- Professional Development
- Medicine & Nursing
- Arts & Crafts
- Health & Wellbeing
- Personal Development
169 Courses
CT04a - Clinical trials in drug development
By Zenosis
New drug development requires major investment in capital, human resources and technical expertise. Strict adherence to regulations on testing and manufacturing standards is also required before a new drug can be marketed. One of the greatest challenges in conducting clinical trials is that of efficiency. As trials become more comprehensive, involving large numbers of participants globally, their duration is prolonged and costs increase. The longer trials last, the shorter is the patent life remaining after market approval and the longer patients must wait for the new product. This short course covers the key components of clinical trials and how these requirements interact with the drug development cycle.

CT04d - Clinical trial endpoints
By Zenosis
In clinical trials, endpoints are measurements to evaluate the results of a new treatment, at an individual patient level. The study data can be extrapolated to patient populations on the basis of clinical similarities to patients participating in the trial. When clinical trial data have been obtained, focus is on the trial endpoints; more specifically, the focus is on whether the trial met or failed the primary endpoint specified before the trial started. The purpose and various types of endpoints are discussed in this short course.
CT03f - Informed consent in clinical trials
By Zenosis
Informed consent in clinical research is an ethical and regulatory requirement. A research subject must enter a study voluntarily, be informed about risks and benefits, and understand the difference between investigation and treatment. Subjects must not be coerced into enrolment, nor must they be enticed by exaggerated claims of benefit. Before they can enrol, all potential subjects must agree, in writing, to participate. In addition to ethical and regulatory imperatives, the potential for litigation by subjects further highlights the importance of rigorous adherence to informed consent principles. In this short course we set out the principles and requirements and provide examples of practical issues confronting healthcare professionals and subjects.
In-Depth Wedding Planning Courses - Extensive, Intensive Training Program
By AP Wedding Consultancy & Academy
5* Wedding Planner Courses UK & Online. Certified, intensive training alongside est. London Consultants. Home-study & online wedding planning courses.

Ease anxiety with yoga
By Diana Woodhead
improve your anxiety with yoga and meditation

CT03g - Clinical trial monitor’s GCP responsibilities
By Zenosis
A clinical trial monitor acts on behalf of the sponsor to support investigational site personnel, verify the accuracy of data recorded, and ensure that the trial is conducted in compliance with the protocol, GCP and other study specific requirements. He or she acts as the ‘eyes and ears’ of the sponsor at the investigational site and provides the main channel of communication between sponsor and investigator. This short course explores the responsibilities of the monitor and provides insight into key challenges. We discuss assessment of investigators and investigational sites, education and trial initiation, monitoring of clinical conduct, including CRF review and source document verification, and trial close-out. We discuss noncompliance and how to deal with it.
GMP01a - GMP – what and why
By Zenosis
Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) is a set of rules for medicines manufacturers to follow so that their products are safe, effective, and of good quality. Everyone who works in a processing, quality control, packaging, or warehouse environment for a pharmaceutical or biotechnology company, or one of their contractors, must understand why GMP is important, how it applies to them, and how to comply with it. This short course explains what GMP is and why it is important, and it gives some lessons from history. It introduces the regulations and guidance documents that are the source of GMP rules. Finally, it touches on regulatory inspections and the consequences that can arise from failure to comply with GMP requirements.

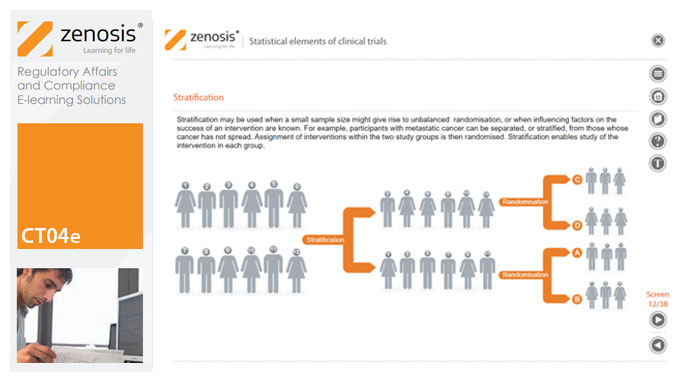
CT04e - Statistical elements of clinical trials
By Zenosis
Analytical statistical elements are essential concepts in the design of clinical trials. This analysis helps us to understand whether a conclusion from a study of a sample of the target population applies generally to that population as a whole. In particular, it helps us to answer the question: Did the treatment effect in the given study occur just by chance? The statistical elements of a well-controlled study minimise the chances of drawing the wrong conclusions, by providing clear thresholds for such errors. The basic statistical elements of a clinical trial include eligibility criteria, randomisation, sample size, power, and blinding, and these are discussed in this short course.
CT03d - Clinical trial sponsor’s GCP responsibilities
By Zenosis
The sponsor of a clinical trial takes responsibility for its initiation, management, and/or financing. A sponsor may transfer any or all of the sponsor’s trial-related duties and functions to a contract research organisation, but the ultimate responsibility for the quality and integrity of the trial data always resides with the sponsor. Duties and functions discussed in this short course include trial design, selection of investigators, QA and QC, data handling and record keeping, finance and compensation, regulatory submissions, management of investigational product(s), safety reporting, monitoring, audit, dealing with noncompliance, and clinical trial reports. ICH guideline E6 (revision 2) encourages sponsors to adopt a risk-based approach to managing the quality of trials. We discuss this approach in general, and aspects such as risk-based monitoring in particular.
Search By Location
- short course Courses in London
- short course Courses in Birmingham
- short course Courses in Glasgow
- short course Courses in Liverpool
- short course Courses in Bristol
- short course Courses in Manchester
- short course Courses in Sheffield
- short course Courses in Leeds
- short course Courses in Edinburgh
- short course Courses in Leicester
- short course Courses in Coventry
- short course Courses in Bradford
- short course Courses in Cardiff
- short course Courses in Belfast
- short course Courses in Nottingham