- Professional Development
- Medicine & Nursing
- Arts & Crafts
- Health & Wellbeing
- Personal Development
411 Courses
What's New, What's Next: Navigating Tech & Policy Shifts in Future Transport
By Cenex (Centre of Excellence for Low Carbon & Fuel Cell Technologies)
Explore the latest in transport tech & policy. Join our in-person workshop to gain practical insights and stay ahead in the future mobility landscape.

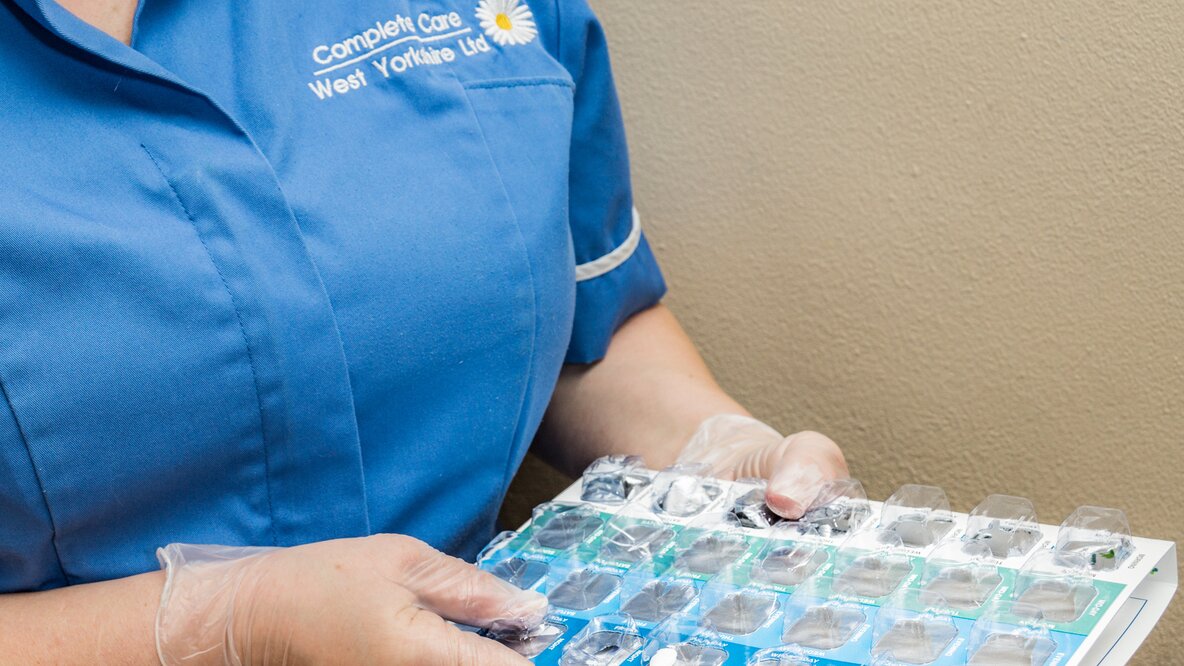
Medication Refresher (CPD accredited)
By Complete Training
The medication and record keeping course is a full day, instructor led course in a fully equipped training room. We use a mixture of training methods such as scenarios, activities, group discussion, games and the use of equipment / technology to cover the different learning styles of the individual. Learners will develop their knowledge, skills and understanding around the administering of medication and the importance of record keeping. Some of the key Learning Outcomes we cover are; Understanding of the legislation surrounding medication Understanding of role and responsibilities Understanding of medication policy and procedures Understanding of boundaries when assisting with medication Explain how and why medication errors occur Explain how to eliminate or reduce risks to individuals safety Aware of who and where to report concerns Understand the importance of thorough documentation Care providers are regulated by the Care Quality Commission (CQC) and as a result must meet the Health and Social Care Act 2014 (Regulation 18 Staffing). Evidence of training and understanding is provided to support providers in their evidence of compliance. Instructions Attendees to arrive on time at 9.30am and will leave around 16.30pm It is important that learners are fit and well to participate in group activities. Directions Complete Care West Yorkshire Ltd. Somerset House, Sandal Castle Centre Asdale Road Wakefield WF2 7JE All training is carried out at our office (Somerset House, map is attached). Please note that we do not provide lunch so you will have to bring your own. Please do not park in the office car park as not all spaces belong to us. There is available parking in Asda and Aldi next door, or the public car park at eth side of Square Pizza Amenities Toilets
Candle Making Course with Belisama Candles (A Peta approved brand )
By Belisama Candles
Learn how to make professional quality fragranced candles using natural wax and vegan ingredients, we are a Peta approved brand.

Legionella Awareness Online Course
By Airborne Environmental Consultants Ltd
Legionella awareness is suitable for any persons wanting to gain an understanding of Legionella and how to prevent or control the risk of exposure to Legionella bacteria. The main subject areas of the course are: What Legionella is Obligations under current Health & Safety legislation and ACoP L8 System hygiene Assessing and managing risk Outbreaks Hot and cold water systems Risks in other types of water systems Multiple choice test (if required).
We deliver Workplace PAT Testing Courses across most of the UK to assist businesses with Compliance. We also work with Bridges into Work and ReACT in association with Careers Wales and the Welsh Government to offer work based skills which some Candidates could be eligible for Government funding.

