- Professional Development
- Medicine & Nursing
- Arts & Crafts
- Health & Wellbeing
- Personal Development
AAT Level 3 Diploma in Accounting
By London School of Science and Technology
Students will learn and develop skills needed for a range of financial processes, including maintaining cost accounting records, advanced bookkeeping and the preparation of financial reports and returns. Course Overview This qualification covers a range of essential and higher-level accounting techniques and disciplines. Students will learn and develop skills needed for a range of financial processes, including maintaining cost accounting records, advanced bookkeeping and the preparation of financial reports and returns. Study the Level 3 Diploma to learn higher accounting techniques and disciplines and qualify for AAT bookkeeping membership (AATQB). The jobs it can lead to: • Accounts assistant • Accounts payable clerk • Audit trainee • Credit controller • Payroll administrator/supervisor • Practice bookkeeper • Finance assistant • Tax assistant • Accounts payable and expenses supervisor Entry requirements: Students can start with any qualification depending on existing skills and experience. For the best chance of success we recommend that students begin their studies with a good standard of English and maths. Course Content: Business Awareness: This unit provides students with an understanding of the business, its environment and the influences that this has on an organisation’s structure, the role of its accounting function and its performance. Students will examine the purpose and types for businesses that exist and the rights and responsibilities of the key stakeholders, as well as gain an understanding of the importance of professional ethics and ethical management within the finance function. Learning outcomes: • Understand business types, structure and governance and the legal framework in which they operate. • Understand the impact of the external and internal environments on business, their performance and decisions. • Understand how businesses and accounts comply with principles of professional ethics. • Understand the impact of new technologies in accounting and the risks associated with data security. • Communicate information to stakeholders. Financial Accounting: Preparing Financial Statements: This unit provides students with the skills required to produce statements of profit or loss and statements for financial position for sole traders and partnerships, using a trial balance. Students will gain the double-entry bookkeeping skills needed to record financial transactions into an organisation’s accounts using a manual bookkeeping system. Learning outcomes: • Understand the accounting principles underlaying final accounts preparation. • Understand the principles of advanced double-entry bookkeeping. • Implement procedures for the acquisition and disposal of non-current assets. • Prepare and record depreciation calculations. • Record period end adjustments. • Produce and extend the trial balance. • Produce financial statements for sole traders and partnerships. • Interpret financial statements using profitability ratios. • Prepare accounting records from incomplete information. Management Accounting Techniques: This unit provides students with the knowledge and skills needed to understand the role of management accounting in an organisation, and how organisations use such information to aid decision making. Students will learn the principles that underpin management accounting methodology and techniques, how costs are handled in organisations and why organisations treat costs in different ways. Learning outcomes: • Understand the purpose and use of management accounting within organisations. • Use techniques required for dealing with costs. • Attribute costs according to organisational requirements. • Investigate deviations from budgets. • Use spreadsheet techniques to provide management accounting information. • Use management accounting techniques to support short-term decision making. • Understand principles of cash management. Tax Processes for Businesses: This unit explores tax processes that influence the daily operations of businesses and is designed to develop students’ skills in understanding, preparing and submitting Value Added Tax (VAT) returns to HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC). The unit provides students with the knowledge and skills that are needed to keep businesses, employers and clients compliant with laws and practices that apply to VAT and payroll. Learning outcomes: • Understand legislation requirements relating to VAT. • Calculate VAT. • Review and verify VAT returns. • Understand principles of payroll. • Report information within the organisation. DURATION 250-300 Hours WHATS INCLUDED Course Material Case Study Experienced Lecturer Refreshments Certificate

