- Professional Development
- Medicine & Nursing
- Arts & Crafts
- Health & Wellbeing
- Personal Development
PV03: Drug Safety and Pharmacovigilance
By Zenosis
Drug safety monitoring and risk management are vitally important for medicinal product developers, licence holders and clinical investigators. In addition to their duty to protect public health, increasingly tight regulation and potentially massive payments to litigants provide strong incentives for pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies to ensure that they maintain efficient systems for drug safety / pharmacovigilance and that all staff are aware of the basic requirements. This course will provide them with an overview of the most important aspects of this discipline, both before and after marketing of products, especially as they apply in Europe and the USA.

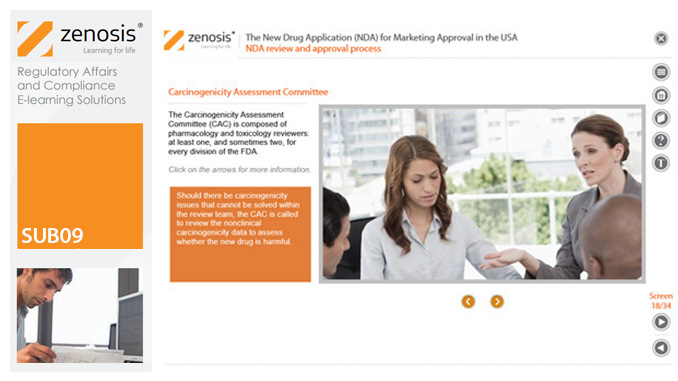
SUB09: The New Drug Application (NDA) for Marketing Approval in the USA
By Zenosis
The New Drug Application (NDA) is the regulatory vehicle through which sponsors formally propose that the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approve a new pharmaceutical for marketing and sale in the USA.
CT04: An Introduction to Clinical Trial Preparation and Design
By Zenosis
This module aims to provide you with effective strategies for the preparation and conduct of a clinical trial, while adhering to regulatory safety standards. Management of data for submission is also covered.

SUB05: Electronic Common Technical Document (eCTD)
By Zenosis
The eCTD is mandatory for all applications for marketing approval and all subsequent related submissions in the European Economic Area, the USA and Canada. Other countries intend to make its use mandatory. The eCTD specification has been developed to facilitate the global electronic submission, review and lifecycle management of medicinal product dossiers for regulatory applications. It broadens the scope of the CTD to include information on variations, renewals and amendments, so that it is no longer a static document but is updatable throughout the life of the product. This module outlines the eCTD specification, discusses the approach to regional differences in dossiers, and provides guidance on creation of an eCTD submission. The module provides a training and reference tool that will be of particular value to those new to the use of the format.

CT09: Good Clinical Practice Inspections and Audits
By Zenosis
The module describes general principles of GCP inspection and audit, discusses preparation for an inspection, and sets out in detail what European and US FDA inspectors will examine. Finally it describes post-inspection actions by the regulator and the inspected party.

VAL07: Computer Systems Validation, Part 2: Implementation
By Zenosis
This module describes the design, development and installation phase, the validation phase, and the operation and maintenance phase of the validation of computerised systems in medicines and healthcare products manufacturing environments. It continues to follow the progress of a pharmaceutical company's project to validate a new dispensary control system.
VAL06: Computer Systems Validation, Part 1: Planning
By Zenosis
In the medicines and healthcare products industries, computerised systems used in automated manufacturing or laboratory processes to which Good Manufacturing Practice requirements apply need to be validated. This module describes the planning of such validation. It follows the work of a pharmaceutical company's team as they validate the dispensary control system for a new production line.

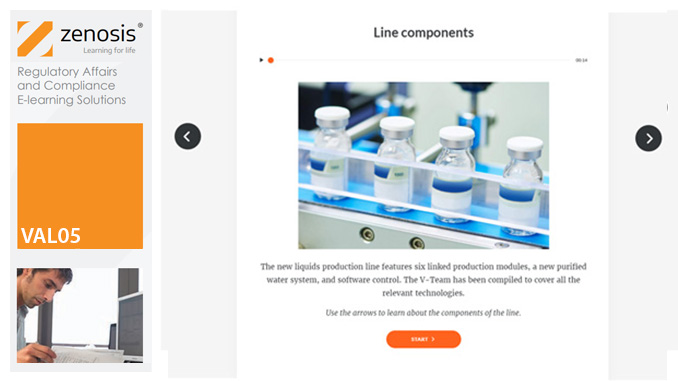
VAL05: Equipment Cleaning Validation
By Zenosis
Manufacturers of medicines and healthcare products must establish, validate and maintain an equipment cleaning programme. This is a regulatory requirement because validated cleaning procedures contribute to the assurance of product purity and safety. This module provides a comprehensive account of equipment cleaning validation requirements and procedures. It follows the work of a pharmaceutical company's validation team as they establish and validate the cleaning program for a new production line.
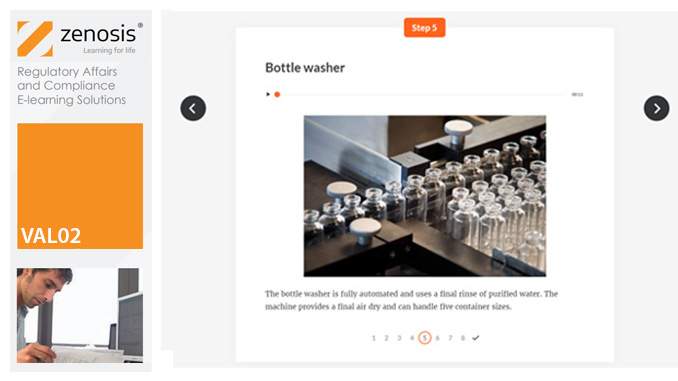
VAL02: Validation Plans and Documentation
By Zenosis
Essential to validation is the provision of documented evidence verifying that manufacturing processes will consistently result in products meeting predetermined quality standards. This module describes the purpose, content and use of validation master plans, project validation plans, and other documentation for validation projects in the medicines and healthcare products industries. It describes the activities of a typical validation team as they carry out a project for a pharmaceutical company.
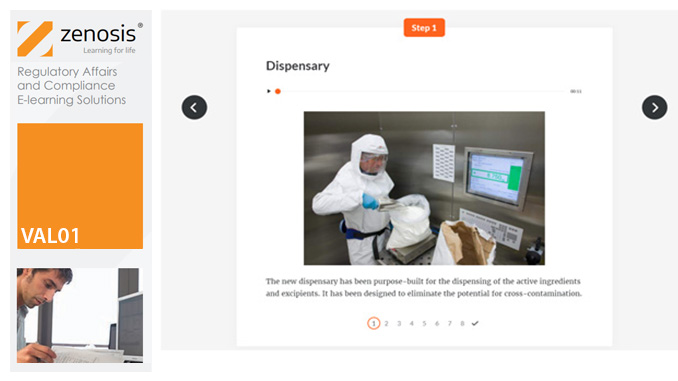
VAL01: Introduction to Validation
By Zenosis
Validation of equipment, services, systems and processes is vitally important in the medicines and healthcare products industries. Regulatory authorities require documented evidence that manufacturing processes will consistently result in products meeting predetermined quality standards. This module provides an introduction to validation and to the regulations and guidance that apply to it. It describes the activities of a typical validation team as they carry out a project for a pharmaceutical company.