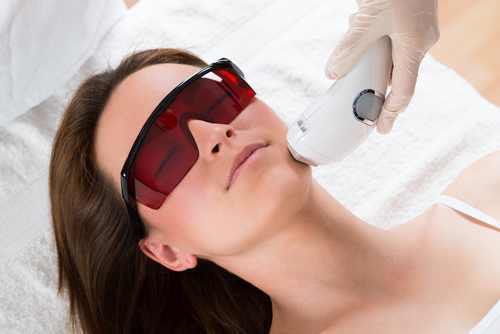
VTCT LEVEL 4 CERTIFICATE IN LASER AND INTENSE PULSED LIGHT (IPL)
By The Angel Academy Of Teaching & Training
Intense Pulsed Light or Laser Hair Removal. Hugely popular in the UK, this treatment leads the way in permanent hair removal. Salons around the UK command very good profits from a course of IPL or laser. In the 2000's, women have the opportunity to be hair free and this has led to an increase in the demand for hair free bodies. Certain cultures dictate that women be as hair free as possible and IPL allows for this. There are certain IPL machines in the market that are virtually pain free, making it possible for a woman to have a 'brazilian' or a 'hollywood' treatment. Please enquire if you wish to know more. How Does IPL Work The treatment involves the application of a focused, broad-spectrumlight (xenon), which is applied to the surface of the skin using a hand-held application head. Selective photo-thermolysis involves the process of the light, which travels across and within the range until it reaches the hair shafts or the root of the hair (the bulb). The bulb is usually where the highest concentration of melanin is located. The melanin is what determines our hair/skin colour and once this melanin has been destroyed there can be no growth. The IPL light is changes into heat. This will literally 'blow up' the root of the hair. If a hair has nowhere to grow with no hair bed, it cannot grow! This intense heat also destroys the papilla. IPL treatments will permanently reduce the total number of body hairs but will not result in a permanent removal of all hair and many factors can trigger re-growth such as hormones, menopause, pregnancy and medication. With an IPL treatment, the hair growth cycle has to be in Anagen (the active stage). The hair growth cycle differs on different areas of the body which is why we need to recommend a course! A- Anagen (active stage) C- Catagen (transitionary stage) T- Telagen (resting phase) As the hair growth cycle process can take between 4-6 weeks, this is why we recommend a client to return for their course every 4 weeks. It has the best track record. IPL & Laser has the best overall results (on large areas), versus any other method, in getting rid of hair for longer periods of time if not permanently. All skin types and hair colours can be identified. IPL (intense pulsed light) it does target pigmentation (this determines hair and skin colour), but an ND Yag Laser is not determined by the Fitzpatrick Scale. What is the difference between Laser and IPL Laser and IPL are identified by their wavelength which is usually shown in nanometres (nm). IPL systems are different to a Laser machine as they have a range of emissions. With the AATT Freeze 1 machine the range for hair removal is 640-1200nm (this is a ruby wavelength). For photo-rejuvenation the range is 540-1100nm (this is a green wavelength). The Poly lightbulb emits a range of wavelengths to appear as a flash of white light The Wavelengths are incoherent and travel in all directions with no order between them The High beam spreads out more rapidly than a laser beam The Focus is on a large area which reduces the risk of eye damage compared with coherent sources such as a laser beam. IPL is the abbreviation of Intense Pulsed Light. The machines have been widespread in use since the beginning of the 1990's. The flash lamp is commonly a xenon (huge uses across industry, photographic and medical) What Does The Course Include? When choosing a course ensure that it includes both theory and a wide variety of practical content. Every course should include: Anatomy and Physiology Types & structure of the hair Health & Safety Management Salon Management Client Care Laser & IPL Hair Removal Application Laser and IPL for Photo-rejuvenation Skin, blood and lymphatic circulation Reproductive and endocrine system Theory of Electric Currents Consultations & Record Cards Contra-indications & contra-actions Aftercare advice Accurate techniques Legislation, Hygiene and Sterilisation What is expected of the student to complete a fast track course? Full attendance of the lesson dates A full commitment to work hard Health & Safety Management Salon Management Client Care Successful Laser & IPL Hair Removal Application Successful Laser and IPL for Photo-rejuvenation Completion of a Portfolio Performing Competent Assessments Producing a Written Assignment Home Study and Practice Please see below our list of upcoming courses. Click on the course for further information, request a call or email regarding the course or book now! Course Days Dates Cost VTCT Level 4 IPL & Laser 2 6/04/2024 7/04/2024 £999 VTCT Level 4 IPL & Laser 2 23/05/2024 24/05/2024 £999 VTCT Level 4 IPL & Laser 2 21/06/2024 22/06/2024 £999 VTCT Level 4 IPL & Laser 2 24/07/2024 25/07/2024 £999
CDM 2015 - Understanding and achieving best practice (In-House)
By The In House Training Company
This course provides participants with a comprehensive understanding of the requirements of the CDM Regulations 2015 and how these should be implemented in practice. The Regulations are put in context with other key health and safety legislation. The programme sets out clearly the roles and responsibilities of the principal duty holders and explores with the participants how these roles may vary on different types of project and procurement routes. The programme examines the content and appropriate level of information that should be included in the Pre-Construction Information and the Construction Phase Plan. The trainer will discuss best practice in implementing CDM through the new 2015 Regulations and Guidance. This course is essential for anyone who is involved in the procurement, planning, design or implementation of construction work. The course will provide you with: An overview of construction health and safety law, liability and enforcement A detailed understanding of the 2015 CDM Regulations and the part they play with other key legislation An explanation of the roles and responsibilities of all duty holders and the requirements for the CDM documentation Clear advice on current best practice for complying with the principles of the CDM Regulations and the changes introduced by the 2015 Regulations An understanding of how risk assessment should be applied practically throughout the design and how this responsibility is then transferred to contractors 1 Introduction Why manage health and safety? The costs of accidents Construction industry statistics Why CDM? Health and safety culture in the construction industry 2 Overview of health and safety law and liabilities Criminal and civil law Liability Enforcement and prosecution Compliance - how far do we go? Statutory duties 3 Health and safety law in construction Framework of relevant legislation Health and Safety at Work etc Act 1974 Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999 Construction (Design and Management) Regulations 2015 Who is responsible for the risks created by construction work? Shared workplaces/shared responsibilities Control of contractors - importance of contract law 4 Construction (Design and Management) Regulations 2015 Scope - What is construction? Application - When do they apply? The CDM Management System Duty holders (Client, Domestic Client, Designer, Principal Designer, Principal Contractor, Contractor) Documents (HSE Notification, Pre-Construction Information, Construction Phase Health & Safety Plan, H&S File) Management process The 2015 Guidance 5 Best practice - key issues in the CDM process The client and client management arrangements Competence and resource under CDM 2015 The role of the Principal Designer in practice Design risk assessment and the role of the Designer The CDM Documents (PCI, PCI Pack, Plan and File) Construction health, safety and welfare Making CDM work in practice 6 Questions, discussion and review