Total MPLS VPN for engineers training course description A hands on course concentrating solely on MPLS VPNs. The course begins with a review of VPN basics before moving onto L3VPNs and MBGP, followed by L2VPNs. What will you learn Compare, contrast and evaluate MPLS L2VPNs versus L3VPNs. Describe, configure and troubleshoot MPLS L3VPNs. Configure and troubleshoot MBGP. Describe, configure and troubleshoot MPLS L2VPNs. Total MPLS VPN for engineers training course details Who will benefit: Anyone working with MPLS VPNs. Prerequisites: Concise MPLS for engineers Duration 2 days Total MPLS VPN for engineers training course contents MPLS VPN basics LSR, PE and P router roles. What is a VPN? MPLS VPN types, MPLS VPN comparison, MPLS L3VPN, L2VPN. VPN architectures. Hands on: Building the base network. L3VPN Separate routing tables, The Virtual Routing Table, VRFs, Route Distinguisher (RD), VNPv4 addresses. Hands on: Minimal VRF configuration, routing between customer and provider (PE-CE). MBGP MP-BGP, IPv4 routing, IPv6 routing, VPNv4 addresses, VPNv6 addresses. Exchanging labels. Exchanging routes. Route targets, communities. Route reflectors. Hands on: MBGP setup. MPLS L3VPN troubleshooting. L2VPN Why L2 not L3? Services: TDM, ATM, Frame Relay, Ethernet. Pseudowires. Hands on: Simple L2VPN configuration. Pseudowires VPWS, AToM, Attachment Circuit, Traffic encapsulation, Ethernet over MPLS. Ethernet MTU considerations. VC types. Hands on: PW configuration and troubleshooting. VPLS Ethernet multipoint connectivity. Virtual Forwarding Instance (VFI), Virtual Switching Instance. Flooding, MAC address management, split horizons. Hierarchical VPLS. Signalling: LDP based. BGP based. Auto discovery. Hands on: VPLS configuration and troubleshooting. Next generation L2VPN E-VPN, PBB-EVPN.

LTE training course description This course is designed to give the delegate an understanding of the technologies used within a 3G UMTS mobile network. During the course we will investigate the UMTS air interface and the use of Wideband-Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) to facilitate high speed data access, together with HSPA to offer mobile broadband services. We will describe the use of soft handover rather than hard handover procedures and soft capacity sharing. The course includes a brief exploration of the UMTS protocol stack and the use of PDP Context and QoS support features. What will you learn Explain the 3G UMTS architecture. Describe the role of a Drifting & Serving RNC. Explain the use of ARQ & HARQ for mobile broadband. Describe how IMS integrates into the architecture. Describe the use of Media Gateway Controllers. Identify the temporary identities used within 3G UMTS. LTE training course details Who will benefit: Anyone working within the telecommunications area, especially within the mobile environment. Prerequisites: Mobile communications demystified Telecommunications Introduction Duration 2 days LTE training course contents LTE Introduction The path to LTE, 3GPP. LTE to LTE advanced. LTE Architecture The core, Access, roaming. Protocols: User plane, Control plane. Example information flows. Bearer management. Spectrum allocation. LTE technologies Transmission, reception, OFDMA, multiple antenna, MIMO. LTE Air interface Air interface protocol stack. Channels, Resource Grid, cell acquisition. Up and downlink controls. Layer 2 protocols. Cell acquisition Power on, selecting networks and cells. RRC connection. Attach procedure. Mobility management Roaming, RRC_IDLE, RRC_CONNECTED, cell reselection, handover, interoperation with UMTS and GSM networks. Voice and text IMS, QoS, policy and charging.

