- Professional Development
- Medicine & Nursing
- Arts & Crafts
- Health & Wellbeing
- Personal Development
2079 Courses in Manchester
Introduction to supply chain management (In-House)
By The In House Training Company
This comprehensive one-day programme has been designed to provide participants with an overview of basic supply chain principles and concepts and to identify potential opportunities for reducing costs, minimising risks and adding value across the supply chain. This could include reducing inventory, procurement, transport and storage costs. Fundamentally, the object of the programme is to empower participants to be able to collaborate with all key stakeholders across the supply chain. This course will help participants: Appreciate the importance of the supply chain as a source of competitive advantage Understand the tools and techniques available to improve supply chain performance Analyse and mitigate risks across the supply chain Identify opportunities for improvements in their respective supply chains Demonstrate competence in the pro-active management of the supply chain

Overview Understand the role of corporate structure, dividends and equity indices in equity markets. Become familiar with the building blocks of repos / stock lending, futures and forwards – and how to use these products. Understand how to price, and risk manage equity swaps and dividend swaps. Gain experience in their uses in trading, corporate finance and portfolio management. Learn how to price equity options and the features that make them different from other asset classes, explore how to use these products for taking equity risk, yield enhancement and portfolio protection. Understand strategies designed to trade / hedge volatility using options. Who the course is for Risk management Finance Sales and trading Treasury Technology Financial Engineering Course Content To learn more about the day by day course content please click here To learn more about schedule, pricing & delivery options, book a meeting with a course specialist now

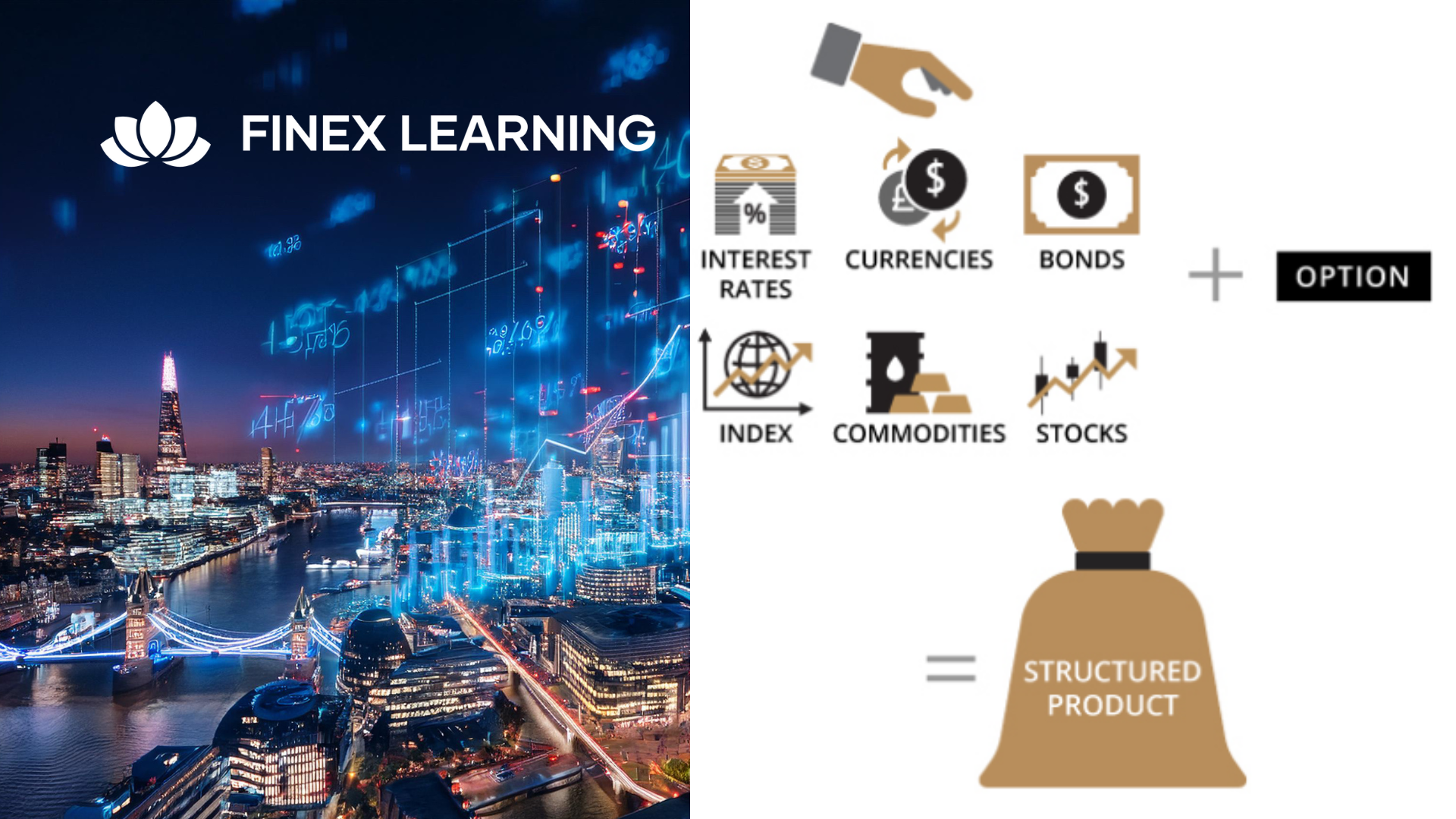
Overview A review of the most enduringly popular structured equity-linked products. This 1 day hands-on programme will help you gain familiarity with 1st generation & 2nd generation structured products convexity – and their applications. Discover techniques for maximising the participation rate to enhance returns for investors. Explore the trade-offs between coupon payments and gearing, and how they affect the risk-return profile of the notes. Explore ladder structures, their relationship to lookbacks, and the benefits they offer to investors. Learn about accumulators, their structuring, and the reasons behind their controversy in the market. Who the course is for Structured Products Desks, Financial Engineers, Product Controllers Traders, Dealing Room Staff and Sales People Risk Managers, Quantitative Analysts and Middle Office Managers Fund Managers, Investors, Senior Managers Researchers and Systems Developers Course Content To learn more about the day by day course content please click here To learn more about schedule, pricing & delivery options, book a meeting with a course specialist now
Mental Health Aware (In-House)
By The In House Training Company
Mental Health First Aid England Aware is an introductory course designed to increase mental health awareness and give an understanding of how to look after wellbeing and challenge stigma. Through an interactive instructor-led live session, you will learn: What mental health is and how to challenge stigma An introduction to some common mental health issues Confidence to support someone who may be experiencing mental ill health Ways to look after your own mental health and support wellbeing Outline What is mental health? Mental Health Continuum Factors that affect mental health Stigma Stress and stress management Spotting signs of distress Mental health conditions:DepressionAnxiety disordersPsychosisEating disordersSuicideSelf-harm Recovery Take 10 Together - starting a supportive conversation Supporting mental health in the workplace Useful statistics Helpful resources

