Dating Coach London, Couples Therapy
Do you have a relationship issue you want to discuss or are you upset about some dating issues you are having, feeling stressed? Get a one day pass and talk to us. Dating advice for singles

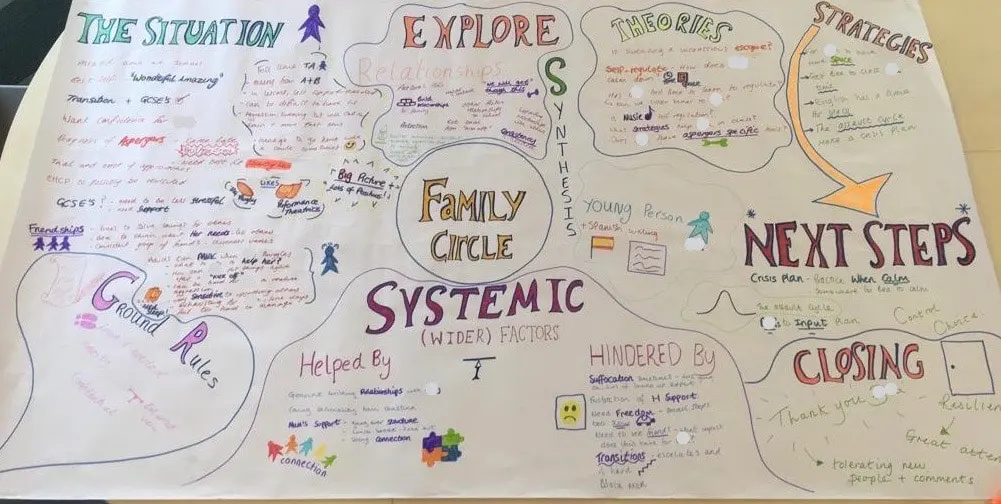
FAMILY CIRCLES
By Inclusive Solutions
Click to read more about this training, in which we demonstrate a live problem solving approach which is based on the active participation of family members. Course Category Inclusion Parents and Carers Behaviour and relationships Problem Solving Description In this training we demonstrate a live problem solving approach which is based on the active participation of family members. ‘Family Circles’ is an evolving new approach to problem solving with families and is based on our years of family work and the development and use of the Circle of Adults process. Inspired by our own Parent Solutions work and the Circle of Adults process as well as Family Group Conferencing and other Restorative Interventions we bring you Family Circles. Essentially the approach involves gathering a family together for a process that is facilitated but majors on the family members offering each other their wisdom and ideas. The approach is capacity focused, person centred approach to working with families rather than the dominant deficit oriented and ‘medical model’ of viewing and planning for or doing things to families. This training can be modelled with a group of professionals or better still with a family. In our work with families we develop the importance of naming stories or theories and seeking linkages and synthesis between what is found out and explored about the family situation and its history. We like participants to sit with the uncertainty, to reflect on the question ‘why’ but without judgement of each other. Deeper reflections may span a whole range of perspectives from ‘within person’ considerations, to situational or systemic possibilities. Health or emotional issues can be reflected on alongside organisational or transactional aspects of what is going on for the family. The better the shared understanding the better the strategy or actions which emerge from these meetings. Quality hypotheses with a close fit to reality lead to more effective implementation in the real world. We encourage ‘loose’ thinking, a search for connections, deeper listening, an ‘open mind’, speculation and exploration without moral judgements. From this stance self-reflection as well as reflection on the situation can produce remarkable insights. The quality of theories or new stories generated is directly influenced by family members’ experiences and the models of learning, behaviour and emotion, systems, educational development, change and so on that they have been exposed to. Learning Objectives To provide opportunities for: Shared problem solving in a safe exploratory climate in which the family will find its own solutions. Individuals to reflect on their own actions and strategies An exploration of whole-family processes and their impact Emotional support and shared understandings of issues at a child, parent, family, school and community level. Feed back to each other on issues, ideas and strategies that are agreed to be worth sharing with them. Who Is It For? Anyone interested in working with families in a way that builds and makes use of their capacities rather than focus on their challenges and difficulties. Social Care teams School staff Community organisers Educational Psychologists Course Content True family empowerment Deepening shared stories and understandings Facilitating groups Problem solving process Handling family group communication Allowing direct feedback and challenge between participants in a safe way Building relationships Process: Family members are welcomed: Introductions are carried out, ground rules and aims clarified whilst coffee is drunk. A recap from the last session is carried out: To follow up developments and reflections after the last meeting. One issue is selected for the main focus Issue presentation: The family member who raised the concern is asked questions to tell the ‘story’ of the issue or problem. Additional questions/information from the group about the problem are gathered: Ground rules may need to be observed carefully here. Individual participants need to be kept focused and prevented from leaping to premature conclusions or to making ‘helpful’ suggestions about strategy. Relationship aspects to the problem are explored. Metaphors and analogies are invited. How would a fly on the wall see your relationship? If you were alone together on a desert island, what would it be like? Impact of previous relationships/spillage from one relationship to another are explored. Eg what situation they are reminded of? For instance, does this situation remind you of any of those angry but helpless feelings you had with your other son when he was an adolescent? This provides opportunities to reflect on how emotions rub off on other people. The parent feels really frustrated, and on reflection we can see that so does the child System/Organisation factors (Family system/school and community systems and so on): What aspects help or hinder the problem? For instance, does the pastoral system of the local school provide space, or time and skilled personnel able to counsel this young person and work actively with their parents? Synthesis. At this stage the Graphic facilitator summarises what they have heard. They then go on to describe linkages and patterns in what they have heard. This can be very powerful. The person doing the graphic work has been able to listen throughout the presentation process and will have been struck by strong messages, emotions and images as they have arisen. The story and meaning of what is happening in the situation may become a little clearer at this point. Typical links may be ‘mirrored emotions’ strong themes such