Docker for engineers training course description Docker is the container platform of choice. This course covers how to use Docker to package your applications with all of their dependencies and then test, deploy, scale and support your containers. Hands on sessions follow all the major sessions. What will you learn Work with Docker images, containers and command line tools. Deploy and test Docker containers. Debug Docker containers. Describe Docker networking, deployment tools, orchestration and security. Docker for engineers training course details Who will benefit: Anyone working with Docker. Prerequisites: Introduction to virtualization. Duration 2 days Docker for engineers training course contents Introduction The birth of Docker, the promise of Docker, what Docker isn't. Docker at a glance Process simplification, broad support and adoption, architecture, getting the most from Docker, the Docker workflow. Installing Docker Important terminology, Docker client, Docker server, test the setup. Working with Docker images Anatomy of a Dockerfile, building an image, running your image, custom base images, storing images. Working with Docker containers What are containers? creating a container, starting a container, auto-restarting a container, stopping a container, killing a container, pausing and unpausing a container, cleaning up containers and images, next steps. Exploring Docker Printing the Docker version, server information, downloading image updates, inspecting a container, getting inside a running container, exploring the shell, returning a result, docker logs, monitoring Docker, exploration. The path to production containers Deploying, testing containers. Debugging containers Process output, process inspection, controlling processes, network inspection, image history, inspecting a container, filesystem inspection, moving along. Docker at scale Docker swarm, centurion, amazon EC2 container service. Advanced topics Pluggable backends, containers in detail, security, networking. Designing your production container platform The twelve-factor app, the reactive manifesto. Conclusion The challenges, the Docker workflow, minimizing deployment artifacts, optimizing storage and retrieval, the payoff, the final word.

Total SIPp course description SIPp is a robust performance testing tool designed for evaluating the SIP protocol. This comprehensive course takes you on a journey from the initial installation of SIPp to mastering fundamental scenarios, exploring diverse architectures, delving into statistics analysis, and crafting XML scenario files. What will you learn Monitor SIP traffic with SIPp. Use SIPp for performance testing. Use the standard SIPp scenarios. Create custom scenarios in XML for SIPp. Total SIPp course details Who will benefit: Those working with SIP. Prerequisites: Definitive SIP for engineers Duration 2 days Total SIPp course contents Introduction What is SIPp? SIP review: UAC, UAS, INVITE, BYE. Sample SIP call flows. Hands on Wireshark, SIP call flow. Installing SIPp Getting SIPp, installing SIPp. Using SIPp Running sipp. sipp with uas scenario, sipp with uac scenario. The integrated scenarios. Online help. Hands on uac, uas. Controlling SIPp Hot keys, commands, UDP socket. Running SIPp in the background. Traffic control. SIPp performance testing. Hands on Changing call rates, remote control, pausing traffic. Monitoring SIP traffic Scenario screen, statistics. Response times, counters. Hands on Monitoring SIP traffic. More integrated scenarios SIPp and media and RTP. 3PCC. 3PCC extended. Transport modes: UDP, TCP, TLS, SCTP, IPv6 mono and multi socket. Hands on Third Party Call Control. XML What is XML? Content, markup, elements, attributes. Start tags, end tags. Hands on Displaying embedded scenarios, looking at the XML files of the integrated scenarios. Creating your own XML scenarios scenario, message commands, send, recv, nop, pause, sendCmd, recvCmd, common sipp scenario attributes, command specific sipp scenario attributes. XML DTD, jEdit. Hands on uac and uas scenario XML files. Recv actions Log and warning, exec, variables, variable types, variable scope. External variables. Hands on RTP streaming, Change a calls network destination, injection files. Regular expressions What is an RE. POSIX 1003.2. Re injection. Validation. Hands on regex example.