Health and Safety Representatives - Roles and Responsibilities (In-House)
By The In House Training Company
This practical course gives participants a brief overview of a range of legal aspects and also incorporates a topical perspective of health and safety matters in the workplace today. The programme will help elected staff safety representatives to grasp in more detail how to comply with the law in practice. 1 The legal framework Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations (MHSWR) Safety Representatives and Safety Committees Regulations Representatives' functions H&S Consultation with Employees Regulation HSG 263 2 'The six pack' Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations (MHSWR) Display Screen Equipment Regulation (DSE) Manual Handling Health, Safety and Welfare Provision and Use of Work Equipment Regulation Personal Protective Equipment Regulation 3 Accident reporting and procedures Reporting Injuries, Diseases and Dangerous Occurrences Regulation (RIDDOR) Accident investigation guidance

This course looks at the key processes in supply chains and how they interact; the most common supply chain terms and how they are utilised to describe supply chain activities. It will cover the definitions of transport modes and how to select the most appropriate one; the role of logistics partners in the extended supply chain and the definition and use of Incoterms. PARTICIPANTS WILL LEARN HOW TO: Explain the term “Supply Chain” Define main activities in Transport & Freight Management Describe the key principles of Warehousing Interpret INCOTERMS COURSE TOPICS INCLUDE: Freight terminology & global trade terminology Warehouse, logistics and transport operations Transport modes Parties involved in international shipments INCOTERMS Freight calculations

Safeguarding Children (Awareness to L3)
By Prima Cura Training
To increase your awareness and understanding of what safeguarding children means, in order to increase your confidence to enable you to make a positive contribution towards the process.