CDM 2015 - Understanding and achieving best practice (In-House)
By The In House Training Company
This course provides participants with a comprehensive understanding of the requirements of the CDM Regulations 2015 and how these should be implemented in practice. The Regulations are put in context with other key health and safety legislation. The programme sets out clearly the roles and responsibilities of the principal duty holders and explores with the participants how these roles may vary on different types of project and procurement routes. The programme examines the content and appropriate level of information that should be included in the Pre-Construction Information and the Construction Phase Plan. The trainer will discuss best practice in implementing CDM through the new 2015 Regulations and Guidance. This course is essential for anyone who is involved in the procurement, planning, design or implementation of construction work. The course will provide you with: An overview of construction health and safety law, liability and enforcement A detailed understanding of the 2015 CDM Regulations and the part they play with other key legislation An explanation of the roles and responsibilities of all duty holders and the requirements for the CDM documentation Clear advice on current best practice for complying with the principles of the CDM Regulations and the changes introduced by the 2015 Regulations An understanding of how risk assessment should be applied practically throughout the design and how this responsibility is then transferred to contractors 1 Introduction Why manage health and safety? The costs of accidents Construction industry statistics Why CDM? Health and safety culture in the construction industry 2 Overview of health and safety law and liabilities Criminal and civil law Liability Enforcement and prosecution Compliance - how far do we go? Statutory duties 3 Health and safety law in construction Framework of relevant legislation Health and Safety at Work etc Act 1974 Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999 Construction (Design and Management) Regulations 2015 Who is responsible for the risks created by construction work? Shared workplaces/shared responsibilities Control of contractors - importance of contract law 4 Construction (Design and Management) Regulations 2015 Scope - What is construction? Application - When do they apply? The CDM Management System Duty holders (Client, Domestic Client, Designer, Principal Designer, Principal Contractor, Contractor) Documents (HSE Notification, Pre-Construction Information, Construction Phase Health & Safety Plan, H&S File) Management process The 2015 Guidance 5 Best practice - key issues in the CDM process The client and client management arrangements Competence and resource under CDM 2015 The role of the Principal Designer in practice Design risk assessment and the role of the Designer The CDM Documents (PCI, PCI Pack, Plan and File) Construction health, safety and welfare Making CDM work in practice 6 Questions, discussion and review

Search By Location
- Legislation Courses in London
- Legislation Courses in Birmingham
- Legislation Courses in Glasgow
- Legislation Courses in Liverpool
- Legislation Courses in Bristol
- Legislation Courses in Manchester
- Legislation Courses in Sheffield
- Legislation Courses in Leeds
- Legislation Courses in Edinburgh
- Legislation Courses in Leicester
- Legislation Courses in Coventry
- Legislation Courses in Bradford
- Legislation Courses in Cardiff
- Legislation Courses in Belfast
- Legislation Courses in Nottingham