Layer 3 switching training course description A hands on switching course for those already familiar with the basics of Ethernet switching. The course focuses on L3 switching along with the QoS and security features that layer 3 switches can add to the network. What will you learn Explain how layer 3 switches work. Troubleshoot layer 3 switching. Implement QoS on switches. Secure networks with L3 switches. Layer 3 switching training course details Who will benefit: Technical staff working with Ethernet switches. Prerequisites: Definitive Ethernet switching for engineers Duration 2 days Layer 3 switching training course contents Switches Switch review, VLANs, inter VLAN routing. Hands on VLANs and tagging, separating networks with routers. VLANs and IP addressing IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways. Hands on L3 switches and VLANs What are layer 3 switches Routers in switches, configuring a switch to route, switch ports, router ports, when to switch, when to route. What is the difference between a router and a L3 switch? Hands on Analysing packet flows through a L3 switch. L3 switches and static routes Why use static routes? Default routes. Hands on Configuring static routes. L3 switches and routing protocols RIP, OSPF. Hands on RIP, OSPF. First hop redundancy Default gateways, VRRP/HSRP/GBLP. Load sharing, critical IP addresses. Interaction between STP and L3 redundancy Hands on VRRP. Multicasting and L3 switches IGMP, IGMP snooping, multicasts and routers, PIM. Hands on Multicasts between VLANs. IPv6 IPv6 and L2 switches, IPv6 and L3 switches. Hands on Adding IPv6 into the network. QoS DSCP, 802.1Q, 802.1p, mapping, classification, policy, Ingress queues, Egress queues. Dropping frames, limiting bandwidth. Hands on Voice through switches. Security Layer 2 security, filtering at layer 3. Hands on Controlling inter VLAN traffic.

HTTP streaming training course description This course looks at the delivery of video streams using HTTP adaptive streaming. Both MPEG DASH and HLS are investigated. Hands on sessions primarily involve using Wireshark to analyse streams. What will you learn Use Wireshark to analyse and troubleshoot HTTP video streams. Explain HTTP adaptive streaming works. Evaluate and compare MPEG DASH and HLS. Use tools to create HTTP adaptive streams. HTTP streaming training course details Who will benefit: Anyone working in the broadcast industry. Prerequisites: TCP/IP foundation for engineers Duration 2 days HTTP streaming training course contents What is HTTP streaming? The old way. Progressive downloads versus streaming. Why not UDP and RTP for delivery? Adaptive bit rate streaming. Standards. Hands on Base network setup. Using WireShark for HTTP streams. HTTP protocol stack IP, TCP, IPv6. HTTP. HTTP 1.0, HTTP 1.1, HTTP 2.0, HTTP header fields. HTML 5. Hands on Analysing HTTP. Adaptive bitrate streaming principles Chunks, fragments, segments. Manifest files. Encoding, resolution, bitrates. Addressing, relative and absolute URLs, redirection. When does the client switch streams? Switch points. Hands on Walk through of client behaviours on a stream. HTTP streaming architecture Server components, distribution components, client software. CDN, caching, multiple servers. Hands on Analysing CDN and Internet delivery. TCP and HTTP streaming interactions TCP ACK, TCP connections, unicast only. TCP flow control, TCP and performance. Hands on TCP window sizes. MPEG DASH Stakeholders, DASH architecture and model, codec agnostic, XML, Media Presentation Description, Media Presentation, segment formats. Hands on MPEG DASH analysis. HTTP Live Streaming and others Stakeholders. Media segments, media playlists, master playlists. Adobe HTTP dynamic streaming, Microsoft smooth streaming. Hands on Analysing HLS. Tools mp4dash, mp4fragment, libdash. Apple developer tools for HLS. Hands on Creating segmented content. Security HTTPS, encryption, content protection. Hands on Encryption analysis. Summary Choosing a streaming method. Impact of live versus VoD. Web sockets.