as loss and separation issues, or repeated processes such as actions triggering rejection. This step provides an excellent grounding for the next process of deepening understanding. What alternative strategies/interventions are open to be used? Brainstormed and recorded. ’Either/ors’ need to be avoided at this time also. This needs to be a shared session in which the family member who is presenting the concern contributes as much as anyone. Care is needed to ensure that this person is not overloaded with other people’s strategies. The final selection of strategy or strategies from the brainstormed list is the problem presenter’s choice. Strategies might include: a special time for the young person, a meeting with the child’s parents to explore how she is being managed at home and to share tactics, a home-school diary, counselling, or an agreed action plan that all are aware of, agreed sanctions and rewards and so forth. Strategies may productively involve processes of restitution and restoration, when ‘sorry’ is not enough. Making it right, rather than punishments or rewards, may then becomes the focus. First Steps. The problem presenter is finally asked to agree one or two first steps which they can carry out over the next 3-7 days. It can help to assign a ‘coach’ who will check in with them to ensure they have carried out the action they have named. This is a time to be very specific. Steps should be small and achievable. The person is just ‘making a start’. A phone call, or making an agreement with a key other person not present at the meeting would be ideal examples. Final reflections. Sometimes referred to as a ‘round of words’ help with closure for all involved. Reflections are on the process not the problem. In large families this is best done standing in a circle. In smaller groups all can remain sitting. Passing around a ‘listening stick’ or something similar such as a stone or light heighten the significance of the process ending and improve listening. Finally the problem presenter is handed the ‘Graphic’ this is their record of the meeting and can be rolled and presented ceremoniously by the facilitators for maximum effect! If you liked this course you may well like: Parent Solutions
M.D.D WHATSAPP MEDIATION PACKAGE (COUPLES)
4.9(27)By Miss Date Doctor Dating Coach London, Couples Therapy
Couples therapy via Whatsapp platform Talk through problems Try to resolve the issue Hear both parties point of view Reflect on the cause of the issues 45 mins x 3 sessions Create an understanding https://relationshipsmdd.com/product/whatsapp-mediation-package/

CRISC Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control
By Nexus Human
Duration 3 Days 18 CPD hours This course is intended for This course is ideal for Professionals preparing to become CRISC certified. Risk practitioners Students or recent graduates Overview At course completions, students will understand the essential concepts in the 4 ISACA CRISC domains: Governance IT Risk Assessment Risk Response and Reporting Information Technology and Security This 3 Day CRISC course is geared towards preparing students to pass the ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control examination. The course covers all four of the CRISC domains, and each section corresponds directly to the CRISC job practice. CRISC validates your experience in building a well-defined, agile risk-management program, based on best practices to identify, analyze, evaluate, assess, prioritize and respond to risks. This enhances benefits realization and delivers optimal value to stakeholders. GOVERNANCE - a. Organizational Governance Organizational Strategy, Goals, and Objectives Organizational Structure, Roles, and Responsibilities Organizational Culture Policies and Standards Business Processes Organizational Assets GOVERNANCE - b. Risk Governance Enterprise Risk Management and Risk Management Framework Three Lines of Defense Risk Profile Risk Appetite and Risk Tolerance Legal, Regulatory, and Contractual Requirements Professional Ethics of Risk Management IT RISK ASSESSMENT - a. IT Risk Identification Risk Events (e.g., contributing conditions, loss result) Threat Modelling and Threat Landscape Vulnerability and Control Deficiency Analysis (e.g., root cause analysis) Risk Scenario Development IT RISK ASSESSMENT - b. IT Risk Analysis and Evaluation Risk Assessment Concepts, Standards, and Frameworks Risk Register Risk Analysis Methodologies Business Impact Analysis Inherent and Residual Risk RISK RESPONSE AND REPORTING - a. Risk Response Risk Treatment / Risk Response Options Risk and Control Ownership Third-Party Risk Management Issue, Finding, and Exception Management Management of Emerging Risk RISK RESPONSE AND REPORTING - b. Control Design and Implementation Control Types, Standards, and Frameworks Control Design, Selection, and Analysis Control Implementation Control Testing and Effectiveness Evaluation RISK RESPONSE AND REPORTING - c. Risk Monitoring and Reporting Risk Treatment Plans Data Collection, Aggregation, Analysis, and Validation Risk and Control Monitoring Techniques Risk and Control Reporting Techniques (heatmap, scorecards, dashboards) Key Performance Indicators Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) Key Control Indicators (KCIs) INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AND SECURITY - a. Information Technology Principles Enterprise Architecture IT Operations Management (e.g., change management, IT assets, problems, incidents) Project Management Disaster Recovery Management (DRM) Data Lifecycle Management System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Emerging Technologies INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AND SECURITY - b. Information Security Principles Information Security Concepts, Frameworks, and Standards Information Security Awareness Training Business Continuity Management Data Privacy and Data Protection Principles