This intensive course equips senior management with the knowledge and skills to develop a logistics strategy that will consistently support business objectives. PARTICIPANTS WILL LEARN HOW TO: Understand the concept of integrated logistics. Critically analyse and evaluate logistics operations. Apply solutions to problems in line with global best practices. Devise and operate effective performance measures. Learn how to create performance improvement plans. Understand how to support inbound and outbound logistic activities. COURSE TOPICS INCLUDE: Mission, strategy and policies for logistics Costs of non-performance and poor performance Logistics planning Land, air and marine transport services Materials storage, preservation and handling Waste management services HSSE policies Sustainable logistics and transport Risk management in logistics Management controls Performance measurement Sustainability

Train the trainer (In-House)
By The In House Training Company
At some point in your life you will have attended a training course or workshop, but what happens when you are asked to deliver one? Some people relish the opportunity while others are challenged by it. Whatever you feel about training others, it is a skill that is admired and can be studied and learned. With the trainer you will be learning the techniques, skills and understanding you need and you will have the chance to deliver a short training session to others, receive feedback and having the confidence to deliver it for real in your job. The training will comprise one day followed by a half day when all those able to attend will deliver and have feedback on a 20 minute training activity. To be able to create and maintain an environment conducive to learning and engagement To understand basic learning theory and practice and the difference between training, facilitating and learning To understand how adults learn and how to apply it as a trainer To be able to plan and deliver a training activity using the appropriate set of skills and behaviours To be able to review and evaluate learning and identify how outcomes are met To manage the learning process and the participant engagement in the training environment To be able to present effectively and appropriately to a variety of audiences To deliver and receive feedback on a short delivered training activity with peers To review and evaluate learning and have an action plan to take back and put into practice DAY ONE (full-day) 1 Welcome, housekeeping, how the day will be run Introductions (and making the most of them) Warm up - breaking the ice followed by review and feedback Creating an environment conducive to learning and engagement; managing expectations well as a trainer Group task with feedback and review in plenary 2 What is training and how do adults learn? Trainer input: David Kolb's Learning Cycle Group tasks 3 How to plan a session and what to include - trainer input Starting at the end and working backwards Linking outcomes to purposeful activities Practice task and planning time for day two using a template 4 The skills and behaviours of a brilliant trainer Modelling skills and behaviours Creative task and discussion 5 Mini reviewing task De-brief - using reviewing in training 6 How to manage the process Trainer input followed by practice Paying conscious attention to language (verbal and non verbal), feelings and responses in the room and managing yourself as a trainer 7 The trainer's toolkit #1 Key tools, materials and templates Choosing different tools and approaches with different audiences Know your audience 8 The trainer's toolkit #2 Key tools, materials and templates continued Addressing trainer good practice 9 Review, evaluation and action planning activities Why and what should we be evaluating and why it's important Action planning task Group review task DAY TWO (half-day) The day will comprise a series of 30 minute timed sessions where each delegate will present and deliver a training activity with the group. The training activity will be prepared and planned in advance and will take 20 minutes (+ or - 2 minutes) to deliver in real time. This will be followed by review and feedback from the trainer and peers to complete the total of 30 minutes as a time slot. Reiteration of the task and discussion can take place with the trainer if needed, and there is time included in Day One to support the training planning.

Fire Wardens - roles and responsibilities (In-House)
By The In House Training Company
All organisations are legally required to have at least one designated Fire Warden. It's also common sense, given that every year there are nearly 20,000 commercial fires in the UK. This course will help participants: Assess their awareness and knowledge of the principles of fire safety and the associated risks involved at work Understand the responsibilities of being a Fire Warden Understand the main types of firefighting equipment 1 Introduction to fire safety What to do in an emergency Causes and effects of fire The fire warden's duties and responsibilities 2 Fire risk control How to raise the alarm Assembly points, roll calls, drills Fire prevention and fire risk assessment Understanding the fire triangle 3 Practical fire safety Types of portable fire extinguishers Maintenance of firefighting equipment Fire signs In-house checks The fire bag/box

Search By Location
- course Courses in London
- course Courses in Birmingham
- course Courses in Glasgow
- course Courses in Liverpool
- course Courses in Bristol
- course Courses in Manchester
- course Courses in Sheffield
- course Courses in Leeds
- course Courses in Edinburgh
- course Courses in Leicester
- course Courses in Coventry
- course Courses in Bradford
- course Courses in Cardiff
- course Courses in Belfast
- course Courses in Nottingham