OTT TV for engineers course description This course covers OTT TV by primarily looking at the delivery of video streams using HTTP adaptive streaming. Both MPEG DASH and HLS are investigated. Hands on sessions involve using Wireshark to analyse streams as well as crafting segmented content. What will you learn Explain what OTT TV is, and how it works. Describe the OTT TV architecture. Use Wireshark to analyse and troubleshoot OTT video streams. Explain how HTTP adaptive streaming works. Evaluate and compare MPEG DASH and HLS. Use tools to create OTT TV adaptive streams. OTT TV for engineers course details Who will benefit: Anyone working in the broadcast industry. Prerequisites: TCP/IP foundation for engineers. Duration 2 days OTT TV for engineers course contents What is OTT TV? Brodeo providers vs ISPs. Progressive downloads versus streaming. Why not UDP and RTP for delivery? Adaptive bit rate streaming. Standards. Hands on: Base network setup. Using WireShark for HTTP streams. HTTP protocol stack IP, TCP, IPv6. HTTP. HTTP 1.0, HTTP 1.1, HTTP 2.0, HTTP header fields. HTML 5. Hands on: Analysing HTTP. Adaptive bitrate streaming principles Chunks, fragments, segments. Manifest files. Encoding, resolution, bitrates. Addressing, relative and absolute URLs, redirection. When does the client switch streams? Switch points. Hands on: Walk through of client behaviours on a stream. OTT TV streaming architecture Server components, distribution components, client software. CDN, caching, multiple servers. Hands on: Analysing CDN and Internet delivery. TCP and HTTP streaming interactions TCP ACK, TCP connections, unicast only. TCP flow control, TCP and performance. Hands on: TCP window sizes. MPEG DASH Stakeholders, DASH architecture and model, codec agnostic, XML, Media Presentation Description, Media Presentation, segment formats. Hands on: MPEG DASH analysis. HTTP Live Streaming and others Stakeholders. Media segments, media playlists, master playlists. Adobe HTTP dynamic streaming, Microsoft smooth streaming. Hands on: Analysing HLS. Tools mp4dash, mp4fragment, libdash. Apple developer tools for HLS. Hands on: Creating segmented content. Security HTTPS, encryption, content protection. Hands on: Encryption analysis. Summary Choosing a streaming method. Impact of live versus VoD. Web sockets.

Signalling training course description An intensive course that defines and explores the signalling methods that are to be found in today's telecommunications services. What will you learn Describe the Functionality and Features of Signalling. Describe the Functionality of Analogue & Digital Subscriber Signalling. Describe the various types of signalling used on different network types. Describe the Functionality of Private Network Signalling. Describe the Functionality of Public Network Signalling. Signalling training course details Who will benefit: Personnel involved with systems design, implementation and support. Prerequisites: Telecommunications Introduction Duration 2 days Signalling training course contents Introduction What is Signalling?, Standards, ITU-T Recommendations, Signalling Categories - Supervisory Addressing, E.164, Call Information, Network Management, Network Components, Inband/Outband Switch Signalling, Analogue Vs Digital Signalling. Analogue Subscriber Signalling Analogue Local Loops/Switches/Trunks, Digital Switches/Local Loops, Telephone Handset, Accessing the Local Exchange, Pulse/Tone Dialling. Digital Subscriber Signalling Integrated Digital Access, DASS2 & DPNSS, DASS2 - Call, IMUX, Euro ISDN, Q.931 Call Control, Message Identification, Message Types, Call Establishment Messages, Call Clearing. Network Types Service Types, Circuit Switched, Packet Switched, Signalling Terminology, In-Channel Signalling, G.704, Performance and Quality, Digital Signalling, CAS, CAS Applications, Foreign Exchange, CCS, Break-In/Out Private Network Signalling Types Networking PABXs, Inter PABX Analogue Signalling Methods, E & M, Tone-On-Idle, Inter PABX Digital Signalling Methods, DPNSS, DPNSS Deployment, PABX Support for DPNSS, DPNSS Call, Q.Sig, Q.Sig support/functionality/protocol, Message Overview, Call Establishment. Public Network Signalling SS7, SS7 Operations, SS7 Topology, SSP, STP, SCP, Database Types - CMSDB NP LIDB HLR VLR, Signalling Modes, Link Types, Further Redundancy, Linksets, SS7 addressing, Point Codes, Sub-System, Global Title Addressing and Translation, ANSI PCs, ITU-T PCs, SS7 Protocol Stack, MTP Level 1, MTP Level 2, Flow Control, FISU, LSSU, MSU, MSU SIF, MTP Level 3, SCCP, TCAP, TUP, Facility Format, Main Facilities, Flow Control Negotiation, Closed User Groups, Reverse Charging, Fast Select Facility, Throughput Class Negotiation, Call Barring, On-Line Facility Registration. BTUP, ISDN ISUP, Supplementary Services, ISUP Call - IAM, Progress/Answer/Suspend/ Resume/Release Messages, Intelligent Network (IN) Introduction, IN Evolution, IN Conceptual Model, IN Target Services & Service Features, Service Independent Building Blocks

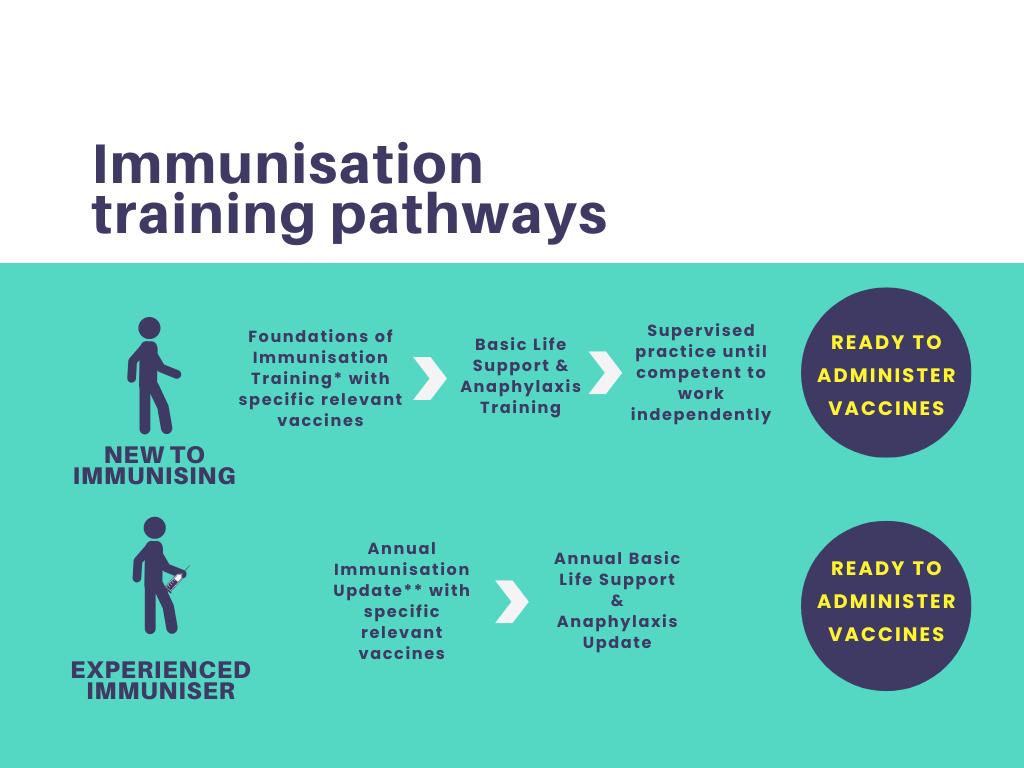
Foundations of Immunisation and Vaccines for Non-Registered Practitioners
By Guardian Angels Training
The "Foundations of Immunisation and Vaccines for Non-Registered Practitioners" course is fully compliant with the National Minimum Standards and Core Curriculum for Immunisation Training and is designed to equip non-registered healthcare professionals with a solid understanding of immunisation concepts, vaccine administration, and the importance of vaccination in public health.
Search By Location
- MA Courses in London
- MA Courses in Birmingham
- MA Courses in Glasgow
- MA Courses in Liverpool
- MA Courses in Bristol
- MA Courses in Manchester
- MA Courses in Sheffield
- MA Courses in Leeds
- MA Courses in Edinburgh
- MA Courses in Leicester
- MA Courses in Coventry
- MA Courses in Bradford
- MA Courses in Cardiff
- MA Courses in Belfast
- MA Courses in Nottingham